13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(1):207-231. doi:10.7150/thno.62708 This issue Cite
Review
Harnessing Tissue-derived Extracellular Vesicles for Osteoarthritis Theranostics
1. Department of Biomedical Engineering, the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, 999077, China.
2. Department of Bioengineering, University of Pennsylvania, PA 16802, USA.
3. Research Institute of Smart Ageing, the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, 999077, China.
* These authors contributed equally
Abstract
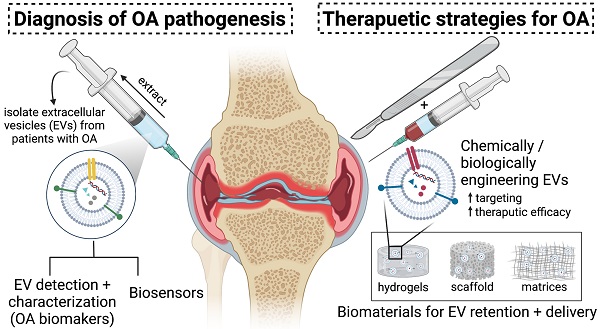
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent chronic whole-joint disease characterized by low-grade systemic inflammation, degeneration of joint-related tissues such as articular cartilage, and alteration of bone structures that can eventually lead to disability. Emerging evidence has indicated that synovium or articular cartilage-secreted extracellular vesicles (EVs) contribute to OA pathogenesis and physiology, including transporting and enhancing the production of inflammatory mediators and cartilage degrading proteinases. Bioactive components of EVs are known to play a role in OA include microRNA, long non-coding RNA, and proteins. Thus, OA tissues-derived EVs can be used in combination with advanced nanomaterial-based biosensors for the diagnostic assessment of OA progression. Alternatively, mesenchymal stem cell- or platelet-rich plasma-derived EVs (MSC-EVs or PRP-EVs) have high therapeutic value for treating OA, such as suppressing the inflammatory immune microenvironment, which is often enriched by pro-inflammatory immune cells and cytokines that reduce chondrocytes apoptosis. Moreover, those EVs can be modified or incorporated into biomaterials for enhanced targeting and prolonged retention to treat OA effectively. In this review, we explore recently reported OA-related pathological biomarkers from OA joint tissue-derived EVs and discuss the possibility of current biosensors for detecting EVs and EV-related OA biomarkers. We summarize the applications of MSC-EVs and PRP-EVs and discuss their limitations for cartilage regeneration and alleviating OA symptoms. Additionally, we identify advanced therapeutic strategies, including engineered EVs and applying biomaterials to increase the efficacy of EV-based OA therapies. Finally, we provide our perspective on the future of EV-related diagnosis and therapeutic potential for OA treatment.
Keywords: Osteoarthritis, Extracellular vesicles, Controlled-release, Biomaterials, Biosensors
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact