13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(18):7853-7883. doi:10.7150/thno.79209 This issue Cite
Review
Clearance pathways of near-infrared-II contrast agents
1. Center for Molecular Imaging Probe, Hunan Province Key Laboratory of Tumor Cellular and Molecular Pathology, Cancer Research Institute, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Hengyang, Hunan 421001, China.
2. Tumor Pathology Research group & Department of Pathology, Institute of Basic Disease Sciences & Department of Pathology, Xiangnan University, Chenzhou, Hunan 423099, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Tropical Medicinal Plant Chemistry of Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hainan Normal University, Haikou, Hainan 571158, China.
Abstract
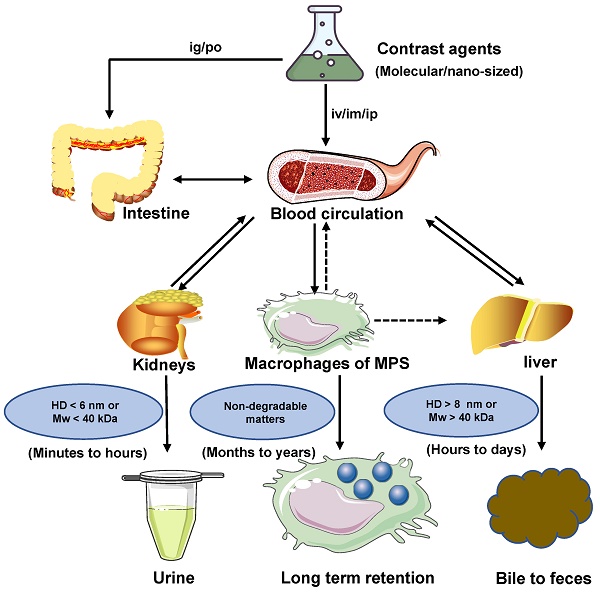
Near-infrared-II (NIR-II) bioimaging gradually becomes a vital visualization modality in the real-time investigation for fundamental biological research and clinical applications. The favorable NIR-II contrast agents are vital in NIR-II imaging technology for clinical translation, which demands good optical properties and biocompatibility. Nevertheless, most NIR-II contrast agents cannot be applied to clinical translation due to the acute or chronic toxicity caused by organ retention in vivo imaging. Therefore, it is critical to understand the pharmacokinetic properties and optimize the clearance pathways of NIR-II contrast agents in vivo to minimize toxicity by decreasing organ retention. In this review, the clearance mechanisms of biomaterials, including renal clearance, hepatobiliary clearance, and mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS) clearance, are synthetically discussed. The clearance pathways of NIR-II contrast agents (classified as inorganic, organic, and other complex materials) are highlighted. Successively analyzing each contrast agent barrier, this review guides further development of the clearable and biocompatible NIR-II contrast agents.
Keywords: near-infrared-II, in vivo imaging, hepatobiliary clearance, renal clearance, biocompatibility
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact