13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(4):1783-1799. doi:10.7150/thno.54056 This issue Cite
Review
Magnetic particles in motion: magneto-motive imaging and sensing
1. Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University School of Medicine, Georgia, USA
2. School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Georgia, USA
3. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Wayne State University, Michigan, USA
4. Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute, Michigan, USA
Abstract
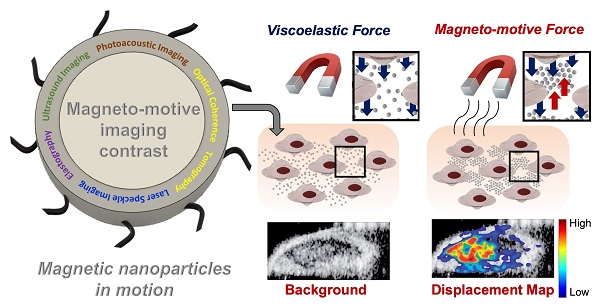
Superparamagnetic nanoparticles have become an important tool in biomedicine. Their biocompatibility, controllable small size, and magnetic properties allow manipulation with an external magnetic field for a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Recently, the magnetically-induced motion of superparamagnetic nanoparticles has been investigated as a new source of imaging contrast. In magneto-motive imaging, an external, time-varying magnetic field is applied to move a magnetically labeled subject, such as labeled cells or tissue. Several major imaging modalities such as ultrasound, photoacoustic imaging, optical coherence tomography, and laser speckle tracking can utilize magneto-motive contrast to monitor biological events at smaller scales with enhanced contrast and sensitivity. In this review article, an overview of magneto-motive imaging techniques is presented, including synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles, fundamental principles of magneto-motive force and its utility to excite labeled tissue within a viscoelastic medium, current capabilities of magneto-motive imaging modalities, and a discussion of the challenges and future outlook in the magneto-motive imaging domain.
Keywords: Magnetic nanoparticles, magneto-motive contrast, biomedical imaging, diagnostics, elastography
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact