13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(15):7507-7526. doi:10.7150/thno.59546 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Circular RNA circRHOBTB3 represses metastasis by regulating the HuR-mediated mRNA stability of PTBP1 in colorectal cancer
1. Department of Colorectal Surgery, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 310058 Hangzhou, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Biological Treatment of Zhejiang Province, 310058 Hangzhou, China.
3. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 310058 Hangzhou, China.
4. Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine of Ministry of Education, Institute of Aging and Regenerative Medicine, Jinan University, 510632 Guangzhou, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Tumor metastasis of colorectal cancer (CRC) is the main cause of death in most patients and the major difficulty in comprehensive CRC treatment. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) affect many biological functions in solid tumors. However, their mechanisms in CRC metastasis remain unclear.
Methods: RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and quantitative real-time PCR were performed to screen differentially expressed circRNAs between CRC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. CCK-8, cell migration and wound healing assays were performed to determine the functions of circRHOBTB3 in cell proliferation and metastasis. RNA pulldown and RNA immunoprecipitation assays were performed to verify the interaction between circRHOBTB3 and the HuR (ELAVL1) protein. Further RNA-seq and rescue experiments were applied to search for the downstream target. We also conducted a mouse xenograft model to elucidate the effect of circRHOBTB3 on cancer metastasis in vivo.
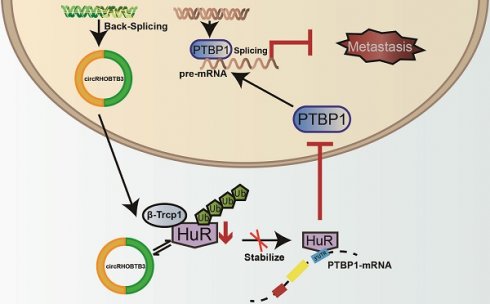
Results: We identified circRHOBTB3 which is markedly downregulated in CRC tissues and cell lines. Furthermore, lower circRHOBTB3 levels were significantly associated with advanced clinical stages and greater risk of metastases. Overexpression of circRHOBTB3 suppresses tumor metastasis in CRC cells. Mechanistically, circRHOBTB3 binds to HuR, which is a ubiquitously expressed and functional RNA-binding protein (RBP) in CRC development, and promotes β-Trcp1-mediated ubiquitination of HuR. Normally, HuR binds to the 3'UTR of target mRNAs to facilitate their stabilization, whereas the interaction between circRHOBTB3 and HuR degrades HuR to reduce the expression level of the downstream target PTBP1. Furthermore, overexpressed circRHOBTB3 suppresses lung metastases in vivo, and this effect can be partly reversed by PTBP1 overexpression. In addition, the transcription of circRHOBTB3 can be improved by both FUS and ADARB2 in CRC cells.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that circRHOBTB3 exerts suppressive effects on CRC aggressiveness through the HuR/PTBP1 axis.
Keywords: circRHOBTB3, colorectal cancer, cancer metastasis, HuR, PTBP1, FUS, ADARB2
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact