13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(4):1381-1400. doi:10.7150/thno.82182 This issue Cite
Research Paper
KLF5 inhibition potentiates anti-PD1 efficacy by enhancing CD8+ T-cell-dependent antitumor immunity
1. Key Laboratory of Animal Models and Human Disease Mechanisms of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Yunnan Province, KIZ-CUHK Joint Laboratory of Bioresources and Molecular Research in Common Diseases, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, China
2. Tongji University Cancer Center, Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
3. Department of Breast and Thyroid Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
4. Medical Faculty of Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China
5. Academy of Biomedical Engineering, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, China
6. School of Life Science, University of Science & Technology of China, Hefei, 230027, Anhui, China
7. Center for Single-Cell Omics and Tumor Liquid Biopsy, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
8. College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350108, China
9. Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
10. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
11. The Third Affiliated Hospital, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650118, China
12. Pathology department, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Health Science Center, Shenzhen 518035, China
#Equal contribution
Abstract
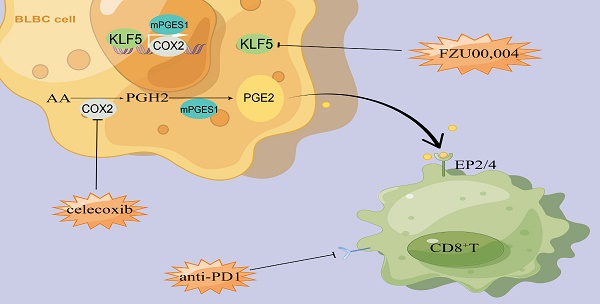
Background: Immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs) are revolutionized therapeutic strategies for cancer, but most patients with solid neoplasms remain resistant to ICBs, partly because of the difficulty in reversing the highly immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). Exploring the strategies for tumor immunotherapy is highly dependent on the discovery of molecular mechanisms of tumor immune escape and potential therapeutic target. Krüppel-like Factor 5 (KLF5) is a cell-intrinsic oncogene to promote tumorigenesis. However, the cell-extrinsic effects of KLF5 on suppressing the immune response to cancer remain unclear.
Methods: We analyzed the immunosuppressive role of KLF5 in mice models transplanted with KLF5-deleted/overexpressing tumor cells. We performed RNA sequencing, immunohistochemistry, western blotting, real time-PCR, ELISA, luciferase assay, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and flow cytometry to demonstrate the effects of KLF5 on CD8+ T cell infiltration and related molecular mechanism. Single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics analysis were applied to further decipher the association between KLF5 expression and infiltrating immune cells. The efficacy of KLF5/COX2 inhibitors combined with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (anti-PD1) therapy were explored in pre-clinical models. Finally, a gene-expression signature depending on KLF5/COX2 axis and associated immune markers was created to predict patient survival.
Results: KLF5 inactivation decelerated basal-like breast tumor growth in a CD8+ T-cell-dependent manner. Transcriptomic profiling revealed that KLF5 loss in tumors increases the number and activated function of T lymphocytes. Mechanistically, KLF5 binds to the promoter of the COX2 gene and promotes COX2 transcription; subsequently, KLF5 deficiency decreases prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) release from tumor cells by reducing COX2 expression. Inhibition of the KLF5/COX2 axis increases the number and functionality of intratumoral antitumor T cells to synergize the antitumorigenic effects of anti-PD1 therapy. Analysis of patient datasets at single-cell and spatial resolution shows that low expression of KLF5 is associated with an immune-supportive TME. Finally, we generate a KLF5/COX2-associated immune score (KC-IS) to predict patient survival.
Conclusions: Our results identified a novel mechanism responsible for KLF5-mediated immunosuppression in TME, and targeting the KLF5/COX2/PGE2 axis is a critical immunotherapy sensitizer.
Keywords: KLF5, COX2, PD1 blocker, CD8+ T cell, breast cancer
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact