13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(20):9738-9751. doi:10.7150/thno.60902 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Osteoblast-derived EGFL6 couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during bone repair
1. School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Western Australia, Perth, WA, Australia.
2. Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
3. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China.
4. Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China.
5. School of Molecular Sciences, University of Western Australia, Perth, WA, Australia.
6. Department of Chemistry, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong, P. R. China.
7. Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China.
8. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Implants, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
Abstract
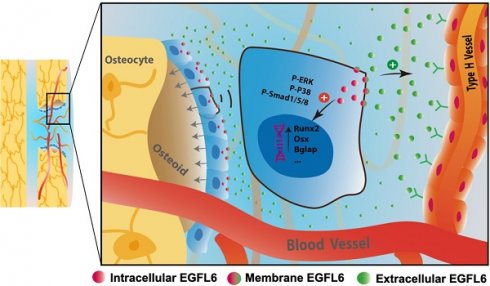
Rationale: Angiogenesis and osteogenesis are highly coupled processes which are indispensable to bone repair. However, the underlying mechanism(s) remain elusive. To bridge the gap in understanding the coupling process is crucial to develop corresponding solutions to abnormal bone healing. Epidermal growth factor-like protein 6 (EGFL6) is an angiogenic factor specifically and distinctively up-regulated during osteoblast differentiation. In contrast with most currently known osteoblast-derived coupling factors, EGFL6 is highlighted with little or low expression in other cells and tissues.
Methods: In this study, primary bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and osteoblastic cell line (MC3T3-E1) were transduced with lentiviral silencing or overexpression constructs targeting EGFL6. Cells were induced by osteogenic medium, followed by the evaluation of mineralization as well as related gene and protein expression. Global and conditional knockout mice were established to examine the bone phenotype under physiological condition. Furthermore, bone defect models were created to investigate the outcome of bone repair in mice lacking EGFL6 expression.
Results: We show that overexpression of EGFL6 markedly enhances osteogenic capacity in vitro by augmenting bone morphogenic protein (BMP)-Smad and MAPK signaling, whereas downregulation of EGFL6 diminishes osteoblastic mineralization. Interestingly, osteoblast differentiation was not affected by the exogenous addition of EGFL6 protein, thereby indicating that EGFL6 may regulate osteoblastic function in an intracrine manner. Mice with osteoblast-specific and global knockout of EGFL6 surprisingly exhibit a normal bone phenotype under physiological conditions. However, EGFL6-deficiency leads to compromised bone repair in a bone defect model which is characterized by decreased formation of type H vessels as well as osteoblast lineage cells.
Conclusions: Together, these data demonstrate that EGFL6 serves as an essential regulator to couple osteogenesis to angiogenesis during bone repair.
Keywords: angiogenesis, osteogenesis, EGFL6, bone defect, bone repair
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact