13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(14):4802-4820. doi:10.7150/thno.83163 This issue Cite
Research Paper
5-aminolevulinate and CHIL3/CHI3L1 treatment amid ischemia aids liver metabolism and reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury
1. Department of Hepatic Surgery and Liver transplantation Center, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University; Organ Transplantation Institute, Sun Yat-sen University; Organ Transplantation Research Center of Guangdong Province, Guangdong Province Engineering Laboratory for Transplantation Medicine, Guangzhou, China.
2. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Liver Disease Research, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Liver disease biotherapy and Translational Medicine of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
4. Department of Anesthesiology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
5. School of Optometry and Ophthalmology and Eye Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China; The State Key Laboratory of Optometry, Ophthalmology and Vision Science, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
# These authors contributed equally.
* Lead contact.
Abstract
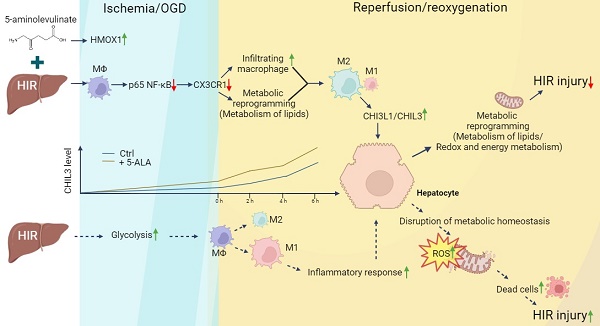
Rationale: Liver resection and transplantation surgeries are accompanied by hepatic ischemia-reperfusion (HIR) injury that hampers the subsequent liver recovery. Given that the liver is the main organ for metabolism and detoxification, ischemia-reperfusion in essence bestows metabolic stress upon the liver and disrupts local metabolic and immune homeostasis. Most of the recent and current research works concerning HIR have been focusing on addressing HIR-induced hepatic injury and inflammation, instead of dealing with the metabolic reprogramming and restoration of redox homeostasis. As our previous work uncovers the importance of 5-aminolevulinate (5-ALA) synthesis during stress adaptation, here we evaluate the effects of supplementing 5-ALA to mitigate HIR injury.
Methods: 5-ALA was supplemented into the mice or cultured cells during the ischemic or oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) phase. Following reperfusion or reoxygenation, cellular metabolism and energy homeostasis, mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and transcriptomic changes were evaluated in HIR mouse models or cultured hepatocytes and macrophages. Liver injury, hepatocytic functional tests, and macrophagic M1/M2 polarization were assessed.
Results: Dynamic changes in the expression of key enzymes in 5-ALA metabolism were first confirmed in donor and mouse liver samples following HIR. Supplemented 5-ALA modulated mouse hepatic lipid metabolism and reduced ATP production in macrophages following HIR, resulting in elevation of anti-inflammatory M2 polarization. Mechanistically, 5-ALA down-regulates macrophagic chemokine receptor CX3CR1 via the repression of RelA following OGD and reoxygenation (OGD/R). Cx3cr1 KO mice demonstrated milder liver injuries and more macrophage M2 polarization after HIR. M2 macrophage-secreted chitinase-like protein 3 (CHIL3; CHI3L1 in human) is an important HIR-induced effector downstream of CX3CR1 deficiency. Addition of CHIL3/CHI3L1 alone improved hepatocellular metabolism and reduced OGD/R-inflicted injuries in cultured mouse and human hepatocytes. Combined treatment with 5-ALA and CHIL3 during the ischemic phase facilitated lipid metabolism and ATP production in the mouse liver following HIR.
Conclusion: Our results reveal that supplementing 5-ALA promotes macrophagic M2 polarization via downregulation of RelA and CX3CR1 in mice following HIR, while M2 macrophage-produced CHIL3/CHI3L1 also manifests beneficial effects to the recovery of hepatic metabolism. 5-ALA and CHIL3/CHI3L1 together mitigate HIR-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and hepatocellular injuries, which may be developed into safe and effective clinical treatments to attenuate HIR injuries.
Keywords: 5-aminolevulinic acid, CX3CR1, chitinase-like 3, chitinase-3-like protein 1, hepatic ischemia-reperfusion
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact