13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(5):2370-2382. doi:10.7150/thno.66905 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ultrasound imaging tracking of mesenchymal stem cells intracellularly labeled with biosynthetic gas vesicles for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
1. The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China.
2. Department of Ultrasound, Institute of Ultrasound in Musculoskeletal Sports Medicine, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, Guangzhou 510317, China.
3. Department of Ultrasound, Hunan Provincial People's Hospital (The First-affiliated Hospital of Hunan Normal University), Changsha, 410061, China.
4. Shenzhen Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen, China.
5. Department of Radiology, Azra Naheed Medical College, Lahore, Pakistan.
6. CAS Key Laboratory of Quantitative Engineering Biology, Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, 518055, China.
#These authors equally contributed to this work.
Abstract
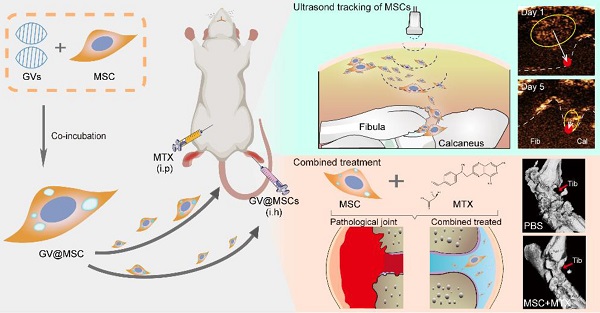
Rationale: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation and damage to articular tissues that can lead to irreversible joint damage and progressive disability. The multipotent mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) play an important role in immune disorders and tissue regeneration. However, their immunosuppressive effects and the underlying mechanisms are largely unclear due to the lack of tools for real-time imaging of MSCs in vivo. Gas vesicles (GVs) are biosynthetic nanobubbles that are ejected from aquatic microbes, such as bacteria and archaea, and have an excellent ultrasound imaging capacity.
Methods: We harvested MSCs from the bone marrow of Sprague Dawley (SD) rats. Then, GVs were synthesized and incubated with MSCs to obtain intracellularly labeled MSCs. We firstly tested the ultrasound imaging of GV@MSCs in vitro and in vivo and then explored the therapeutic effect of GV@MSCs combined with methotrexate (MTX) in RA rats.
Results: These GV@MSCs showed significant contrast-enhanced ultrasound signals without a loss of viability and differentiation capacity. In addition, the GV@MSCs could be imaged in real-time for 5 days using ultrasound both in vitro and in vivo, making it possible to visually track their migration and homing to the joint cavity from the subcutaneous layer of lateral malleolus joints in the injected RA rats. Furthermore, GV@MSCs significantly enhanced the curative effect of methotrexate (MTX) against RA, resulting in decreased paw thickness, lower arthritis index score, reduced bone erosion and cartilage destruction, compared to the PBS, free MTX, and GV@MSCs groups.
Conclusion: We developed a novel therapeutic strategy against RA using GVs-loaded MSCs that can be tracked in vivo in real-time.
Keywords: Gas vesicles, Ultrasound, Imaging tracking of cells, Mesenchymal stem cells, Rheumatoid arthritis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact