13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(2):483-509. doi:10.7150/thno.79625 This issue Cite
Review
Nanomaterial-based CT contrast agents and their applications in image-guided therapy
1. Institute for Translational Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, College of Medicine, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266021, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Birth Regulation and Control Technology of National Health Commission of China, Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital of Shandong Province affiliated to Qingdao University, Jinan, 250014, China.
3. Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, College of Medicine, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266021, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
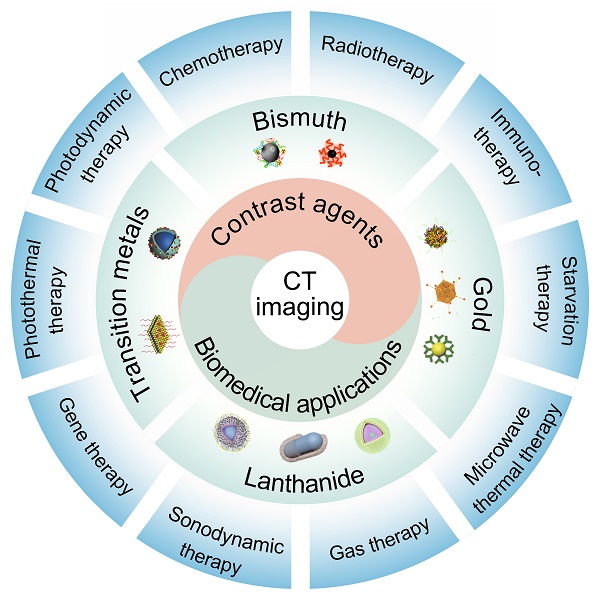
Computed tomography (CT), a diagnostic tool with clinical application, comprehensive coverage, and low cost, is used in hospitals worldwide. However, CT imaging fails to distinguish soft tissues from normal organs and tumors because their mass attenuation coefficients are similar. Various CT contrast agents have been developed in recent years to improve the sensitivity and contrast of imaging. Here, we review the progress of nanomaterial-based CT contrast agents and their applications in image-guided therapy. The CT contrast agents are classified according to their components; gold (Au)-based, bismuth (Bi)-based, lanthanide (Ln)-based, and transition metal (TM)-based nanomaterials are discussed. CT image-guided therapy of diseases, including photothermal therapy (PPT), photodynamic therapy (PDT), chemotherapy, radiotherapy (RT), gas therapy, sonodynamic therapy (SDT), immunotherapy, starvation therapy, gene therapy (GT), and microwave thermal therapy (MWTT), are reviewed. Finally, the perspectives on the CT contrast agents and their biomedical applications are discussed.
Keywords: material science, contrast agent, CT imaging, diagnosis, therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact