13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(8):2424-2438. doi:10.7150/thno.81714 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Therapeutic effect of ultra-long-lasting human C-peptide delivery against hyperglycemia-induced neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy
Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Kangwon-do 24341, Korea
*C.-H.M. and A.-J.L. contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
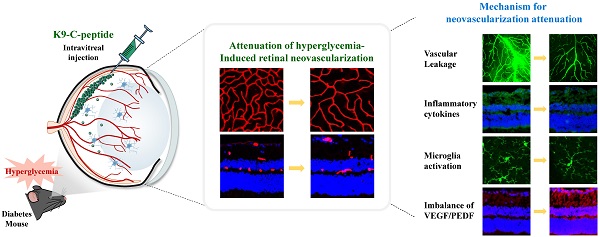
Rationale: Neovascularization is a hallmark of the late stages of diabetic retinopathy (DR) leading to blindness. The current anti-DR drugs have clinical disadvantages including short circulation half-lives and the need for frequent intraocular administration. New therapies with long-lasting drug release and minimal side effects are therefore needed. We explored a novel function and mechanism of a proinsulin C-peptide molecule with ultra-long-lasting delivery characteristics for the prevention of retinal neovascularization in proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).
Methods: We developed a strategy for ultra-long intraocular delivery of human C-peptide using an intravitreal depot of K9-C-peptide, a human C-peptide conjugated to a thermosensitive biopolymer, and investigated its inhibitory effect on hyperglycemia-induced retinal neovascularization using human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs) and PDR mice.
Results: In HRECs, high glucose conditions induced oxidative stress and microvascular permeability, and K9-C-peptide suppressed those effects similarly to unconjugated human C-peptide. A single intravitreal injection of K9-C-peptide in mice resulted in the slow release of human C-peptide that maintained physiological levels of C-peptide in the intraocular space for at least 56 days without inducing retinal cytotoxicity. In PDR mice, intraocular K9-C-peptide attenuated diabetic retinal neovascularization by normalizing hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress, vascular leakage, and inflammation and restoring blood-retinal barrier function and the balance between pro- and anti-angiogenic factors.
Conclusions: K9-C-peptide provides ultra-long-lasting intraocular delivery of human C-peptide as an anti-angiogenic agent to attenuate retinal neovascularization in PDR.
Keywords: neovascularization, diabetic retinopathy, K9-C-peptide, human C-peptide, long-term delivery
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact