13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(18):7884-7902. doi:10.7150/thno.73218 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Multiomic analysis for optimization of combined focal and immunotherapy protocols in murine pancreatic cancer
1. Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA 94305, USA
2. Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA 94305, USA
3. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of California Davis, School of Medicine, Sacramento, CA 95817, USA
4. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, University of California Davis, School of Medicine, Sacramento, CA 95817, USA
5. Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of California Davis, Davis, CA 95616, USA
6. Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, 94305, USA
7. Department of Biomedical Data Science, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA 94305, USA
8. Division of Medical Oncology/Hematology, Northwell Health Cancer Institute, New Hyde Park, NY 10042 USA
Abstract
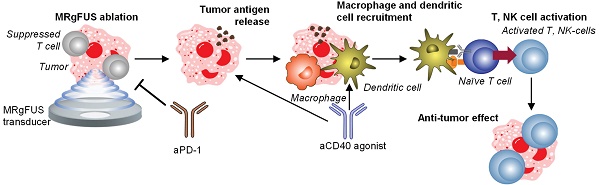
Background: Although combination immunotherapies incorporating local and systemic components have shown promising results in treating solid tumors, varied tumor microenvironments (TMEs) can impact immunotherapeutic efficacy.
Method: We designed and evaluated treatment strategies for breast and pancreatic cancer combining magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS) ablation and antibody therapies. With a combination of single-cell sequencing, spectral flow cytometry, and histological analyses, we profiled an immune-suppressed KPC (Kras+/LSL-G12D; Trp53+/LSL-R172H; Pdx1-Cre) pancreatic adenocarcinoma (MT4) model and a dense epithelial neu deletion (NDL) HER2+ mammary adenocarcinoma model with a greater fraction of lymphocytes, natural killer cells and activated dendritic cells. We then performed gene ontology analysis, spectral and digital cytometry to assess the immune response to combination immunotherapies and correlation with survival studies.
Result: Based on gene ontology analysis, adding ablation to immunotherapy enriched immune cell migration pathways in the pancreatic cancer model and extensively enriched wound healing pathways in the breast cancer model. With CIBERSORTx digital cytometry, aCD40 + aPD-1 immunotherapy combinations enhanced dendritic cell activation in both models. In the MT4 TME, adding the combination of aCD40 antibody and checkpoint inhibitors (aPD-1 and aCTLA-4) with ablation was synergistic, increasing activated natural killer cells and T cells in distant tumors. Furthermore, ablation with immunotherapy upregulated critical Ly6c myeloid remodeling phenotypes that enhance T-cell effector function and increased granzyme and protease encoding genes by as much as 100-fold. Ablation combined with immunotherapy then extended survival in the MT4 model to a greater extent than immunotherapy alone.
Conclusion: In summary, TME profiling informed a successful multicomponent treatment protocol incorporating ablation and facilitated differentiation of TMEs in which ablation is most effective.
Keywords: Combination immunotherapy, Focused ultrasound, Digital cytometry, Spectral cytometry, Sequencing
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact