13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(17):8570-8586. doi:10.7150/thno.62046 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Milk-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate ulcerative colitis by regulating the gut immunity and reshaping the gut microbiota
1. College of Food Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China, 5 Yushan Road, Qingdao 266003, P. R. China
2. Department of Surgery, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, 1E Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 119228, Singapore
3. Nanomedicine Translational Research Programme, Centre for NanoMedicine, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117609, Singapore
4. Departments of Diagnostic Radiology, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 119074, Singapore
5. Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543, Singapore
6. Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117575, Singapore
7. Clinical Imaging Research Centre, Centre for Translational Medicine, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117599, Singapore
8. Cardiovascular Research Institute (CVRI), National University Heart Centre Singapore (NUHCS), 14 Medical Drive, Singapore 117599, Singapore
9. Department of Physiology, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, 2 Medical Drive, Singapore 117593, Singapore
10. Key Laboratory of Precision Nutrition and Food Quality, Department of Nutrition and Health, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100083, China
Abstract
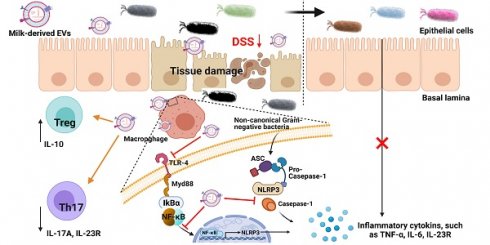
Rationale: Bovine milk constitutes an essential part of human diet, especially for children, due to its enrichment of various nutrients. We recently developed an effective protocol for the isolation of extracellular vesicles from milk (mEVs) and discovered that mEVs contained large amounts of immune-active proteins and modulated the gut immunity and microbiota in healthy mice. Here, we aimed to explore the therapeutic effects of mEVs on inflammatory bowel disease.
Methods: MicroRNAs and protein content in mEVs were analyzed by RNA sequencing and proteomics, respectively, followed by functional annotation. Ulcerative colitis (UC) was induced by feeding mice with dextran sulfate sodium. Intestinal immune cell populations were phenotyped by flow cytometry, and the gut microbiota was analyzed via 16S rRNA sequencing.
Results: We showed that abundant proteins and microRNAs in mEVs were involved in the regulation of immune and inflammatory pathways and that oral administration of mEVs prevented colon shortening, reduced intestinal epithelium disruption, inhibited infiltration of inflammatory cells and tissue fibrosis in a mouse UC model. Mechanistically, mEVs attenuated inflammatory response via inhibiting TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Furthermore, mEVs were able to correct cytokine production disorder and restore the balance between T helper type 17 (Th17) cells and interleukin-10+Foxp3+ regulatory T (Treg) cells in the inflamed colon. The disturbed gut microbiota in UC was also partially recovered upon treatment with mEVs. The correlation between the gut microbiota and cytokines suggests that mEVs may modulate intestinal immunity via influencing the gut microbiota.
Conclusions: These findings reveal that mEVs alleviate colitis by regulating intestinal immune homeostasis via inhibiting TLR4-NF-κB and NLRP3 signaling pathways, restoring Treg/Th17 cell balance, and reshaping the gut microbiota.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles, ulcerative colitis, Treg/Th17 cell balance, intestinal immunity, gut microbiome
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact