13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(15):7589-7599. doi:10.7150/thno.61259 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A platelet-mimicking theranostic platform for cancer interstitial brachytherapy
1. Department of Radiation and Medical Oncology, Hubei Key Laboratory of Tumor Biological Behaviors, Hubei Cancer Clinical Study Center, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, China.
2. Institute of Biomedical Health Technology and Engineering, Shenzhen Bay Laboratory, Shenzhen 518132, China.
3. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, Shenzhen People's Hospital, Shenzhen 518020, China.
Abstract
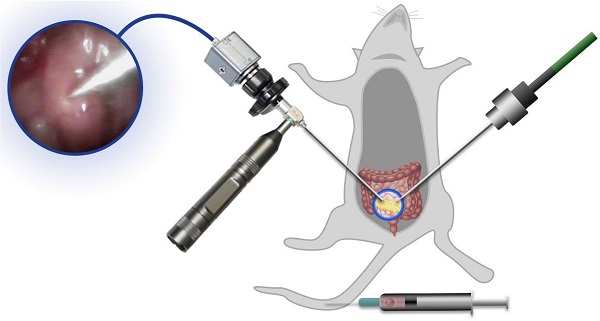
Rational: Interstitial brachytherapy (BT) is a promising radiation therapy for cancer; however, the efficacy of BT is limited by tumor radioresistance. Recent advances in materials science and nanotechnology have offered many new opportunities for BT.
Methods: In this work, we developed a biomimetic nanotheranostic platform for enhanced BT. Core-shell Au@AuPd nanospheres (CANS) were synthesized and then encapsulated in platelet (PLT)-derived plasma membranes.
Results: The resulting PLT/CANS nanoparticles efficiently evaded immune clearance and specifically accumulated in tumor tissues due to the targeting capabilities of the PLT membrane coating. Under endoscopic guidance, a BT needle was manipulated to deliver appropriate radiation doses to orthotopic colon tumors while sparing surrounding organs. Accumulated PLT/CANS enhanced the irradiation dose deposition in tumor tissue while alleviating tumor hypoxia by catalyzing endogenous H2O2 to produce O2. After treatment with PLT/CANS and BT, 100% of mice survived for 30 days.
Conclusions: Our work presents a safe, robust, and efficient strategy for enhancing BT outcomes when adapted to treatment of intracavitary and unresectable tumors.
Keywords: biomimetic, radiosensitization, brachytherapy, colon cancer, hypoxia
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact