13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(8):2710-2720. doi:10.7150/thno.82620 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MegaPro, a clinically translatable nanoparticle for in vivo tracking of stem cell implants in pig cartilage defects
1. Department of Radiology, Molecular Imaging Program at Stanford (MIPS), Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.
2. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.
3. Department of Veterinary Medicine, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.
#These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
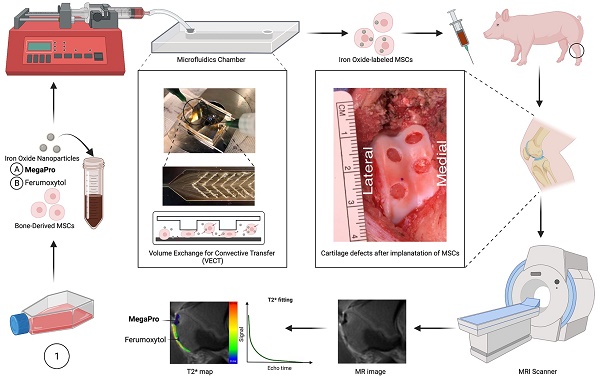
Rationale: Efficient labeling methods for mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are crucial for tracking and understanding their behavior in regenerative medicine applications, particularly in cartilage defects. MegaPro nanoparticles have emerged as a potential alternative to ferumoxytol nanoparticles for this purpose.
Methods: In this study, we employed mechanoporation to develop an efficient labeling method for MSCs using MegaPro nanoparticles and compared their effectiveness with ferumoxytol nanoparticles in tracking MSCs and chondrogenic pellets. Pig MSCs were labeled with both nanoparticles using a custom-made microfluidic device, and their characteristics were analyzed using various imaging and spectroscopy techniques. The viability and differentiation capacity of labeled MSCs were also assessed. Labeled MSCs and chondrogenic pellets were implanted into pig knee joints and monitored using MRI and histological analysis.
Results: MegaPro-labeled MSCs demonstrated shorter T2 relaxation times, higher iron content, and greater nanoparticle uptake compared to ferumoxytol-labeled MSCs, without significantly affecting their viability and differentiation capacity. Post-implantation, MegaPro-labeled MSCs and chondrogenic pellets displayed a strong hypointense signal on MRI with considerably shorter T2* relaxation times compared to adjacent cartilage. The hypointense signal of both MegaPro- and ferumoxytol-labeled chondrogenic pellets decreased over time. Histological evaluations showed regenerated defect areas and proteoglycan formation with no significant differences between the labeled groups.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that mechanoporation with MegaPro nanoparticles enables efficient MSC labeling without affecting viability or differentiation. MegaPro-labeled cells show enhanced MRI tracking compared to ferumoxytol-labeled cells, emphasizing their potential in clinical stem cell therapies for cartilage defects.
Keywords: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), MegaPro nanoparticles, mechanoporation, MRI tracking, cartilage defects
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact