13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(11):3897-3913. doi:10.7150/thno.85250 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Macrophage promotes fibroblast activation and kidney fibrosis by assembling a vitronectin-enriched microenvironment
1. State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, National Clinical Research Center of Kidney Disease, Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University.
2. Guangdong Provincial Institute of Nephrology, Guangzhou, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
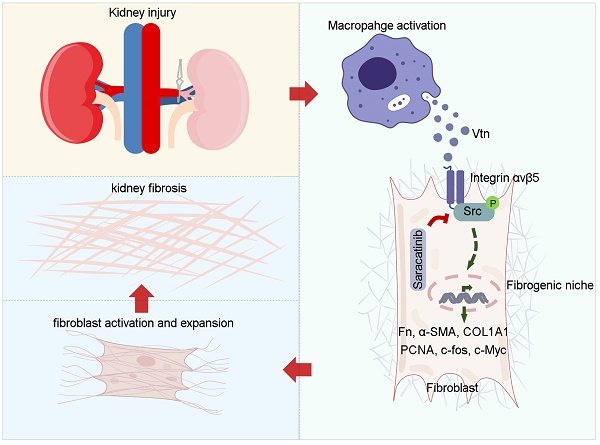
Background: Renal infiltration of inflammatory cells including macrophages is a crucial event in kidney fibrogenesis. However, how macrophage regulates fibroblast activation in the fibrotic kidney remains elusive. In this study, we show that macrophages promoted fibroblast activation by assembling a vitronectin (Vtn)-enriched, extracellular microenvironment.
Methods: We prepared decellularized kidney tissue scaffold (KTS) from normal and fibrotic kidney after unilateral ischemia-reperfusion injury (UIRI) and carried out an unbiased quantitative proteomics analysis. NRK-49F cells were seeded on macrophage-derived extracellular matrix (ECM) scaffold. Genetic Vtn knockout (Vtn-/-) mice and chronic kidney disease (CKD) model with overexpression of Vtn were used to corroborate a role of Vtn/integrin αvβ5/Src in kidney fibrosis.
Results: Vtn was identified as one of the most upregulated proteins in the decellularized kidney tissue scaffold from fibrotic kidney by mass spectrometry. Furthermore, Vtn was upregulated in the kidney of mouse models of CKD and primarily expressed and secreted by activated macrophages. Urinary Vtn levels were elevated in CKD patients and inversely correlated with kidney function. Genetic ablation or knockdown of Vtn protected mice from developing kidney fibrosis after injury. Conversely, overexpression of Vtn exacerbated renal fibrotic lesions and aggravated renal insufficiency. We found that macrophage-derived, Vtn-enriched extracellular matrix scaffold promoted fibroblast activation and proliferation. In vitro, Vtn triggered fibroblast activation by stimulating integrin αvβ5 and Src kinase signaling. Either blockade of αvβ5 with neutralizing antibody or pharmacological inhibition of Src by Saracatinib abolished Vtn-induced fibroblast activation. Moreover, Saracatinib dose-dependently ameliorated Vtn-induced kidney fibrosis in vivo. These results demonstrate that macrophage induces fibroblast activation by assembling a Vtn-enriched extracellular microenvironment, which triggers integrin αvβ5 and Src kinase signaling.
Conclusion: Our findings uncover a novel mechanism by which macrophages contribute to kidney fibrosis via assembling a Vtn-enriched extracellular niche and suggest that disrupting fibrogenic microenvironment could be a therapeutic strategy for fibrotic CKD.
Keywords: Vitronectin, macrophage, fibroblast activation, kidney fibrosis, integrin αvβ5, Src signaling, ECM scaffold
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact