13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(1):35-47. doi:10.7150/thno.66466 This issue Cite
Review
Single-stranded circular DNA theranostics
1. Molecular Sciences and Biomedicine Laboratory, State Key Laboratory for Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering and College of Biology, Collaborative Innovation Center for Molecular Engineering and Theranostics, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China.
2. Department of Pharmaceutics and Center for Pharmaceutical Engineering and Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, 23298, USA.
3. Massey Cancer Center, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, 23298, USA.
4. Institute for Structural Biology, Drug Discovery and Development, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA, 23219, USA.
Abstract
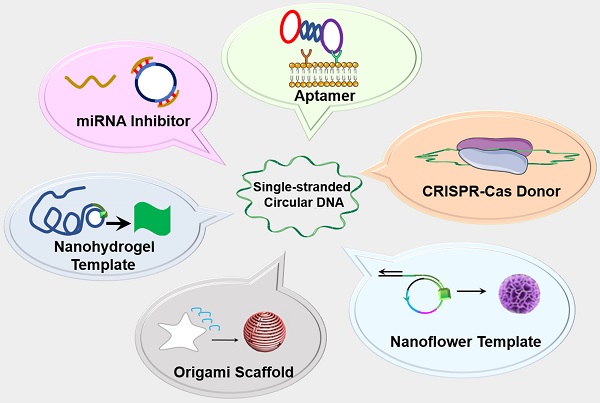
The past decade has witnessed the blossom of nucleic acid therapeutics and diagnostics (theranostics). Unlike conventional small molecule medicines or protein biologics, nucleic acid theranostics have characteristic features such as the intrinsic ability as “information drugs” to code and execute genetic and theranostic information, ready programmability for nucleic acid engineering, intrinsic stimulatory or regulatory immunomodulation, versatile functionalities, and easy conformational recovery upon thermal or chemical denaturation. Single-stranded circular DNA (circDNA) are a class of single-stranded DNAs (ssDNA) featured with their covalently-closed topology. In addition to the basic advantages of nucleic acids-based materials, such as low cost, biocompatibility, and simplicity of chemical modification, the lack of terminals in circDNA prevents exonuclease degradation, resulting in enhanced biostability relative to the corresponding linear ssDNA. circDNA has been explored for versatile theranostic applications. For instance, circDNA has been extensively studied as templates for bioanalytical signal amplification and the synthesis of nano-/micro-/macro- biomaterials via rolling circle amplification (RCA) and rolling circle transcription (RCT) technologies. circDNA has also been commonly used as the scaffolds for the self-assembly of versatile DNA origami. Finally, circDNA has been implemented as theranostic aptamers, miRNA inhibitors, as well as clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-CRISPR-associated proteins (CRISPR-Cas) gene editing donors. In this review article, we will discuss the chemistry, characteristic properties, and the theranostic applications of circDNA (excluding double-stranded circular DNA such as plasmids); we will also envision the challenges and opportunities in this research field.
Keywords: Circular DNA, theranostics, aptamer, rolling circle amplification, miRNA inhibitors
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact