13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(1):406-419. doi:10.7150/thno.86221 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Efficient 3D imaging and pathological analysis of the human lymphoma tumor microenvironment using light-sheet immunofluorescence microscopy
1. Department of Hematology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
2. Hematology Department, Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China.
3. School of Optical and Electronic Information - Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
4. Department of Pathology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
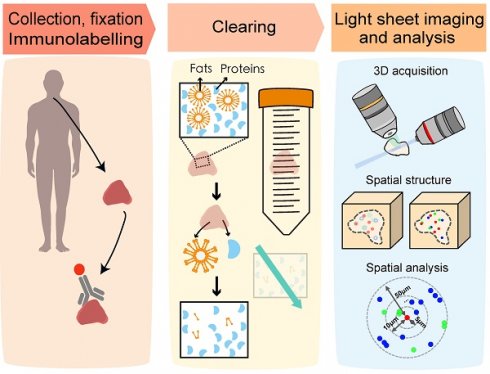
Rationale: The composition and spatial structure of the lymphoma tumor microenvironment (TME) provide key pathological insights for tumor survival and growth, invasion and metastasis, and resistance to immunotherapy. However, the 3D lymphoma TME has not been well studied owing to the limitations of current imaging techniques. In this work, we take full advantage of a series of new techniques to enable the first 3D TME study in intact lymphoma tissue.
Methods: Diverse cell subtypes in lymphoma tissues were tagged using a multiplex immunofluorescence labeling technique. To optically clarify the entire tissue, immunolabeling-enabled three-dimensional imaging of solvent-cleared organs (iDISCO+), clear, unobstructed brain imaging cocktails and computational analysis (CUBIC) and stabilization to harsh conditions via intramolecular epoxide linkages to prevent degradation (SHIELD) were comprehensively compared with the ultimate dimensional imaging of solvent-cleared organs (uDISCO) approach selected for clearing lymphoma tissues. A Bessel-beam light-sheet fluorescence microscope (B-LSFM) was developed to three-dimensionally image the clarified tissues at high speed and high resolution. A customized MATLAB program was used to quantify the number and colocalization of the cell subtypes based on the acquired multichannel 3D images. By combining these cutting-edge methods, we successfully carried out high-efficiency 3D visualization and high-content cellular analyses of the lymphoma TME.
Results: Several antibodies, including CD3, CD8, CD20, CD68, CD163, CD14, CD15, FOXP3 and Ki67, were screened for labeling the TME in lymphoma tumors. The 3D imaging results of the TME from three types of lymphoma, reactive lymphocytic hyperplasia (RLN), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), were quantitatively analyzed, and their cell number, localization, and spatial correlation were comprehensively revealed.
Conclusion: We present an advanced imaging-based method for efficient 3D visualization and high-content cellular analysis of the lymphoma TME, rendering it a valuable tool for tumor pathological diagnosis and other clinical research.
Keywords: lymphoma tumor microenvironment, tissue clearing, light-sheet microscopy, three-dimensional imaging, 3D spatial analysis.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact