13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(13):6607-6615. doi:10.7150/thno.58321 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A SCID mouse-human lung xenograft model of SARS-CoV-2 infection
1. State Key Laboratory of Molecular Vaccinology and Molecular Diagnostics, National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Diseases, School of Life Sciences, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102, Fujian, P. R. China.
2. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361004, P. R. China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, P. R. China.
4. Joint Institute of Virology (Shantou University and The University of Hong Kong), Guangdong-Hongkong Joint Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases, Shantou University, Shantou, P. R. China.
5. Research Unit of Frontier Technology of Structural Vaccinology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Xiamen 361102, Fujian, P. R. China.
#Principal co-authors with equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
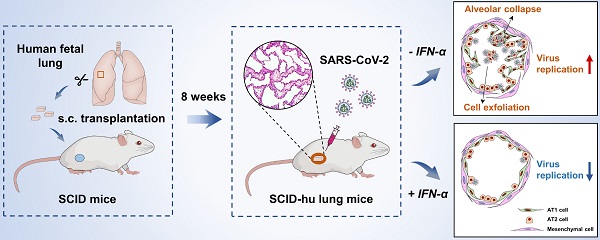
SARS-CoV-2 infection, which is responsible for the current COVID-19 pandemic, can cause life-threatening pneumonia, respiratory failure and even death. Characterizing SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis in primary human target cells and tissues is crucial for developing vaccines and therapeutics. However, given the limited access to clinical samples from COVID-19 patients, there is a pressing need for in vitro/in vivo models to investigate authentic SARS-CoV-2 infection in primary human lung cells or tissues with mature structures. The present study was designed to evaluate a humanized mouse model carrying human lung xenografts for SARS-CoV-2 infection in vivo.
Methods: Human fetal lung tissue surgically grafted under the dorsal skin of SCID mice were assessed for growth and development after 8 weeks. Following SARS-CoV-2 inoculation into the differentiated lung xenografts, viral replication, cell-type tropism and histopathology of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and local cytokine/chemokine expression were determined over a 6-day period. The effect of IFN-α treatment against SARS-CoV-2 infection was tested in the lung xenografts.
Results: Human lung xenografts expanded and developed mature structures closely resembling normal human lung. SARS-CoV-2 replicated and spread efficiently in the lung xenografts with the epithelial cells as the main target, caused severe lung damage, and induced a robust pro-inflammatory response. IFN-α treatment effectively inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in the lung xenografts.
Conclusions: These data support the human lung xenograft mouse model as a useful and biological relevant tool that should facilitate studies on the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 lung infection and the evaluation of potential antiviral therapies.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, infection, human lung, xenograft, humanized mouse model
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact