13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(15):6455-6508. doi:10.7150/thno.73436 This issue Cite
Review
Efficacy and safety of small extracellular vesicle interventions in wound healing and skin regeneration: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies
1. Centre for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, Jalan Yaacob Latif, 56000, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
2. Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Malaya, 50603, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
3. School of Pharmacy, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, Taylor's University, 47500, Subang Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia.
4. Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, Jalan Yaacob Latif, 56000, Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
5. Department of Molecular and Comparative Pathobiology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA; Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA; Richman Family Precision Medicine Center of Excellence in Alzheimer's Disease, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA.
Abstract
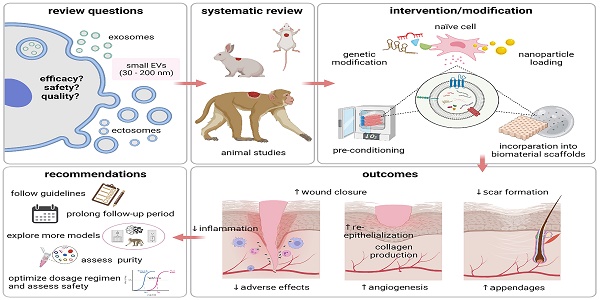
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) have been proposed as a possible solution to the current lack of therapeutic interventions for endogenous skin regeneration. We conducted a systematic review of the available evidence to assess sEV therapeutic efficacy and safety in wound healing and skin regeneration in animal models. 68 studies were identified in Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed that satisfied a set of prespecified inclusion criteria. We critically analyzed the quality of studies that satisfied our inclusion criteria, with an emphasis on methodology, reporting, and adherence to relevant guidelines (including MISEV2018 and ISCT criteria). Overall, our systematic review and meta-analysis indicated that sEV interventions promoted skin regeneration in diabetic and non-diabetic animal models and influenced various facets of the healing process regardless of cell source, production protocol and disease model. The EV source, isolation methods, dosing regimen, and wound size varied among the studies. Modification of sEVs was achieved mainly by manipulating source cells via preconditioning, nanoparticle loading, genetic manipulation, and biomaterial incorporation to enhance sEV therapeutic potential. Evaluation of potential adverse effects received only minimal attention, although none of the studies reported harmful events. Risk of bias as assessed by the SYRCLE's ROB tool was uncertain for most studies due to insufficient reporting, and adherence to guidelines was limited. In summary, sEV therapy has enormous potential for wound healing and skin regeneration. However, reproducibility and comprehensive evaluation of evidence are challenged by a general lack of transparency in reporting and adherence to guidelines. Methodological rigor, standardization, and risk analysis at all stages of research are needed to promote translation to clinical practice.
Keywords: extracellular vesicle, exosome, wound healing, skin regeneration, animal models
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact