13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(15):6595-6610. doi:10.7150/thno.77532 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Resection-inspired histopathological diagnosis of cerebral cavernous malformations using quantitative multiphoton microscopy
1. College of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350108, China.
2. Key Laboratory of OptoElectronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350007, China.
3. Department of Neurosurgery, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, China.
4. Department of Radiology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, China.
5. Department of General Surgery, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China.
6. Department of Pathology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350004, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
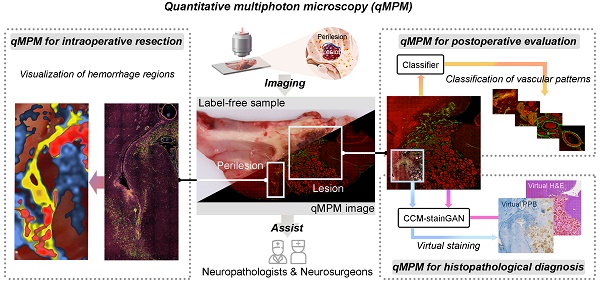
Rationale: Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is prone to recurring microhemorrhage, which can lead to drug-resistant epilepsy. Surgical resection is the first choice to control seizures for CCM-associated epilepsy. At present, removal of resection-related tissue only depends on cautious visual identification of CCM lesions and perilesional yellowish hemosiderin rim by the neurosurgeon. Inspired by the resection requirements, we proposed quantitative multiphoton microscopy (qMPM) for a histopathology-level diagnostic paradigm to assist clinicians in precisely complete resection.
Methods: A total of 35 sections specimens collected from 12 patients with the CCM-related epilepsy were included in this study. First, qMPM utilized a label-free multi-channel selective detection to image the histopathological features based on the spectral characteristics of CCM tissues. Then, qMPM developed three customized algorithms to provide quantitative information, a vascular patterns classifier based on linear support vector machine, visualization of microhemorrhage regions based on hemosiderin-related parameters, and the CCM-oriented virtual staining generative adversarial network (CCM-stainGAN) was constructed to generate two types of virtual staining.
Results: Focused on CCM lesion and perilesional regions, qMPM imaged malformed vascular patterns and micron-scale hemosiderin-related products. Four vascular patterns were automatically identified by the classifier with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.97. Moreover, qMPM mapped different degrees of hemorrhage regions onto fresh tissue while providing three quantitative hemosiderin-related indicators. Besides, qMPM realized virtual staining by the CCM-stainGAN with 98.8% diagnostic accuracy of CCM histopathological features in blind analysis. Finally, we provided pathologists and surgeons with the qMPM-based CCM histopathological diagnostic guidelines for a more definitive intraoperative or postoperative diagnosis.
Conclusions: qMPM can provide decision-making supports for histopathological diagnosis, and resection guidance of CCM from the perspectives of high-resolution precision detection and automated quantitative assessment. Our work will promote the development of MPM diagnostic instruments and enable more optical diagnostic applications for epilepsy.
Keywords: Multiphoton microscopy, cerebral cavernous malformations, hemosiderin, blood vessel, deep learning.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact