13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(18):7903-7919. doi:10.7150/thno.76873 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Mutant Kras and mTOR crosstalk drives hepatocellular carcinoma development via PEG3/STAT3/BEX2 signaling
1. Key Laboratory of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Institute of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University (Army Medical University), Chongqing, 400038, China.
2. School of Medicine, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, 518055, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
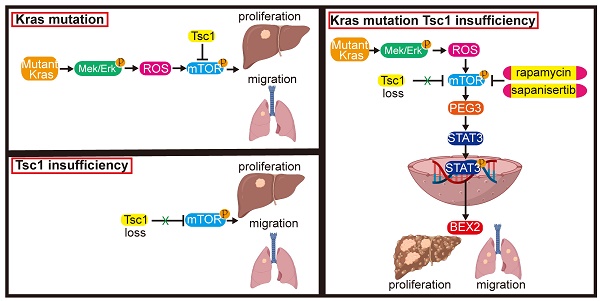
Background & Aims: Abnormal activation of mTOR through loss of tuberous sclerosis complex (Tsc) frequently occurs in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Mutant Kras could induce aggressive HCCs. Here, we aim to identify the predictive or prognostic biomarkers for HCC patients with Kras mutant and mTOR hyperactivation, and to provide potential therapeutic approaches for this subtype of HCCs.
Methods: We generated transgenic mice in which hepatocytic mTOR was hyperactivated through Tsc1 insufficiency with or without oncogenic KrasG12D. Bioinformatics and gain- or loss-of-function studies were used to illustrate the mechanisms underlying oncogenic pathway alterations. Transcriptional profiling was used to identify biomarker for the subtype of HCC. The therapeutic efficacy of targeting mTOR was tested in a liver orthotropic homogeneous murine model.
Results: Oncogenic KrasG12D facilitated mTOR activation via the Mek/Erk/ROS axis, leading to HCC tumorigenesis and metastasis. Inhibition of Mek/Erk enhanced the anticancer effect of mTOR inhibitor via reduction of mTOR activity. Paternally expressed 3 (PEG3) was responsible for Kras/Erk- and mTOR-driven HCC. Elevated PEG3 protein interacted with STAT3 and promoted its transcriptional activity, resulting in the upregulation of proliferation- and metastasis-related proteins. Targeting mTOR significantly inhibited these actions in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, in clinical samples, PEG3 was identified as a new poor prognostic marker for HCC patients with Kras/Erk and mTOR hyperactivation.
Conclusion: These findings reveal the underlying mechanism of hepatocytic Kras/Erk-driven mTOR activation and its downstream targets (PEG3 and STAT3) in HCC, identify PEG3 as a new prognostic biomarker for HCC with Kras/Erk and mTOR hyperactivation, and provide a potential therapeutic strategy for this subset of HCC patients.
Keywords: Kras/Mek/Erk, PEG3, hepatocellular carcinoma, STAT3, Cancer therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact