13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(20):9904-9917. doi:10.7150/thno.66518 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Clinically translatable gold nanozymes with broad spectrum antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity for alleviating acute kidney injury
1. Marshall Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, International Cancer Center, Laboratory of Evolutionary Theranostics (LET), School of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen University Health Science Center, Shenzhen 518060, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China.
3. National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology, Beijing Key Laboratory of Oral Digital Medicine, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
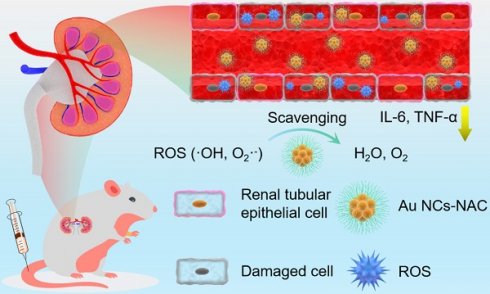
Rationale: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with aberrant generation of oxidative species and inflammation, leading to high mortality of in-hospitalized patients. Although N-acetylcysteine (NAC) showed positive effects in alleviating contrast-induced AKI, the clinical applications are strongly restrained due to the low bioavailability, low renal accumulation, short renal retention time, and high dosage-induced toxicity.
Methods: We addressed the clinical dilemma of NAC by developing ultrasmall gold nanoclusters (1-2 nm) capped with NAC (denoted as Au NCs-NAC) as a nanozyme-based antioxidant defense system for AKI alleviation. Rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI mice model was developed, and the same dose of free NAC (as a control) and NAC onto Au NCs (Au NCs-NAC) was used for in vivo investigation of AKI restoration.
Results: The as-developed gold nanozyme exhibited high bioavailability and good physicochemical stability as compared to NAC. Meanwhile, Au NCs-NAC showed broad-spectrum antioxidant activity of Au NCs-NAC, offering in vitro renoprotective effects, as well as macrophages by relieving inflammation under hydrogen peroxide or lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Notably, owing to the smaller size than kidney threshold (5.5 nm), Au NCs-NAC displayed preferential renal enrichment (< 2 h) and longer retention (> 24 h) in AKI mice as revealed by fluorescence imaging, thereby largely enhancing the restoration of renal function in AKI mice than free NAC by protecting the kidneys from oxidative injury and inflammation without systemic toxicity, as demonstrated by tissues staining, inflammatory cytokines and biomarkers detection, and mice survival rate.
Conclusion: Owing to the synergistic anti-inflammatory/antioxidative effects, and enhanced bioavailability and renal accumulation/retention, Au NCs-NAC displayed far superior therapeutic performance than NAC alone. This work will facilitate the development of high-performance antioxidative nanoplatforms, as well as overcome the clinical limitations of small molecular drugs for AKI treatment and other inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: N-acetylcysteine, Gold nanoclusters, Acute kidney injury, Anti-inflammatory, Reactive oxygen species, Nanozyme
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact