13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(4):1454-1469. doi:10.7150/thno.80821 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Controlled intracellular aggregation of magnetic particles improves permeation and retention for magnetic hyperthermia promotion and immune activation
1. National Engineering Research Center for Biomaterials, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610064, P. R. China
2. College of Biomedical Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610065, P. R. China
3. Development and Related Diseases of Women and Children Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, P. R. China
4. Nanomedicine Research Center, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, China
Abstract
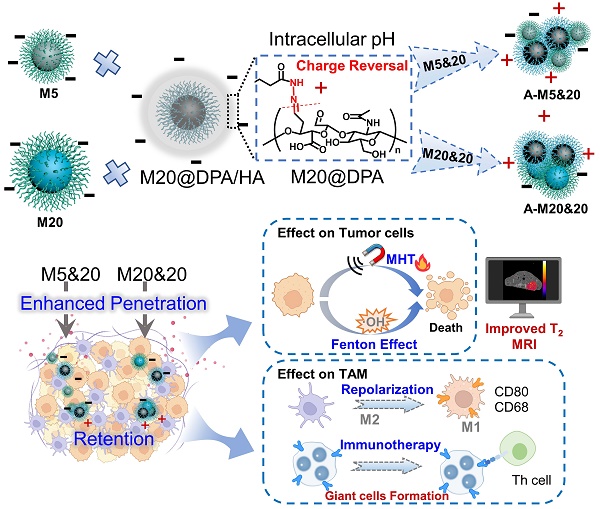
Rationale: Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are the most used inorganic nanoparticles in clinics with therapeutic and imaging functions, but the inefficient magneto-thermal conversion efficiency, fast leakage, and uneven distribution impair their imaging sensitivity and therapeutic efficacy in tumors.
Methods: Herein, we rationally designed a system containing pH-controllable charge-reversible MNPs (M20@DPA/HA) and negatively charged MMPs with different sizes (M5 and M20), which could induce intracellular aggregation. The dynamic hydrazone bonds with pH controllability were formed by the surface hydrazides on MNPs and aldehydes of hyaluronic acid (HA). Under the acidic pH, intracellular aggregation of the complex composed by M20@DPA/HA and M5 (M5&20), or M20@DPA/HA and M20 (M20&20) were investigated. In addition, the magnetic hyperthermia therapy (MHT) efficiency of tumor cells, tumor-associated macrophages polarization, giant cells formation and immune activation of tumor microenvironment were explored via a series of cell and animal model experiments.
Results: Through physical and chemical characterization, the aggregation system (M20&20) exhibited a remarkable 20-fold increase in magnetothermal conversion efficiency compared to individual MNPs, together with enhanced penetration and retention inside the tumor tissues. In addition, it could promote immune activation, including repolarization of tumor-associated macrophages, as well as the formation of giant cells for T cell recruitment. As a result, the M20&20 aggregation system achieved a high degree of inhibition in 4T1 mouse mammary tumor model, with little tumor growth and metastasis after magnetic hyperthermia therapy.
Conclusions: A controlled intracellular aggregation system was herein developed, which displayed an aggregation behavior under the acidic tumor microenvironment. The system significantly enhanced MHT effect on tumor cells as well as induced M1 polarization and multinucleated giant cells (MGC) formation of TAM for immune activation. This controlled aggregation system achieved barely tumor growth and metastasis, showing a promising strategy to improve MNPs based MHT on deteriorate cancers.
Keywords: Intracellular aggregation, magnetic hyperthermia therapy, immune activation, giant cell, magnetic resonance imaging
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact