13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(13):6334-6354. doi:10.7150/thno.59342 This issue Cite
Review
Multifunctional nanoplatforms co-delivering combinatorial dual-drug for eliminating cancer multidrug resistance
1. School of Preclinical Medicine, Chengdu University, Chengdu 610106, P. R. China.
2. Evidence-Based Medicine Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, P. R. China.
3. College of Medicine, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, P. R. China.
4. School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, P. R. China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Received 2021-2-12; Accepted 2021-3-26; Published 2021-4-19
Abstract
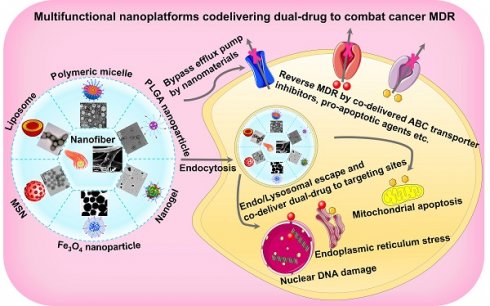
Clinically, the primary cause of chemotherapy failure belongs to the occurrence of cancer multidrug resistance (MDR), which directly leads to the recurrence and metastasis of cancer along with high mortality. More and more attention has been paid to multifunctional nanoplatform-based dual-therapeutic combination to eliminate resistant cancers. In addition to helping both cargoes improve hydrophobicity and pharmacokinetic properties, increase bioavailability, release on demand and enhance therapeutic efficacy with low toxic effects, these smart co-delivery nanocarriers can even overcome drug resistance. Here, this review will not only present different types of co-delivery nanocarriers, but also summarize targeted and stimuli-responsive combination nanomedicines. Furthermore, we will focus on the recent progress in the co-delivery of dual-drug using such intelligent nanocarriers for surmounting cancer MDR. Whereas it remains to be seriously considered that there are some knotty issues in the fight against MDR of cancers via using co-delivery nanoplatforms, including limited intratumoral retention, the possible changes of combinatorial ratio under complex biological environments, drug release sequence from the nanocarriers, and subsequent free-drug resistance after detachment from the nanocarriers. It is hoped that, with the advantage of continuously developing nanomaterials, two personalized therapeutic agents in combination can be better exploited to achieve the goal of cooperatively combating cancer MDR, thus advancing the time to clinical transformation.
Keywords: co-delivery, dual-drug, multifunctional nanoplatform, multidrug resistance, cancer therapy
Introduction
According to global cancer statistics, there have been 18.1 million new cases and 9.6 million cancer deaths worldwide [1]. So, cancer is still one of the deadliest malignant diseases [2]. Chemotherapy is the leading clinical treatment modality of cancers nowadays [3], but one long-term challenge to this conventional strategy is the occurrence of cancer multidrug resistance (MDR) [2, 4], which becomes the simultaneous development of resistance to structurally and mechanistically unrelated drugs [5]. About half a million new cancer cases show the state of MDR every year while undergoing chemotherapy [6], which leads to a large number of cancer metastases and relapses, accounting for nearly 10% to 90% [7]. Especially, it accounts for over 90% of chemotherapy failures in clinical metastatic cases [8, 9]. Accordingly, higher doses of the chemotherapeutics usually need to be administrated with high frequency, bringing about serious toxicity that directly affects the survival time of cancer patients [10, 11].
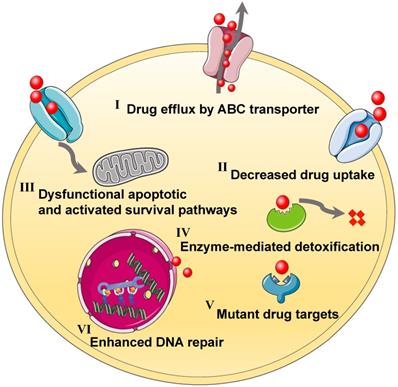
Tumor genetic diversity often gives rise to temporary responses to chemotherapy agents, followed by multiple drugs tolerance resulting from various complex mechanisms, including intrinsic resistance or acquired resistance in the cancer cells [12-14]. In detail, the development of MDR may be classified into the following pathways (Figure 1): the changes of drug influx/efflux, the enhancement of DNA repair capacity, the alteration of drug metabolism that enables the detoxification, the mutations of drug targets, and the activation of parallel signal pathways [15, 16]. It follows that the MDR mechanisms can often easily alter other pathways to allow the cancer cells to thrive, and ultimately resulting in ineffective chemotherapy [17]. To circumvent the MDR, co-administration of two kinds of agents that can concurrently tackle various survival routes in tumor cells is powerful for addressing the MDR and reinforcing antitumor potency [18]. Meanwhile, this combined strategy may regulate the genetic blocks responsible for cancer cell mutations and postpone the adaption process of drug resistance. Furthermore, while both drugs are adopted in combination for treating the resistant cancers, the ideal combination pattern with an optimized ratio can be selected out based on underlying MDR mechanisms. For instance, chemotherapeutic agents can be mixed with MDR reversal inhibitors (e.g., P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor), tyrosine kinase inhibitors or pro-apoptotic agents, to collaboratively conquer the MDR of cancers [19]. Although various resistance suppressants or reversal reagents have been developed for clinical use in last decades, they still face the same problems as free small-molecule drugs, such as short half-life, severe toxic side effects, or poor therapeutic activity, thereby limiting their clinical efficacy [20, 21]. Fortunately, the emerging of nanotechnology can serve to resolve these dilemmas by simultaneous delivering double payloads, increasing drug solubility, improving pharmacokinetic distribution, enhancing accumulation and retention, and controlling drug release on demand [4, 22]. The relevant studies focusing on nanotechnology-based combination therapy have sharply increase within the past decades, thus more and more efforts have been devoted to the nanosized drug delivery systems co-delivering dual drugs for synergistic antitumor [4]. In this context, a variety of multifunctional nanoplatforms can be designed for carrying the rational combination of dual cargoes based on the relevant resistance mechanisms, in order to achieve the optimal tumor inhibition effect by eliminating drug resistance in advance.
In this review, we first introduce various categories of co-delivery nanoplatforms and their functional diversities that contain specific cell targeting and stimulus-responsive release. Then we emphatically collate and summarize the detailed strategies for circumventing the MDR based on the co-delivery of two types of therapeutic agents by using nanocarriers. Last, we make an in-depth discussion on the applications of co-delivery nanoplatforms to overcome MDR mechanisms in cancer therapy, and summarize the existing challenges in the current therapeutic strategies and in clinical use. From this, we offer our own insights to improve the combinatorial therapy modalities based on multifunctional nanoplatforms, laying a theoretical foundation for future clinical trials. In addition, some nanoplatforms possessing the potential to clinically develop co-delivery nanomedicines are briefly prospected. Altogether, this review focuses on recent research publications and attempts to explore various therapeutic ways, in which advanced nanoplatforms can be designed to better deliver both drugs simultaneously, thus tenaciously combating cancer MDR from multiple possible angles.
Schematic illustration of various MDR mechanisms, including (I) drug efflux by ABC transporter, (II) decreased drug uptake, (III) dysfunctional apoptotic and activated survival pathways, (IV) enzyme-mediated detoxification, (V) mutant drug targets, (VI) enhanced DNA repair. Abbreviations: MDR: multidrug resistance; ABC: ATP-binding cassette.
Rational design of multifunctional nanoplatforms for co-delivering dual drugs
Co-delivery of dual-drug based on nanoplatforms may become a powerful strategy that contributes to a perfect efficacy of anti-MDR. Generally, by virtue of the drug-carrying capacity of the nanocarriers, the dual-drug package with different physicochemical properties can be delivered simultaneously and maintain a certain combination ratio. Also, nanocarriers carrying combinatorial drugs can easily access the tumor site by enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect (a passive targeting mode) or ligand-mediated active targeting [23]. Additionally, stimulus-responsive nanocarriers can control the release of two drugs under certain stimulating circumstances, thereby increasing treatment concentration. After entering the cells in endocytic manner, the dual-drug-loaded nanocarriers encapsulated into endo/lysosomes can help preferentially evade the MDR [24], and then responsively facilitate endosomal escape of both drugs into the cytoplasm to reverse the corresponding MDR pathway, thus recovering intracellular contents of therapeutants [25]. Accordingly, rational design of multifunctional nanoplatforms, holding appropriate nano-structure/morphology, targeting capacity and stimulus response, will be extremely beneficial to co-deliver dual-drug for eliminating the MDR of cancers in a recent perspective [26].
Different types of nanosystems for co-delivering dual-drug
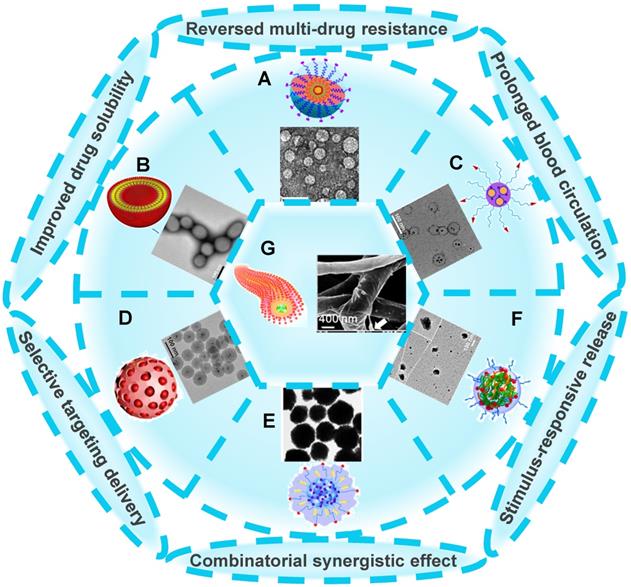
There are a wide variety of nanoscale drug delivery systems, including micelles, liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs), etc. Herein, we mainly emphasize the design of the nanocarriers based on material category for developing ideal co-delivery nanotherapeutics (Figure 2), characterized with increased solubility, prolonged circulation, targeting delivery, on-demand release, reversed resistance and synergistic treatment. Additionally, a summary of co-delivery of dual-drug through different nanocarriers for treating various cancers is displayed in Table 1. It also reflects that different kinds of nanocarriers possess diverse drug-loading mechanisms due to their unique structural characteristics, which facilitate the co-encapsulation of two drugs with different physicochemical properties into one single nanosystem, and is further conductive to the synergistic treatment of cancers.
Various nanocarrier platforms for co-delivering dual therapeutics, including (A) polymeric micelle, reproduced with permission from Ref. [27], Copyright © 2016, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (B) Liposome, reproduced with permission from Ref. [28], Copyright © 2017, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (C) Polymeric nanoparticle, reproduced with permission from Ref. [29], Copyright © 2014, American Chemical Society. (D) MSN, reproduced with permission from Ref. [30], Copyright © 2020, American Chemical Society. (E) Fe3O4 nanoparticle, reproduced with permission from Ref. [31], Copyright © 2020, American Chemical Society. (F) Polymeric nanogel, reproduced with permission from Ref. [32], Copyright © 2018, American Chemical Society, and (G) nanofiber, reproduced with permission from Ref. [33], Copyright © 2019, American Chemical Society. Abbreviations: MSN: mesoporous silica nanoparticle; Fe3O4: iron oxide.
Various nanoformulations for co-delivery of dual anticancer therapeutics
| Nanoformulation | Combined therapeutics | Drug-loading mechanism | Target | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric micelle | THZ/DOX | Hydrophobic forces | Breast cancer | [34] |
| DOX/PTX | Electrostatic forces/hydrophobic forces | Lung cancer | [35] | |
| PTX/TR3 siRNA | Hydrophobic forces/electrostatic forces | Pancreatic cancer | [36] | |
| Msurvivin T34A gene/DOX | Electrostatic forces/hydrophobic forces | Melanoma | [37] | |
| Polymeric nanoparticle | Retinoic acid/DOX | Hydrophobic forces | Breast cancer | [38] |
| AntimiR10b/antimiR-21 | Electrostatic forces | Breast cancer | [39] | |
| CDDP/RAPA | Hydrophobic forces | Melanoma | [29] | |
| MiR-34a/DOX | Electrostatic forces/hydrophobic forces | Breast cancer | [40] | |
| Liposome | RanGTP/DOX | Passive diffusion | Breast cancer | [41] |
| PTX/TRAIL | Hydrophobic forces/electrostatic absorption | Melanoma | [42] | |
| VEGF siRNA/PTX | Electrostatic absorption/hydrophobic forces | Breast cancer | [43] | |
| DFO/YC-1 | Passive diffusion/hydrophobic forces | Pancreatic cancer | [44] | |
| MSN | CPT/DOX | Hydrophobic forces/covalent binding | Cervical cancer | [45] |
| P-gp siRNA/DOX | Electrostatic absorption/hydrophobic forces | Breast cancer | [46] | |
| Fe3O4 nanoparticle | DOX/CDDP | Covalent binding | Breast cancer | [47] |
| Nanogel | CDDP/DOX | Chelation/electrostatic interaction/π-π stacking interaction | Breast cancer | [48] |
| Epigallocatechin gallate/siRNA | Electrostatic interaction | Breast cancer | [32] | |
| NGO | ADM/anti-miR-21 | Hydrophobic forces/electrostatic forces | Breast cancer | [49] |
Polymeric micelles
Polymeric micelle with core-shell structure can be developed by the self-assembly of amphiphilic polymers in aqueous solution, which is often used as a drug delivery nanocarrier to improve the hydrophobicity and bioavailability of drugs. The micellar hydrophilic shell is usually modified with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), which can prolong the drug circulation in blood. If the hydrophilic moiety in micelles is composed of cationic polymer, which can bind negatively charged drugs (e.g., nucleic acid drugs) via electrostatic forces. Besides, their hydrophobic inner core can be easily loaded with lipid-soluble drugs through hydrophobic interaction. Accordingly, micelles can be served as a suitable vehicle for simultaneously co-loading two drug models with different physicochemical properties. Generally, micellar carriers are commonly designed for carrying two chemotherapeutic agents [34, 50, 51]. For example, Lv and co-workers developed a micelle consisting of amphiphilic methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-glutamic acid)-b-poly(L-lysine) triblock copolymer decorated with deoxycholate (mPEG-b-PLG-b-PLL/DOCA), where the outer PEG segment extended the blood circulation, the middle PLG shell loaded the adriamycin (ADM) via electrostatic forces, and hydrophobic DOCA modified PLL encapsulated another chemotherapeutic paclitaxel (PTX) through hydrophobic interaction [35]. The experimental outcomes demonstrated that co-delivery of ADM and PTX using micelles exhibited synergistic antitumor effect on the A549 lung cancer.
Otherwise, the micellar structure can be utilized as a vector for delivering the combined chemotherapeutic and gene-based agents (siRNAs or microRNAs) [36, 52]. Chen et al. reported that a triblock copolymer composed of poly(2-(diisopropyl amino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDPA), poly(N-(2,2′-dithiobis(ethylamine)) aspartamide) PAsp (AED) and PEG, which formed a nanomicelle that could encapsulate doxorubicin (DOX) via hydrophobic force and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 siRNA by electrostatic adsorption [53]. As a result, the administration of Bcl-2 siRNA significantly aggravated DOX-mediated Bcl-2 down-regulation, leading to synergistically increased apoptosis of SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cells. Shi et al. also synthesized a type of triblock copolymer based on MPEG-PCL-g-PEI to prepare the cationic micelles, thereby effectively co-delivering chemotherapeutic drug and functional gene for enhancing tumor-suppression potency [37].
Polymeric nanoparticles
Polymer nanoparticles own a polymerized solid core, which can facilitate the loading of hydrophobic drugs by mixing the drugs with the polymer solution [54]. Namely, while the polymers self-assemble into particles, drug molecules are physically trapped in nanoparticles via hydrophobic or electrostatic forces. This class of nanocarrier can be developed by the self-assembly of various biodegradable copolymers like poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), polysaccharides or poly-L-lactide (PLA) [38, 55, 56], characterized with structural stability, uniform size distribution and programmed drug release. For PLGA nanoparticles, Guo et al. developed spherical PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles with a uniform size of approximately 50 nm, which physically co-encapsulated rapamycin (RAPA) and cisplatin (CDDP) for synergistic enhanced antitumor activity, alongside RAPA could sensitize A375 melanoma cells to CDDP [57]. Also, Rammohan et al. synthesized PEGylated PLGA polymeric carrier loading with two antisense-miRNAs through electrostatic bonding, simultaneously combating the anti-apoptosis and metastasis induced by miRNAs [39]. For polysaccharide-based nanoparticles, chondroitin sulfate (CS), dextran (DEX), hyaluronic acid (HA) and chitosan have often been used to form polymeric nanoparticles. It has been reported that a protoporphyrin (PpIX)-conjugated CS can self-assemble into nanoparticles, which concurrently loaded a resistance reversal agent Apatinib (APA) and an anticancer drug DOX by hydrophobic forces, and successfully reversed the MDR in breast cancer via Apa-improved DOX sensitivity [55]. Wang et al. fabricated polymeric nanoparticles composed of DEX [58], which simultaneously encapsulated PpIX via covalent grafting and the anticancer drug camptothecin (CPT) via hydrophobic interaction for chemo-photodynamic therapy. Deng et al. designed a novel nanoparticle based on HA and chitosan by iontropic gelation technique, then incorporating MiR-34a mimic and DOX via electrostatic interaction [59]. For PLA nanoparticles, the form of PLA-drug conjugates is synthesized by adapting metal alkoxide chemistry, and then these polymer-drug prodrugs self-assemble into polymeric nanoparticles through a single-step nanoprecipitation method. Namely, drug compounds are incorporated into single polymeric nanoparticles through covalent conjugation, resulting in a high loading efficiency. Aryal et al. used DOX and CPT as two chemotherapeutic drugs to separately develop DOX-PLA and CPT-PLA prodrugs, then loading into the lipid-coated polymeric nanoparticles with over 90% loading efficiency [56].
Liposomes
Liposomes usually consists of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine and cholesterol, presenting as spherical vesicle with a lipid bilayer shell and an inner aqueous core, which can enable the concurrent co-delivery of lipophilic and hydrophilic drugs [60]. Drug encapsulation into liposomes is achieved by either active extrusion or passive diffusion through the lipid bilayers. Specifically, three types of drugs present different loading ways of liposomes, including lipophilic drugs locating in the lipid bilayer shell via hydrophobic interaction, hydrophilic drugs locating in aqueous inner core via passive diffusion, and nucleic acid drugs locating in the cationic liposomal surface via electrostatic adsorption. Based on these loading properties, liposome-mediated co-delivery of combinatorial dual-drug becomes imperative and worthy of development. Generally, liposomes are often used to carry two chemotherapeutic drugs or a combination of chemotherapeutic and nucleic acid drugs [61, 62]. For example, Zhang et al. investigated a method that 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-methoxy(polyethyleneglycol) (DSPE-PEG2000), dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC), soybean phosphatidylcholine (SPC) and cholesterol (CHOL) were used to prepare liposomes, for co-encapsulating dexamethasone (DAT) and docetaxel (DTX) into hydrophobic lipid bilayer shell and achieving the property of continuous drug release [63]. In another research, liposomes were constructed by the self-assembly of DSPE-PEG2000, soybean lecithin (S100) and CHOL (3:1:1, w:w:w) [42], to co-deliver a combination of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and PTX for enhanced anti-melanoma effects. Of which, TRAIL was attached to negatively charged liposomal surface via electrostatic adsorption while PTX was physically encapsulated inside the lipid bilayer shell. In addition, liposomal structure can also be used to co-deliver chemotherapeutics and nucleic acid drugs (e.g., siRNA). To this end, in addition to encapsulating chemotherapeutic drugs into the lipid bilayer or aqueous inner core, the introduction of cationic 1,2-Dioleoyl-3-Trimethylammonium-Propane (DOTAP) or the positive protamine into liposomes will be beneficial to compress and load nucleic acid drugs through electrostatic forces [43, 62, 64].
Other nanocarriers
Other types of nanomedicines have also been studied for synchronously co-delivering dual payloads, such as MSNs [46, 65], iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles [66], nanofibers [33, 67], nanogels [32, 68] and carbon nanomaterials [49, 69], etc. Among them, MSNs are an effective and easily functionalized vehicle for controlled drug release through stimulus-responsiveness. For example, Li et al. developed a stimulus-responsive nanocarriers based on MSNs for co-entrapping CPT and DOX, resulting in the synergistic chemotherapy against the tumor [45]. Additionally, for Fe3O4 materials-based nanoplatforms, Dutta et al. prepared surfactant-stabilized Fe3O4 magnetic nanocarriers through self-assembly of anionic surfactant and sodium dodecyl sulphate on hydrophobic (oleic acid coated) nanoparticles, which highly possessed water dispersibility and an average diameter of 10 nm, which were further applied to co-deliver DOX and curcumin (CUR) [66]. For the research on nanogel-based nanocarriers, Wu et al. reported that the stimulus-responsive polymeric nanogels with less than 100 nm composed of poly(acrylic acid) were employed as co-delivery system for DOX and CDDP, to overcome the MDR of MCF-7/ADR human breast cancer cells [48]. Furthermore, for carbon materials-based nanocarriers, Zhi et al. constructed this type of nanoplatforms based on PEI-modified graphene oxide (NGO) and polystyrene sulfonate, enabling co-delivery of anti-miR-21 and ADM for the reversal of MDR in MCF-7/ADR tumor cells [49].
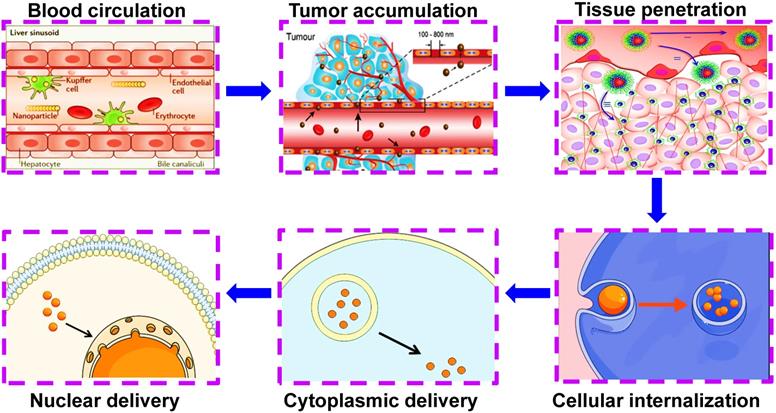
Nanocarriers can help transport therapeutic agents across a series of physiological barriers, thus successfully escaping from the reticuloendothelial system during blood circulation, completing EPR-mediated tumor accumulation, tumor microenvironmental delivery (the penetration of stromal barriers) and intracellular delivery (lysosomal escape, cytoplasmic release or organelle release). Reproduced with permission from Ref. [72], Copyright © 2017, Royal Society of Chemistry. Abbreviations: EPR: enhanced permeability and retention.
Various functionalities of nanocarriers for co-delivering dual-drug
Ideal co-delivery nanocarriers should possess specific selectivity toward cancer cells, accompanied by triggered drug release in response to external stimuli (heat, light, ultrasound and magnetic field) or internal stimuli (pH, reduction, and enzyme) [70]. By means of targeted and stimulus-responsive capacities, nanocarriers can help transport therapeutic agents across a series of physiological barriers, thus successfully completing tumor microenvironmental delivery (the penetration of stromal barriers) and intracellular delivery (lysosomal escape, cytoplasmic release or organelle release) (Figure 3) [71, 72]. Herein, we will make a brief review on the targeted and stimulus-responsive co-delivery nanotherapeutics in cancer treatment.
Targeted nanocarriers
Targeted drug delivery with nanocarriers is crucial to improve treatment efficacy and reduce side effects. Generally, targeting is commonly divided into passive targeting mode (such as EPR effect) or ligand-mediated active targeting mode [73, 74]. In this review, we will mainly emphasize the active targeting capacity of co-delivery nanocarriers endowed by a series of ligands. Among them, folate (FA) receptor is a desired drug delivery target due to its overexpression in most cancer cells [74], and FA-modified nanoplatforms have been investigated for the targeted co-delivery of dual-drug combination [48, 62]. Also, transferrin (TF) is an ideal ligand that selectively binds to the transferrin receptor (TFR) overexpressed on the membrane of cancer cells [75], showing potential application in actively targeted drug delivery. Lang et al. employed TFR1-targeting liposomes to co-transport dual therapeutics to pancreatic tumor cells, facilitating efficient uptake by tumor cells with high expression of TFR1 [44]. Besides, some special peptides, regarded as targeting ligands, will endow the modified nanocarriers with an active targeting function [42]. In a study by Li et al. [36], plectin-1 targeted peptide (PTP, NH2-KTLLPTP-COOH) was grafted on the dendrimer micelles for targeted co-delivery of nuclear receptor siRNA (siTR3) and PTX in pancreatic cancer treatment. Consequently, these PTP-modified micelles specifically accumulated in cancer cells through PTP-mediated cellular membrane-targeting. For another example, the integrin Rvβ3-specific ligand (RGD4C) and the cell-penetrating peptide TAT conjugated the poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PEO-b-PCL) conferred the membrane penetration and active targeting to the micellar system, which facilitated specifically targeted co-delivery of siRNA and DOX to overcome MDR of breast cancer [76]. Additionally, phagocytosis of nanotherapeutics can also be facilitated by the affinity between polysaccharides (e.g., HA or CS) and cell membrane receptors. Hence, these polysaccharide components have been used for targeted functionalization of nanocarriers, thus leading to specifically co-delivering dual drugs mediated by CD44 receptors overexpressed in many cancer cells [32, 55, 77].
Stimulus-responsive nanocarriers
Great efforts have been devoted to the exploration of responsive nanomedicines that respond to environmental stimuli. In this part, we will focus on the nanocarriers with different stimuli responses for controlled release of combined dual-drug.
Among many stimulants, pH sensitivity is most exploited to trigger drug release [78]. Usually, pH 6.8-7.2 of tumor microenvironment and pH 5-6 of endosomes and pH 4.5-5.5 of lysosomes, as acid pH gradients, may be applied for responsive drug release in co-delivered nanocarriers [79, 80]. According to the previous studies, co-delivery nanocarriers with a pH-response can respond to lysosomal acid stimulation through the modification of acid-labile groups (e.g., hydrazone bond) [45, 65, 81] or pH-sensitive polymers (e.g., PDPA) and poly(L-histidine) (PHis)) [53, 77, 82], thus facilitating the release of dual therapeutic payloads to effectively reverse tumor MDR. Besides, 2,3-dimethylmaleic anhydride (DMA), as an acid-sensitive compound, has been used to grafted onto diverse polymers like PLL [51], which made copolymer micelles easily change from a negative charge to a positive charge under the weak acid environment of tumor, which further benefited to enter the cancer cells and successfully released both drugs for the reversal of MDR. More importantly, pH-sensitive nanotherapeutics can rapidly release drugs inside the cells, thereby exceeding MDR-mediated drug efflux concentrations and achieving effective therapeutic concentrations that inhibit drug-resistant tumor cells [83].
The appearance of redox potential gradient in the microenvironment inside and outside tumor cells may be used as a stimulant to improve drug delivery efficiency [84]. Among most reductive substances, glutathione (GSH) is a most used redox irritant. This is because GSH concentrations in tumor cytoplasm (~10 mM) is approximately 7 times higher than those in normal cells, and even higher in drug-resistant cancer cells [85]. It has been demonstrated that disulfide bonds (-ss-), as covalently linked group, are usually used to respond to intracellular GSH-mediated redox stimulation, followed by thiol-disulfide exchange reactions [86]. Accordingly, nano-drug delivery systems (e.g., MSNs and micelles) often introduce disulfide bonds to facilitate reductive responsive drug release, which may rapidly unload both therapeutic payloads upon exposure to GSH-rich tumor cytoplasm through self-disassembly, so as to maximize their anticancer potency [53, 65, 87]. Furthermore, co-delivery of dual-drug by using redox-responsive nanocarriers may be in favor to overcome tumor MDR. For instance, Yin et al. designed a bio-reducible polymeric nanoparticle decorated with disulfide bonds for co-delivering combinatorial nucleic acid drugs, leading to a synergistic inhibition effect on the resistant tumor [88]. Additionally, Sun's team reported the development of redox-responsive nanoplatforms, which was rapidly degraded with complete release of PTX and APA under the cellular enriched GSH, and resulted in effective circumvention of MDR in breast cancer [89].
Enzyme, as a common type of response stimulant, may be used to control drug release while enzyme-responsive nanomedicines locate in an enzyme-rich lysosomal environment or tumor stromal environment. Enzyme-sensitive moieties, such as esterase-sensitive ester linkages [90, 91] or matrix metalloproteinases-2 (MMP2)-responsive peptide segments [92, 93], are generally covalently incorporated into the nanosystems for triggered drug release under the tumor physical environment. For instance, Liang et al. fabricated a nanocapsule with a covalent modification of a hydrolyzable ester bond, facilitating quick release of combinatorial chemo-drugs through the hydrolysis of the ester bond mediated by the esterase [28]. Interestingly, some metabolic or detoxification enzymes in MDR tumor cells are closely connected with the MDR mechanisms, which may be served as potential stimuli for controlled drug delivery in MDR cancer treatment [15]. Whereas little attention has been paid to the exploitation of enzyme-responsive co-delivery nanocarriers for reversing the MDR of cancers.
Applications in other physical stimuli (e.g., magnetic field or ultrasound) have also been extensively explored for cancer combination therapy. Among these stimuli, the magnetic field-responsive nano-drug delivery system is closely related to the utilization of the magnetic materials [94]. Lu et al. designed magnetic field-responsive Fe3O4-loaded MSNs for cancer thermo-chemotherapy, resulting in the quick heating and remotely triggered drug release upon exposure to a magnetic field [95]. For the study on ultrasound as a stimulus, it has been generally reported that ultrasound-responsive nanoplatforms are usually designed for cancer chemo-sonodynamic therapy [96]. Also, ultrasound-sensitive co-delivery nanosystems may be investigated for overcoming tumor MDR. In a study by Yin et al. [97], ultrasound-sensitive nanobubbles were formed by the hetero-assembly of micelles and liposomes, which were further used to simultaneously co-deliver PTX and siRNA for combating chemotherapeutic resistant hepatocellular carcinoma. Else, Baghbani et al. have investigated an ultrasound-responsive alginate/perfluorohexane nanodroplet for co-delivering DOX and CUR, which rapidly released dual payloads by low frequency ultrasound and exerted the reversal of MDR in ovarian cancer by the synergistic effects of both drugs [98].
Overcoming drug resistance by co-delivery of combinatorial drugs using nanocarriers
Diverse types and functions in co-delivery nanoplatforms have been briefly described above. Taken together, whether these multifunctional nanocarriers can successfully deliver the two drugs into tumor cells is crucial for the subsequent reversal of drug resistance. Indeed, in addition to endow drugs good solubility, long metabolism, selective targeting and controlled release in time and space, these co-delivery nanocarriers may even reverse drug resistance through endocytic internalization. However, once the drug is released into the cytoplasm and converted into a free state, it is still subject to the effects of MDR mechanisms. To address it, the drug delivery systems should not only be rationally designed with multiple functions, but also deliver an optimized two-drug combination with the ability to evade or inhibit the MDR. Among various underlying MDR mechanisms, the altered expression of Bcl-2-related apoptotic proteins and the overexpression of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette (ABC) transporters severally represent intrinsic resistance and acquired resistance [99, 100]. The former is independent of drug efflux pump, mainly related to mitochondrial apoptotic pathway involving the regulation of pro-apoptotic p53 transcriptional targets like Bax and anti-apoptotic factors like Bcl-2 [101]. The latter is closely associated with the upregulated expression of a family of energy-dependent drug efflux pumps (ABC transporters) [46], leading to the efflux of a variety of hydrophobic anticancer drugs such as DOX, CPT, and PTX. One of the most common transporter is P-gp (also known as MDR1), primarily existing in leukemia, liver, ovarian, breast, pancreatic cancers, etc. [101, 102]. According to multiple target genes involved in different MDR mechanisms, we can freely choose the appropriate therapeutants that may modulate the corresponding MDR pathway to be combined with chemotherapy drugs, and then co-encapsulated in “two in one” nanosystems to increase chemosensitivity of cancer cells by reversing resistance. So far, a broad class of chemo-sensitizers have been developed to normalize the apoptosis pathway or suppress ABC drug transporters, such as ABC transporter inhibitors or pro-apoptotic agents [54].
Next, there is a main discussion about the studies of various combinatorial nanomedicines in overcoming different tumor MDR mechanisms. Herein, the MDR mechanisms of tumor are primarily involved in ABC transporter (P-gp)-mediated drug efflux and the aberrant expression of apoptosis-related protein. Of which, the descriptions of the reversal of ABC transporter-based MDR are showed in Section 3.1 and 3.2, and the discussions about the reversal of dysfunctional apoptosis-induced MDR are mainly presented in Section 3.3 and 3.4. Meanwhile, a research on overcoming abnormal DNA repair-mediated MDR is also described in the discussion of Section 3.4. It's worth noting that, there have been relatively few reports on co-delivery nanomedicines to overcome other resistance mechanisms like aberrant DNA repair, enzyme-mediated detoxification, and mutant drug targets. Thus we do not have a systematic summary of the researches on these related resistance mechanisms in this review. Instead, more efforts should be devoted to these studies. Additionally, different combinations of dual-drug in co-delivery nanocarriers for the reversal of MDR are summarized in Table 2.
Various dual-drug combinations in nanocarriers for reversing cancer MDR
| Nanoformulation | Drug combinations | Reversal mechanism of MDR | Target | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric micelle | DOX and HCPT | Evade the recognition of drug efflux pumps by π-π stacking and collateral sensitivity between dual drugs | Breast cancer | [27] |
| DOX and APA | Recover the chemosensitivity by competitively inhibiting P-gp activity | Breast cancer | [55] | |
| DOX and LPA | Inhibit MDR transporters by LPA interacting with the substrate-binding site | Breast cancer | [103] | |
| DOX and TPGS2000 | TPGS2000-mediated inhibition of P-gp pump activity by reducing MMP and depletion of ATP | Breast cancer | [77] | |
| MDR-1 siRNA and DOX | Bypass P-gp-mediated DOX resistance through siRNA silencing P-gp | Breast cancer | [76] | |
| DOX and DSF | Evade drug resistance by disulfiram blocking the activity of P-gp | Breast cancer | [81] | |
| Ceramide and PTX | Overcome PTX resistance by ceramide-mediated aggravation of cell apoptosis | Ovarian cancer | [104] | |
| Polymeric nanoparticle | DOX and CyA | Inhibit MDR by CyA directly binding to P-gp drug pump | Leukemia | [105] |
| DOX and CUR | Reverse MDR by the downregulated expression of P-gp | Ovarian cancer | [98] | |
| PDTC and DOX | Block chemoresistance by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway | Liver cancer | [106] | |
| GEM and [FeFe]TPP | Reverse MDR by H2 causing the reduction of P-gp efflux pump function | Bladder cancer | [107] | |
| DOX and BNN6 | Overcome DOX resistance by NO inhibiting the expression of P-gp | Ovarian cancer | [108] | |
| Liposome | CDDP and Bcl-2/Survivin/P-gp siRNAs | Reverse MDR by blocking apoptosis and P-gp mediated resistance pathways | Ovarian cancer | [109] |
| DOX and VER | Overcome DOX resistance by VER inhibiting P-gp activity | Breast cancer | [110] | |
| RanGTP and DOX | Reverse Ran-mediated MDR by inhibiting the Ran DNA damage repair function | Breast cancer | [41] | |
| PTX and TCS | Overcome PTX resistance by TCS reversing PTX-caused caspase 9 phosphorylation and inducing caspase 3-dependent apoptosis | Lung cancer | [111] | |
| PTX and DETA NONOate | Reverse PTX resistance by NO-mediated downregulation of P-gp | Lung cancer | [112] | |
| MSN | DOX and CTAB | CTAB-mediated inhibition of P-gp activity by depletion of ATP | Breast cancer | [113] |
| P-gp siRNA and DOX | Recover DOX sensitivity by siRNA silencing the expression of P-gp | Breast cancer | [114] | |
| Nanogel | CDDP and DOX | Overcome drug resistance by synergistic chemotherapy | Breast cancer | [48] |
| PTX and MDR1 siRNA | Recover PTX sensitivity by siRNA knocking down MDR1 | Ovarian cancer | [115] |
Co-delivery of two chemotherapeutic drugs
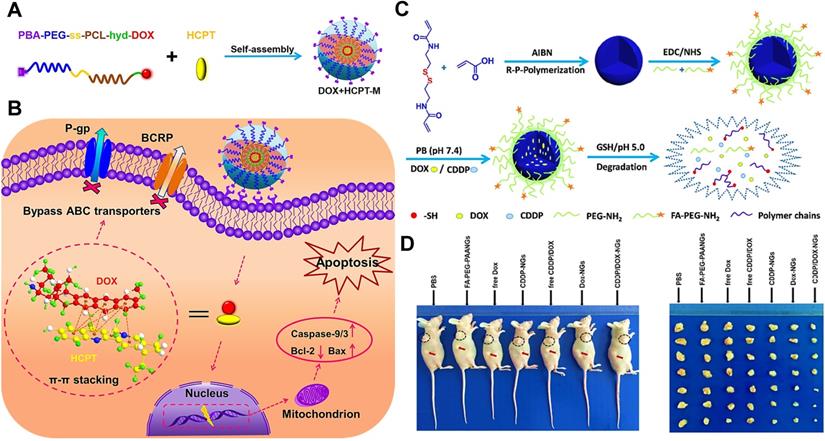
(A) The formation of DOX+HCPT-M micelles via the self-assembly of DOX-conjugated polymer with free HCPT. (B) Schematic illustration of co-delivery of a π-π stacked combination of DOX and HCPT using an intelligent micellar platform for overcoming breast cancer MDR. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [27], Copyright © 2016, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (C) Schematic illustration of the preparation, surface modification, dual-drug loading and drug releasing of the designed polymeric nanogels. (D) In vivo antitumor activity evaluation of different therapeutic formulations in BALB/c nude mice bearing MCF-7/ADR tumors. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [48], Copyright © 2017, American Chemical Society. Abbreviations: P-gp: P-glycoprotein; BCRP: breast cancer resistance protein; DOX: doxorubicin; HCPT: 10-hydroxycamptothecin; CDDP: cisplatin; FA: folate.
Chemotherapy as a first-line model in clinical cancer treatment is still highly favored. Generally, the combination of both chemical cytotoxins with different pharmacological properties can synergistically increase cytotoxicity in clinical trials. However, most chemotherapeutic drugs are identified as the substrates of the MDR, thereby limiting their clinical use [116]. To solve this issue, the emerging of nanotechnology may not only help free chemical cytotoxins improve hydrophobicity, metabolism, bioavailability and targeting, but also circumvent MDR through lysosomal delivery. Nonetheless, there is still the possibility of pumping drugs out once the drug is delivered to the cytoplasm. Hence, co-delivery nanocarriers should be pluripotently designed and take full advantage of the merits of both chemical drugs that collaboratively overcome unfavorable drug resistance.
In our previous work, we developed targeted/pH/reduction-sensitive polymer micelles to co-deliver the combination of DOX and 10-hydroxycamptothecin (HCPT), for defeating the MDR in MCF-7/ADR breast cancer therapy (Figure 4A-B) [27]. Since both traditional drugs have π-π conjugated aromatic moieties, they could be synchronously encapsulated to this single micellar platform through π-π stacking forces. As a result, the two chemotherapeutics released from these smart nanoplatforms could successfully bypass the recognition of drug efflux pumps (P-gp and BCRP) through a subtle change of molecular structure (Figure 4B), resulting from non-covalent π-π conjugation and collateral sensitivity [117]. Yu et al. also reported that the combined DOX and HCPT doped in PLGA nanoparticles could indeed overcome MDR of cancer cells, thereby achieving enhanced therapeutic efficacy through synergistic effects between two chemotherapeutics [118]. Besides, Wu and his colleagues investigated that DOX and CDDP were simultaneously incorporated into polymeric nanogels via π-π stacking, chelation and electrostatic force (Figure 4C) [48]. Because this combined dual-drug formulation can not only overwhelm the cellular repair mechanisms [119], but also show obviously synergistic effect in phase III clinical trials [120, 121]. Eventually, this co-delivery nanosystem could effectively overcome MDR in MCF-7/ADR cancer cells and exhibit significant antitumor efficacy (Figure 4D).
(A) The formation and light-triggered decomposition of versatile polymeric nanoparticles co-delivering anticancer therapeutic DOX and APA. (B) Schematic illustration of the mechanism of the reversal of cancer MDR via ACP-Dox+Apa nanoparticles. (C) The tumor tissue images of the MCF-7/ADR tumor-bearing nude mice. (D) Tumor growth profiles. (E) H&E, Ki67 and TUNEL analyses of tumor tissues from MCF-7/ADR xenografts-bearing nude mice. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [55], Copyright © 2018, American Chemical Society. Abbreviations: APA: apatinib; PpIX: protoporphyrin IX; ROS: reactive oxygen; PDT: photodynamic therapy; H&E: hematoxylin and eosin; TUNEL: terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling.
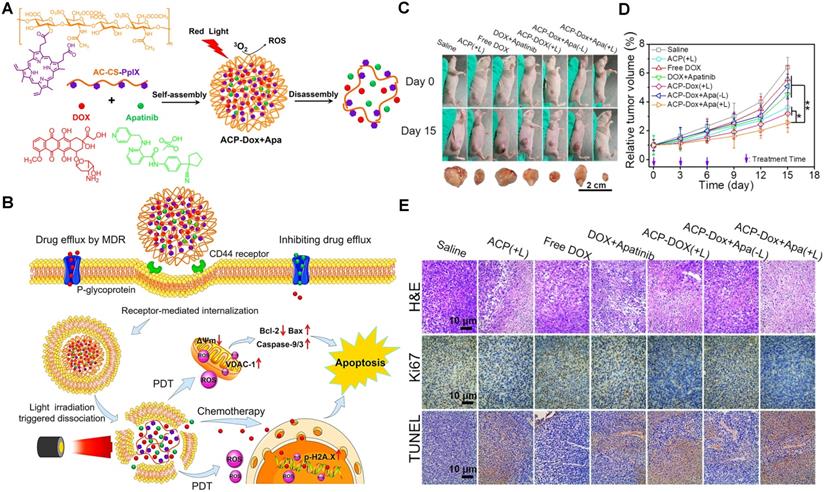
It has been reported that some tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) may either restore the apoptotic signaling pathway to sensitize resistant tumor cells to chemotherapeutics [122], or immediately attenuate the ATPase activity in P-gp to reinforce the cytotoxicity efficacy of antitumor [123]. Therefore, co-delivery nanocarriers may be also constructed to combine TKIs with traditional chemical drugs, leading to regulating the cell survival/death-related mechanisms for overwhelming the MDR of cancers [124]. For instance, APA, as one of TKIs, may observably waken P-gp-mediated MDR and potentiate the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic drugs [125]. In our previous study, we designed a light-responsive polysaccharide nanoparticle loading with the combination of DOX and APA (Figure 5A) [55]. When exposed to light irradiation, this nanoparticle instantly disassociated to release dual cargoes. After that, the released APA could recover the sensitivity of DOX by competitively inhibiting the P-gp activity, thus enhancing anticancer potency (Figure 5B-E). In addition, lapatinib (LPA), another type of TKI, may also reverse MDR of tumor cells by suppressing the P-gp. In a study by Wang et al., the micelles co-loading with DOX and LPA were developed for combating the resistant breast cancer, which successfully overcame the MDR through LPA-mediated inhibition of efflux pumps, and significantly promoting the in vitro/in vivo antitumor efficacy [103].
Co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and ABC transporter inhibitors
Macromolecular nanocarriers can directly evade the recognition of ABC transporters through endocytic pathways, contributing to taking the carried payloads away from the transmembrane multidrug efflux pumps [126]. Afterwards, the nanocarriers release the dual drugs from lysosomes to cytoplasm, where both of them may still be expelled through the drug efflux pumps. Therefore, drug cargoes carried by nanocarriers should hold the ability to overwhelm the drug efflux kinetics. To this end, we need to choose one ideal agent for effectively relieving the resistance of cancer cells to the other chemotherapy drug. Here, we will focus on many kinds of drug-resistance modulators that can obviously reverse the MDR of cancers. First, several surfactants like D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) and pluronic P123, can be used to decrease the P-gp activity accompanied by the decline of ATP [77, 127]. Second, siRNAs can be utilized to downregulate the expression of MDR-related genes for enhancing the sensitivity of resistant tumor cells to chemotherapeutics [128]. Third, some chemosensitizers like verapamil can be employed for blocking ABC transporters. Last, some gaseous signaling molecules, such as nitric oxide (NO), hydrogen (H2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2), can be used as ABC transporter inhibitors to reverse the MDR by downregulating the expression level of P-gp.
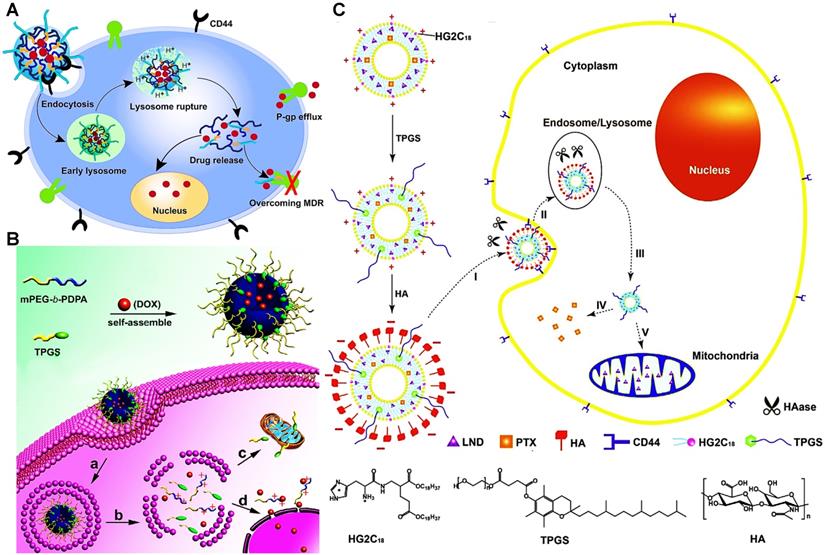
(A) Disclosure of the reversal mechanism of MDR via DOX-loaded micelles (HPHM/TPGS2000). After HPHM/TPGS2000 were selectively uptook by MCF-7/ADR cells via CD44 receptor-mediated endocytosis, pH-triggered release of TPGS2000 could suppress P-gp efflux pump to restore the chemosensitivity of DOX. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [77], Copyright © 2014, Elsevier. (B) The preparation and mechanism of mitochondria-targeted pH-responsive PDPA/TPGS@DOX micelles to overcome DOX resistance in breast cancer cells. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [131], Copyright © 2015, Elsevier. (C) Schematic design of multifunctional liposomes for co-delivery of TPGS and chemotherapeutics to reverse MDR in cancer treatment. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [133], Copyright © 2015, Elsevier. Abbreviations: TPGS: D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate; HA: hyaluronic acid; HG2C18: 1,5-dioctadecyl-N-histidyl-L-glutamate; LND: lonidamine; PTX: paclitaxel.
Chemotherapeutic drugs and surfactants
A broad range of P-gp inhibitors has been explored for bypassing P-gp-mediated MDR mechanism by blocking drug efflux. Among them, TPGS and pluronics are capable of playing a role in defeating the P-gp-mediated MDR through the inhibition of P-gp activity, and these polymeric inhibitors have good biosafety [129, 130]. For example, Qiu et al. fabricated a mixed polymeric micellar system to co-deliver DOX and TPGS for combating MDR of breast cancer (Figure 6A) [77]. By virtue of TPGS, a high amount of cellular uptake of dual-drug-loaded micelles was obtained in drug-resistant MCF-7/ADR tumor cells, attributed to the potentiated reversal effect of P-gp-induced MDR by TPGS, and restoring the sensitivity of anticancer DOX. Consequently, the micellar system exhibited higher and comparable cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells and MCF-7/ADR cells, respectively. Meanwhile, it has been found that the micelles carrying TPGS can effectively suppress P-gp activity, resulting from the decline of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and ATP, but without inhibition of P-gp expression. In another study, Yu et al. doped TPGS into the DOX-loaded micelles. As expected, TPGS successfully inhibited the P-gp-mediated MDR and restore the chemosensitivity of DOX-resistant MCF-7/ADR cells (Figure 6B) [131]. In addition to using micelles as nanocarriers for co-delivering chemotherapeutics and TPGS, some studies have also reported that the development of PLGA nanoparticles or liposomes have been used to combine chemotherapeutic drugs with TPGS [132, 133], and finally indicating that these types of combinatorial nanomedicines have significant potential for efficiently combating drug resistance in cancer treatment (Figure 6C). In another work, He et al. introduced a surfactant cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) identified as a structure-directing agent for developing MSNs loading with chemotherapeutic DOX, thus promoting the inhibition efficacy of ATP by CTAB, leading to enhanced reversal effect of P-gp efflux pump [113, 134]. Consequently, the release of DOX from MSNs could continuously accumulate inside the MCF-7/ADR cells, and then induce the extensive apoptosis of MCF-7/ADR cells.
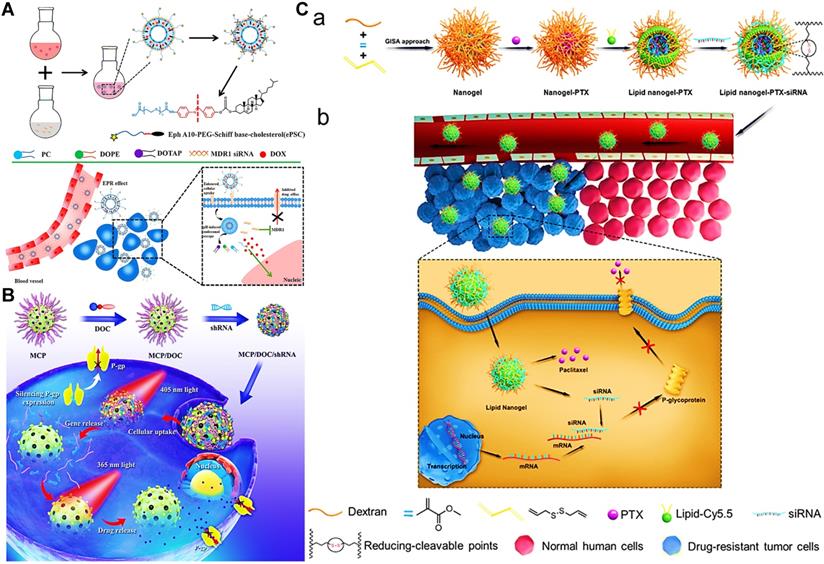
(A) Schematic illustration of the approach to overcome MDR by multifunctional liposomes co-delivering DOX and MDR1 siRNA. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [139], Copyright © 2018, American Chemical Society. (B) Schematic illustration of photo-responsive MSNs loading with shRNA and DOX for optimizing the synergistic therapy in MDR cancer cells. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [140], Copyright © 2018, American Chemical Society. (C) Schematic illustrations of a) the fabrication of MDR1 siRNA/PTX co-delivered lipid nanogels, and b) the reversal mechanism of MDR by co-delivered lipid nanogels. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [115], Copyright © 2020, Elsevier. Abbreviations: MDR1: multidrug resistance gene 1; shRNA: short-hairpin RNA; GISA: graft copolymerization-induced self-assembly; PTX: paclitaxel; siRNA: small interfering RNA.
Chemotherapeutic drugs and siRNAs
RNA interference technology like siRNA may also be used to combine with chemotherapeutic drugs, due to its precise downregulation of the expression of MDR-related genes [135]. Nevertheless, their therapeutic applications have been impeded by the short half-life in blood, lack of cellular targeting, and poor membrane permeability [136]. To address these issues mentioned, different classes of nanocarriers have been constructed to concurrently delivery siRNA and chemotherapeutic drugs in vitro and in vivo, followed by the enhanced transfection efficacy of siRNA and knockout effect of MDR-related genes [99, 137, 138]. For example, Zhang et al. designed actively targeted and pH-sensitive liposomes to co-load DOX and MDR1 siRNA for overcoming MDR of breast cancer (Figure 7A) [139]. Such co-delivery liposomes increased the sensitivity of MCF-7/ADR cells to DOX via MDR1 siRNA-induced P-gp downregulation, and exhibited an enhanced therapeutic potency. In another study, to ensure prerelease of RNA molecules than chemotherapeutic drugs with a sufficient interval, Wu et al. fabricated a photo-responsive MSN loading with DOX and P-gp shRNA to overcome MDR of HepG2 liver cancer cells, by which sequential release of shRNA and DOX could be achieved by using 405 and 365 nm light irradiations, respectively (Figure 7B) [140]. Eventually, these MSNs could result in enhanced DOX retention inside MDR cancer cells by the initial release of shRNA silencing P-gp expression, and bring out an optimized chemotherapeutic effect. Furthermore, Wang et al. designed a biomimetic lipid/DEX hybrid nanogel to co-deliver MDR1 siRNA and PTX for inhibiting PTX-resistant ovarian cancer (Figure 7C) [115], in which MDR1 siRNA could knock down MDR1 to promote the accumulation of PTX in cancer cells, thereby achieving an efficient inhibitory effect against highly PTX-resistant cancer cells.
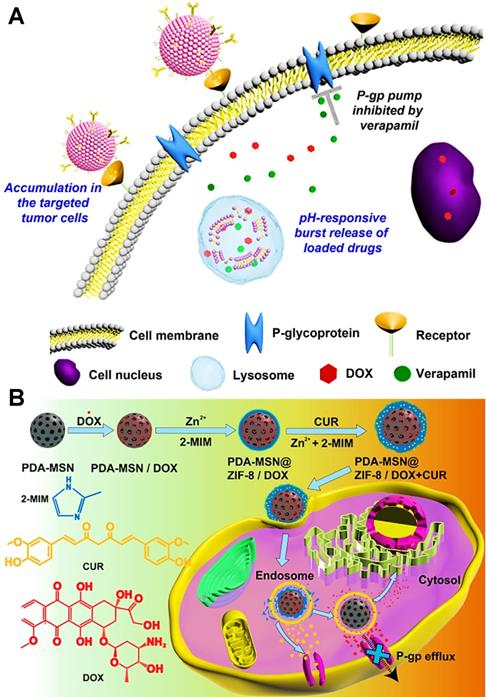
(A) Schematic illustration of the mechanism of reversal MDR by pH-responsive mixed liposomes co-delivering DOX and VER. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [110], Copyright © 2014, Elsevier. (B) Schematic diagram showing the preparation of DOX and CUR loaded hybrid nanocarriers and the synergistic MDR reversal therapy. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [145], Copyright © 2018, American Chemical Society. Abbreviations: VER: verapamil; PDA: polydopamine; MSN: mesoporous silica nanoparticle; CUR: curcumin; ZIF-8: zeolite imidazolate frameworks-8.
Chemotherapeutic drugs and chemosensitizers
Therapeutic nanoplatforms containing a combination of chemical drug and chemosensitizer can be further used to realize the suppression effect of cancer MDR. Among most chemosensitizers, verapamil (VER) has been identified as a common P-gp inhibitor to reverse MDR of cancer. For instance, Liu et al. constructed pH-responsive mixed liposomes for co-delivery of DOX and VER to suppress drug resistance in breast cancer, in which the increased intracellular accumulation of DOX was attributed to the inhibition of P-gp pump function by VER (Figure 8A) [110]; Qin et al. developed a hydrogel nanoparticle for co-encapsulating DOX and VER to significantly improve the uptake and cytotoxicity of DOX by reversing MDR in resistant tumor cells [141]; Maiti et al. developed redox-responsive and core-cross-linked micelles for simultaneous delivery of DOX and VER toward drug-resistant MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells [142], which significantly improved chemosensitivity by VER and enhanced anticancer efficacy in vitro. Besides, Soma et al. have reported that co-delivery of chemosensitizer cyclosporin A (CyA) and chemotherapeutic DOX with a single nanocarrier display nearly 2-fold increase of cytotoxicity, resulting from the reversal action of CyA against MDR in DOX-resistant leukemia cells [105]. Some studies have also indicated that CUR served as an ideal chemosensitizer possesses the ability to reverse MDR of cancer cells through the inhibition of P-gp pump [143, 144]. In a research by Wang et al., hybrid nanocarriers based on polydopamines and MSNs were prepared to simultaneously load with DOX and CUR for overcoming MDR of breast cancer (Figure 8B) [145]. As expected, the released CUR suppressed the drug efflux function of P-gp, subsequently facilitating intracellular accumulation of DOX and synergistic effects on killing MDR tumor cells. Furthermore, disulfiram (DSF) is another type of chemosensitizer, which can be used as a P-gp inhibitor. Duan and co-workers have investigated a micelle-mediated co-delivery of DOX and DSF [81]. The DSF released from this nanosystem directly decreased the P-gp activity, thus reversing MDR to sufficiently exert therapeutic effect of DOX in DOX-resistant breast cancer cells.
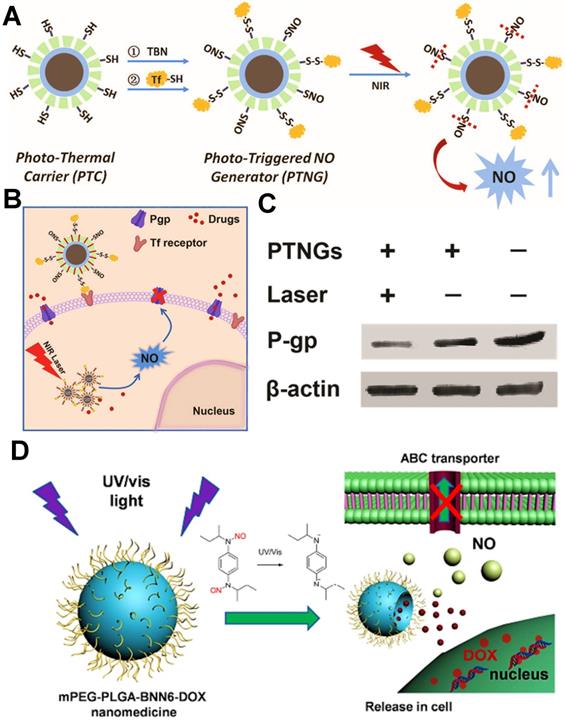
(A) Schematic illustration of the fabrication of phototriggered NO nanogenerators (PTNGs). (B) Schematic diagram of the endocytosis of PTNGs and the subsequent P-gp reversal by phototriggered release of NO. (C) Western blot for the detection of P-gp expression. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [146], Copyright © 2017, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (D) mPEG-PLGA-BNN6-DOX nanoparticles release NO in response to UV/Vis irradiation, which further increase the sensitivity of cancer cells to DOX via inhibiting P-gp-mediated MDR. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [108], Copyright © 2016, American Chemical Society. Abbreviations: NO: nitric oxide; Tf: transferrin; UV/vis: ultraviolet/visible.
Chemotherapeutic drugs and gas therapy agents
Some gaseous therapeutic agents (e.g., NO, H2, SO2) have been served as ABC transporter inhibitors to reverse tumor MDR. Among them, NO is the most prominent gasotransmitter, playing a key role in inhibiting P-gp expression. From this, several relevant studies have reported that light-triggered NO-generating nanoplatforms can show great potential for conquering MDR cancer. For instance, Guo et al. designed intelligent near-infrared (NIR) laser-triggered NO nanogenerators for reversing DOX-resistant breast cancer (Figure 9A-C) [146], which were fabricated by integrating photothermal agents and S-nitrosothiols (SNO, a heat-sensitive NO donor) into a single nanoparticle. Such nanogenerators could be converted into ample heat to trigger NO release from SNO through NIR laser, and then the NO molecules further effectively reversed MDR by decreasing the expression of P-gp transporter. Consequently, the intracellular accumulation of DOX was effectively increased in MDR cancer cells. In another research by Fan et al., they proposed a NO-promoted chemosensitization of DOX strategy, which were based on a biodegradable mPEG-PLGA nanoparticles co-delivering DOX and BNN6 (an ultraviolet-visible (UV/Vis)-sensitive NO donor) for overcoming MDR in ovarian cancer (Figure 9D) [108]. Once exposure to UV/Vis illumination, the BNN6 from these nanomedicines could decompose into NO gas to inhibit the P-gp. The generated NO further broke the nanoparticle shell to release DOX, leading to a remarkable gas/chemotherapeutic effect on defeating the MDR cancer. In addition to light triggering NO production, Wan et al. investigated a NO synthetase-mediated NO nanogenerator based on the heparin/FA nanoparticles loading with L-arginine (a NO donor) and DOX [147]; Chen et al. developed a pH-sensitive NO generation liposomal system for delivering DETA NONOate (a NO donor) and PTX [112]; Chu et al. constructed a GSH-triggered NO-generating polyprodrug nanoparticle by integrating CDDP prodrug and NO prodrug monomer (StNO) [148]. Overall, these multifunctional nanoplatforms with NO release could enable effective reversal of MDR in cancer chemotherapy.
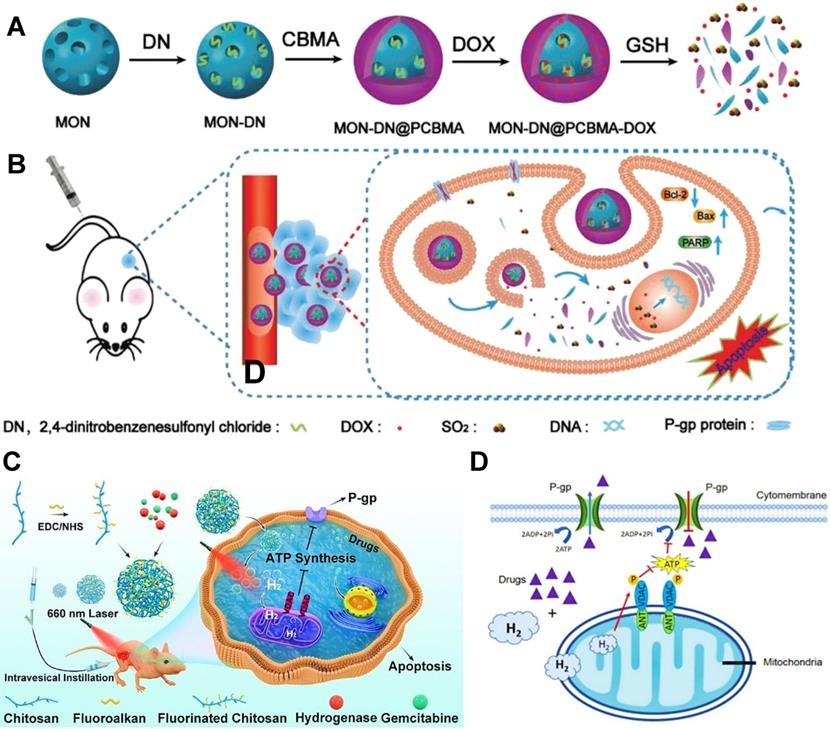
Moreover, SO2 or H2 can be used to reverse P-gp-mediated MDR in cancers. For example, Yao et al. developed a GSH-responsive SO2-releasing nanosystem based on mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles (MONs) and poly(carboxybetaine methacrylate) (PCBMA) (Figure 10A) [149], which concurrently loaded SO2 prodrug molecules (DN, 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonylchloride) and DOX. The release of SO2 from DN under intracellular GSH could downregulate the expression of P-gp, thus sensitizing breast cancer cells to chemotherapy (Figure 10B). Sun et al. proposed a photo-activated H2 nanogenerator based on the fluorinated chitosan [107], which co-delivered [FeFe]TPP (a catalyst of H2 production) and gemcitabine (GEM) for enhanced chemotherapy in bladder cancer (Figure 10C). Upon a 660 nm illumination, these nanogenerators could efficiently generate H2 to cause the reduction of efflux pump function, which attenuated drug transport capacity of P-gp and improved the therapeutic efficacy of GEM (Figure 10D).
(A) Schematic illustration of the redox-responsive SO2-releasing nanosystem for producing synergistic effect of chemotherapy and gas therapy. (B) Mechanism of the reversal of MDR by the released SO2 and combination therapy. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [149], Copyright © 2020, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (C) Schematic illustration of the in situ photo-activated H2 nanogenerator ([FeFe]TPP/GEM/FCS) for enhanced chemotherapy of bladder cancer. (D) Mechanism of the recovery of chemosensitivity by H2 suppressing P-gp pump. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [107], Copyright © 2020, American Chemical Society. Abbreviations: MON: mesoporous organosilica nanoparticle; PCBMA: poly(carboxybetaine methacrylate); GEM: gemcitabine; FCS: fluorinated chitosan.
Co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and pro-apoptotic agents
One of the aforementioned MDR mechanisms is closely relevant to the regulation of apoptosis or survival pathways. Generally, the repair of dysfunctional apoptotic signaling by pro-apoptotic agents is capable of bypassing MDR of cancer cells [150]. Therefore, we may exploit various therapeutic nanocarriers to co-encapsulate chemotherapy drugs with apoptosis-induced compounds, thereby recovering the chemosensitivity in MDR cancer cells by influencing this classical death pathway. Ceramide (CER) as a type of apoptosis inducer plays a vital role in programmed cell death pathway. Whereas resistant tumor cells often restrain the apoptosis initiation by overexpressing glucosylceramide synthase that inactivates the CER. To address it, Van et al. used polymeric micelles to co-deliver a combination of PTX with CER against PTX-resistant ovarian cancer. Owning to CER-mediated aggravation of cell apoptosis, these co-delivery micelles could promote the PTX sensitivity in MDR cells and generate a 100-fold increase in cytotoxity [104]. Likewise, van Vlerken et al. adopted PTX and CER combination therapy based on a polymer-blend nanoplatform for both resistant ovarian and breast cancers, which successfully circumvented MDR by CER-mediated an enhancement in apoptotic signaling [150]. Additionally, since the hyper-expression of NF-κB may cause drug resistance of cancer cells, some pro-apoptotic agents related to NF-κB signaling pathway have been developed to block chemotherapeutic resistance in cancer treatment [151]. A previous study has indicated that, co-delivery of DOX and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC, a NF-κB inhibitor) using chitosan-based nanoparticles can successfully reverse MDR of human liver cancer cells by PDTC-induced inactivation of NF-κB pathway [152]. Cheng et al. also reported co-delivery of DOX and PDTC by a pH-sensitive polymeric nanoparticle based on poly(ortho ester urethanes) copolymers for overcoming MDR in breast cancer [153]. The acid-triggered release of PDTC could significantly reverse MDR and increase intracellular DOX accumulation through inhibiting NF-κB pathway, thus resulting in enhanced DOX-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in resistant breast cancer cells.
Co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and peptides/proteins
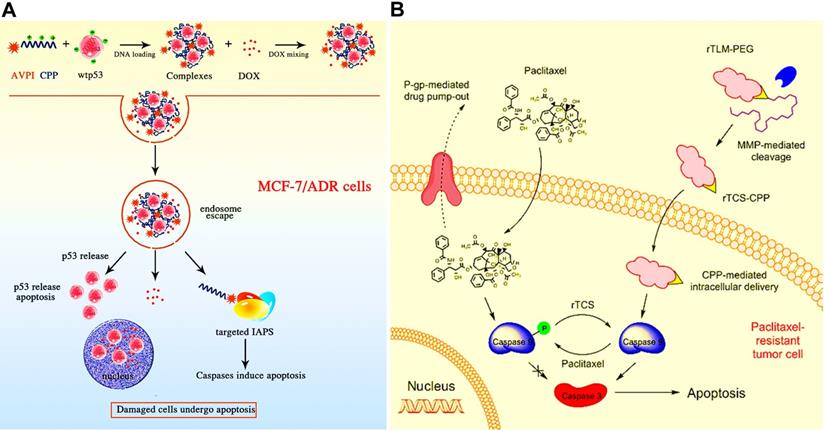
Peptides or proteins with high selectivity and potency are also identified as a model drug that defended the MDR mechanisms [154]. Many co-delivery nanocarriers have been designed to co-encapsulate peptides/proteins and chemotherapeutic agents against the tough MDR tumor. For example, Haggag et al. constructed liposomes co-delivering DOX and a Ras-related nuclear protein (Ran-GTP) inhibitory peptide for inhibiting DOX-resistant breast cancer [41]. In this study, the aberrant repair of DNA damage by Ran-GTP resulted in the occurrence of drug-resistance mechanism. Herein, the use of a Ran-GTP inhibitory peptide could effectively reverse the Ran-overexpression mediated MDR via inhibiting the DNA repair function of Ran, thus achieving enhanced DOX sensitivity and improved antitumor effect. Moreover, some chimeric peptides can also be served as a potent pro-apoptotic agent for overcoming tumor MDR. In a work, co-delivery of AVPIR8 chimeric peptide and p53 DNA using the self-assembly nanoparticles significantly increased the DOX sensitivity in the resistant MCF-7/ADR cells (Figure 11A) [155]. In addition to peptides, several therapeutic proteins (e.g., trichosanthin (TCS)) are emerging as candidates for overcoming cancer MDR [156]. For instance, a co-delivery liposomal carrier carrying a combination of TCS and PTX were constructed to circumvent PTX resistance in A549 lung cancer cells by reversing PTX-caused caspase 9 phosphorylation and inducing caspase 3-dependent apoptosis, and successfully suppressed the PTX-resistant A549 tumor growth in vivo (Figure 11B) [111].
Conclusion and outlook
With the accelerated advance in personalized and precision medicine, the exploitation of nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy is also becoming a booming research field. At present, a variety of nanoscale transport vehicles with different functional characteristics have been born at the right moment, which endue these drug delivery platforms with tumor selective targeting, tumor environmental or external physical stimulus responsiveness. Such an intelligent controlled-release system can better target tumor cells and be further internalized to release drugs in response to specific tumor physiological conditions or external physical stimuli. In addition, while designing these nanomedicines, we may consider either directly wrapping therapeutic drugs into the carrier under physical action or doping the drug molecules into the carrier by chemical graft. Here, MDR as a common feature of many cancers has undoubtedly become one of the most intractable challenges on the road to cancer treatment, which seriously affects the anticancer effect of chemotherapy, resulting in a high recurrence rate and a low survival rate in clinical cancer cases. Therefore, two drug models with different pharmaceutical and functional properties are considered to be integrated into an intelligent nanoplatform to combat tumor MDR. With the advantages of targeting and stimulus response of the nanoplatforms, therapeutic cargoes will be expected to be transported into drug-resistant tumor cells, and the synergistic effect of dual drugs can successfully reverse MDR and produce enhanced anti-tumor effects.
(A) Schematic illustration of co-delivery of cell-penetrating AVPI-R8/p53 DNA nanocomplex for overcoming drug resistance. Upon nanocomplex entered the resistant MCF-7/ADR cells, the p53 DNA and AVPIR8 chimeric peptide released from endosomal escape could induce caspase-dependent apoptosis, thereby easing DOX-resistance to potentiate the toxicity of resistant tumor cells. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [155], Copyright © 2014, American Chemical Society. (B) Schematic illustration of co-delivery of TCS (a ribosome-inactivating protein) and PTX by a liposomal carrier for reversal of chemoresistance in lung cancer. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [111], Copyright © 2017, American Chemical Society. Abbreviations: AVPI: the Smac N-terminal tetrapeptide; CPP: cell-penetrating peptide; IAPs: inhibitors of apoptosis proteins; TCS: trichosanthin; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase.
Nonetheless, there are still some severe challenges in the research on co-delivery of dual-drug using multifunctional nanoplatforms for treating multidrug resistant cancers. First, although nanomaterials can help drugs penetrate and accumulate within the resistant tumors, the actual number of drugs that can be delivered into tumor tissues is still limited. So, we also need to redouble our efforts in the development of drug delivery systems for combination therapy. Second, it is crucial to select the optimal combinatorial ratio of dual drugs, which directly affects the inhibitory effects on tumor cells, including synergistic, antagonistic, and non-additive effects. Moreover, due to the influence of complex in vivo physiological barriers, it is very likely to cause the changes of combinatorial ratio at any time, thus affecting the therapeutic effect of tumor. Third, the sequence and timing of each drug release from nanovehicles is also worth exploring, which directly affects how individual drug works. For instance, when using a nanocarrier co-delivering siRNA and DOX to treat multi-drug resistant cancers, it can be planned to first release siRNA to reverse MDR by inhibiting P-gp level, so as to increase the sensitivity and retention of subsequent release of DOX, and to maximize the anticancer toxicity of DOX. In addition, it is also critical to select the type of individual therapeutic agent in drug delivery systems. When two chemotherapeutic drugs are used in combination, the cross-tolerance generated in combination therapy should be avoided, instead of the dual-drug combination group that can generate collateral sensitivity. Last, when nanocarriers unload the therapeutic cargoes inside the tumor tissues or cells, these free-state drugs will still be affected by MDR mechanisms, likely resulting in drug molecules being inactivated or pumped out of cells in large quantities. Thus we may select appropriate MDR reversal agents that alleviate chemotherapy tolerance, such as surfactants, small molecule drugs, nucleic acid drugs, gaseous therapeutic agents or peptides/proteins, to restore the sensitivity of drug-resistant tumor cells to chemotherapeutic drugs.
Besides, taking nanotechnology-based combination therapeutics from bench to bedside is extremely challenging nowadays. The main reason for this is that, the development of co-delivery nanomedicines usually holds significantly higher level of complexity and difficulty in manufacturing, characterization and assessment, which will incur high costs and low benefits for future large-scale production in industry. For example, the precise ratio control of dual drugs in nanosystems is a big challenge in production, often resulting in batch-to-batch inconsistency. Moreover, it has been found that some certain nanomaterials are relevant to oxidative stress, undesirable inflammatory responses, and genotoxicity [18]. Accordingly, the latent adverse effects in nanomaterials should be also considered while designing combination therapies. Based on these issues, the clinical application of combinatorial nanomedicines still remains immature and unavailable, which makes it urgent to do a lot of pre-clinical basic work to increase the possibility of co-delivery nanomedicines to clinical translation in the future.
Nevertheless, several nanoplatforms possess the potential to clinically develop co-delivery nanomedicines. As is well-known, the first anticancer nano-drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) was liposome-based Doxil, and liposomes are currently widely used as nanocarriers for the clinical development of anticancer nanomedicines. The reasons why liposomes are favored in clinical practice may be as follows: (1) from the perspective of bionics, the phospholipid bilayer of liposomes is similar to the structure and components of animal cell membranes, which is more conducive to the delivery of drugs under complex physiological environment; (2) the synthesis of liposomes is controllable and regenerative, and its clinical evaluation and monitoring system has been well established; (3) the rich experience in the production and management of liposome drugs can be further used for reference. Therefore, we believe that liposome-based co-delivery nanomedicines that can eliminate cancer MDR will be available on the market in the near future. Furthermore, other FDA-approved carrier materials, such as PLGA and Fe3O4, also have unique advantages in developing co-delivery nanomedicines. In conclusion, with the rapid development of nanotechnology, more and more nanomaterials will be applied to clinical research, which makes it more possible to adopt co-delivery nanomedicines for the clinical treatment of multidrug resistant cancers.
Abbreviations
MDR: multidrug resistance; P-gp: P-glycoprotein; EPR: enhanced permeability and retention; MSNs: mesoporous silica nanoparticles; THZ: thioridazine; DFO: deferoxamine; YC-1: lificiguat; DOCA: deoxycholate; PLL: poly(L-lysine); ADM: adriamycin; PTX: paclitaxel; PDPA: poly(2-(diisopropyl amino)ethyl methacrylate); PEG: poly(ethylene glycol); DOX: doxorubicin; PLGA: poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid); PLA: poly-L-lactide; RAPA: rapamycin; CDDP: cisplatin; CS: chondroitin sulfate; DEX: dextran; HA: hyaluronic acid; PpIX: protoporphyrin IX; APA: Apatinib; CPT: camptothecin; DAT: dexamethasone; DTX: docetaxel; DSPE-PEG2000: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-methoxy(polyethyleneglycol); CHOL: cholesterol; TRAIL: tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; Fe3O4: iron oxide; CUR: curcumin; NGO: graphene oxide; FA: folate; TF: transferrin; TFR: transferrin receptor; GSH: glutathione; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; ABC: ATP-binding cassette; HCPT: 10-hydroxycamptothecin; TKIs: tyrosine kinase inhibitors; LPA: lapatinib; TPGS: D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate; NO: nitric oxide; H2: hydrogen; SO2: sulfur dioxide; MMP: mitochondrial membrane potential; CTAB: cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide; VER: verapamil; CyA: cyclosporin A; DSF: disulfiram; NIR: near-infrared; SNO: S-nitrosothiols; UV/Vis: ultraviolet-visible; GEM: gemcitabine; CER: ceramide; PDTC: pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; Ran-GTP: Ras-related nuclear protein; TCS: trichosanthin; FDA: Food and Drug Administration.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51703189), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No. 2019YJ0245 and 2020YFH0052), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2682019CX76 and 2682020ZT94) and the Key Project of Sichuan Science and Technology Innovation Engineering (No. 2019129).
Competing Interests
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394-424
2. Yin Q, Shen J, Zhang Z, Yu H, Li Y. Reversal of multidrug resistance by stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems for therapy of tumor. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2013;65:1699-1715
3. Bouwman P, Jonkers J. The effects of deregulated DNA damage signalling on cancer chemotherapy response and resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:587-598
4. Hu CM, Zhang L. Nanoparticle-based combination therapy toward overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1104-1111
5. Bock C, Lengauer T. Managing drug resistance in cancer: lessons from HIV therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:494-501
6. Huang IP, Sun SP, Cheng SH, Lee CH, Wu CY, Yang CS. et al. Enhanced chemotherapy of cancer using pH-sensitive mesoporous silica nanoparticles to antagonize P-glycoprotein-mediated drug resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:761-769
7. Wu Q, Yang ZP, Nie YZ, Shi YQ, Fan DM. Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 2014;347:159-166
8. DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL. et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. Ca-Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:252-271
9. Mader RM, Schmidt WM, Steger GG, Krupitza G. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. Int J Clin Pharmcol Ther. 2009;47:49-50
10. Shapira A, Livney YD, Broxterman HJ, Assaraf YG. Nanomedicine for targeted cancer therapy: Towards the overcoming of drug resistance. Drug Resist Updates. 2011;14:150-163
11. Garbuzenko OB, Saad M, Pozharov VP, Reuhl KR, Mainelis G, Minko T. Inhibition of lung tumor growth by complex pulmonary delivery of drugs with oligonucleotides as suppressors of cellular resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:10737-10742
12. Marusyk A, Almendro V, Polyak K. Intra-tumour heterogeneity: a looking glass for cancer? Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:323-334
13. Wilting RH, Dannenberg JH. Epigenetic mechanisms in tumorigenesis, tumor cell heterogeneity and drug resistance. Drug Resist Updates. 2012;15:21-38
14. Shen J, Wang QW, Hu QD, Li YB, Tang GP, Chu PK. Restoration of chemosensitivity by multifunctional micelles mediated by P-gp siRNA to reverse MDR. Biomaterials. 2014;35:8621-8634
15. Gillet JP, Gottesman MM. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;596:47-76
16. Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:714-726
17. Lee HJ, Zhuang G, Cao Y, Du P, Kim HJ, Settleman J. Drug resistance via feedback activation of Stat3 in oncogene-addicted cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:207-221
18. Kemp JA, Shim MS, Heo CY, Kwon YJ. "Combo" nanomedicine: Co-delivery of multi-modal therapeutics for efficient, targeted, and safe cancer therapy. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2016;98:3-18
19. Yap TA, Omlin A, de Bono JS. Development of therapeutic combinations targeting major cancer signaling pathways. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:1592-1605
20. Dong X, Mattingly CA, Tseng MT, Cho MJ, Liu Y, Adams VR. et al. Doxorubicin and paclitaxel-loaded lipid-based nanoparticles overcome multidrug resistance by inhibiting P-glycoprotein and depleting ATP. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3918-3926
21. Bansal T, Akhtar N, Jaggi M, Khar RK, Talegaonkar S. Novel formulation approaches for optimising delivery of anticancer drugs based on P-glycoprotein modulation. Drug Discovery Today. 2009;14:1067-1074
22. Gao Z, Zhang L, Sun Y. Nanotechnology applied to overcome tumor drug resistance. J Controlled Release. 2012;162:45-55
23. Duncan R. The dawning era of polymer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2003;2:347-360
24. Liu J, Zhao Y, Guo Q, Wang Z, Wang H, Yang Y. et al. TAT-modified nanosilver for combating multidrug-resistant cancer. Biomaterials. 2012;33:6155-6161
25. Wang H, Zhao Y, Wang H, Gong J, He H, Shin MC. et al. Low-molecular-weight protamine-modified PLGA nanoparticles for overcoming drug-resistant breast cancer. J Controlled Release. 2014;192:47-56
26. Woodcock J, Griffin JP, Behrman RE. Development of novel combination therapies. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:985-987
27. Wei X, Wang Y, Xiong X, Guo X, Zhang L, Zhang X. et al. Codelivery of a π-π stacked dual anticancer drug combination with nanocarriers for overcoming multidrug resistance and tumor metastasis. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26:8266-8280
28. Liang X, Gao C, Cui L, Wang S, Wang J, Dai Z. Self-Assembly of an amphiphilic Janus camptothecin-floxuridine conjugate into liposome-like nanocapsules for more efficacious combination chemotherapy in cancer. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1703135
29. Guo S, Lin CM, Xu Z, Miao L, Wang Y, Huang L. Co-delivery of cisplatin and rapamycin for enhanced anticancer therapy through synergistic effects and microenvironment modulation. ACS Nano. 2014;8:4996-5009
30. Yu Q, Deng T, Lin FC, Zhang B, Zink JI. Supramolecular assemblies of heterogeneous mesoporous silica nanoparticles to co-deliver antimicrobial peptides and antibiotics for synergistic eradication of pathogenic biofilms. ACS Nano. 2020;14:5926-5937
31. Zhang Y, Fu X, Jia J, Wikerholmen T, Xi K, Kong Y. et al. Glioblastoma therapy using codelivery of cisplatin and glutathione peroxidase targeting siRNA from iron oxide nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:43408-43421
32. Ding J, Liang T, Min Q, Jiang L, Zhu JJ. "Stealth and fully-laden" drug carriers: self-assembled nanogels encapsulated with epigallocatechin gallate and siRNA for drug-resistant breast cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:9938-9948
33. Cheng G, Yin C, Tu H, Jiang S, Wang Q, Zhou X. et al. Controlled co-delivery of growth factors through layer-by-layer assembly of core-shell nanofibers for improving bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 2019;13:6372-6382
34. Ke XY, Lin Ng VW, Gao SJ, Tong YW, Hedrick JL, Yang YY. Co-delivery of thioridazine and doxorubicin using polymeric micelles for targeting both cancer cells and cancer stem cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35:1096-1108
35. Lv S, Tang Z, Li M, Lin J, Song W, Liu H. et al. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel by PEG-polypeptide nanovehicle for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Biomaterials. 2014;35:6118-6129
36. Li Y, Wang H, Wang K, Hu Q, Yao Q, Shen Y. et al. Targeted co-delivery of PTX and TR3 siRNA by PTP peptide modified dendrimer for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Small. 2017;13:1602697
37. Shi S, Shi K, Tan LW, Qu Y, Shen GB, Chu BY. et al. The use of cationic MPEG-PCL-g-PEI micelles for co-delivery of Msurvivin T34A gene and doxorubicin. Biomaterials. 2014;35:4536-4547
38. Sun R, Liu Y, Li SY, Shen S, Du XJ, Xu CF. et al. Co-delivery of all-trans-retinoic acid and doxorubicin for cancer therapy with synergistic inhibition of cancer stem cells. Biomaterials. 2015;37:405-414
39. Devulapally R, Sekar NM, Sekar TV, Foygel K, Massoud TF, Willmann JK. et al. Polymer nanoparticles mediated codelivery of antimiR-10b and antimiR-21 for achieving triple negative breast cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2015;9:2290-2302
40. Deng XW, Cao MJ, Zhang JK, Hu KL, Yin ZX, Zhou ZX. et al. Hyaluronic acid-chitosan nanoparticles for co-delivery of M1R-34a and doxorubicin in therapy against triple negative breast cancer. Biomaterials. 2014;35:4333-4344
41. Haggag Y, Abu Ras B, El-Tanani Y, Tambuwala MM, McCarron P, Isreb M. et al. Co-delivery of a RanGTP inhibitory peptide and doxorubicin using dual-loaded liposomal carriers to combat chemotherapeutic resistance in breast cancer cells. Expert Opin Drug Delivery. 2020;17:1655-1669
42. Huang SQ, Zhang YC, Wang LY, Liu W, Xiao LY, Lin Q. et al. Improved melanoma suppression with target-delivered TRAIL and Paclitaxel by a multifunctional nanocarrier. J Controlled Release. 2020;325:10-24
43. Feng Q, Yu MZ, Wang JC, Hou WJ, Gao LY, Ma XF. et al. Synergistic inhibition of breast cancer by co-delivery of VEGF siRNA and paclitaxel via vapreotide-modified core-shell nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2014;35:5028-5038
44. Lang J, Zhao X, Wang X, Zhao Y, Li Y, Zhao R. et al. Targeted co-delivery of the iron chelator deferoxamine and a HIF1alpha inhibitor impairs pancreatic tumor growth. ACS Nano. 2019;13:2176-2189
45. Li ZY, Liu Y, Wang XQ, Liu LH, Hu JJ, Luo GF. et al. One-pot construction of functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the tumor-acidity-activated synergistic chemotherapy of glioblastoma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:7995-8001
46. Meng H, Mai WX, Zhang H, Xue M, Xia T, Lin S. et al. Codelivery of an optimal drug/siRNA combination using mesoporous silica nanoparticles to overcome drug resistance in breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano. 2013;7:994-1005
47. Khafaji M, Zamani M, Vossoughi M, Iraji Zad A. Doxorubicin/cisplatin-loaded superparamagnetic nanoparticles as a stimuli-responsive co-delivery system for chemo-photothermal therapy. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:8769-8786
48. Wu H, Jin H, Wang C, Zhang Z, Ruan H, Sun L. et al. Synergistic cisplatin/doxorubicin combination chemotherapy for multidrug-resistant cancer via polymeric nanogels targeting delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:9426-9436
49. Zhi F, Dong H, Jia X, Guo W, Lu H, Yang Y. et al. Functionalized graphene oxide mediated adriamycin delivery and miR-21 gene silencing to overcome tumor multidrug resistance in vitro. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60034
50. Zhang D, Xu Q, Wang N, Yang YT, Liu JQ, Yu GH. et al. A complex micellar system co-delivering curcumin with doxorubicin against cardiotoxicity and tumor growth. Int J Nanomed. 2018;13:4549-4561
51. Huo Q, Zhu JH, Niu YM, Shi HH, Gong YX, Li Y. et al. pH-triggered surface charge-switchable polymer micelles for the co-delivery of paclitaxel/disulfiram and overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:8631-8647
52. Li HM, Fu Y, Zhang T, Li YP, Hong XY, Jiang JY. et al. Rational design of polymeric hybrid micelles with highly tunable properties to co-deliver microRNA-34a and vismodegib for melanoma therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25:7457-7469
53. Chen WC, Yuan YY, Cheng D, Chen JF, Wang L, Shuai XT. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and siRNA with reduction and pH dually sensitive nanocarrier for synergistic cancer therapy. Small. 2014;10:2678-2687
54. Hu CMJ, Zhang LF. Nanoparticle-based combination therapy toward overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:1104-1111
55. Wei X, Liu L, Guo X, Wang Y, Zhao J, Zhou S. Light-activated ROS-responsive nanoplatform codelivering apatinib and doxorubicin for enhanced chemo-photodynamic therapy of multidrug-resistant tumors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:17672-17684
56. Aryal S, Hu CM, Zhang L. Polymeric nanoparticles with precise ratiometric control over drug loading for combination therapy. Mol Pharmcol. 2011;8:1401-1407
57. Guo ST, Lin CM, Xu ZH, Miao L, Wang YH, Huang L. Co-delivery of cisplatin and rapamycin for enhanced anticancer therapy through synergistic effects and microenvironment modulation. ACS Nano. 2014;8:4996-5009
58. Wang Y, Wei G, Zhang X, Xu F, Xiong X, Zhou S. A step-by-step multiple stimuli-responsive nanoplatform for enhancing combined chemo-photodynamic therapy. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1605357
59. Deng X, Cao M, Zhang J, Hu K, Yin Z, Zhou Z. et al. Hyaluronic acid-chitosan nanoparticles for co-delivery of MiR-34a and doxorubicin in therapy against triple negative breast cancer. Biomaterials. 2014;35:4333-4344
60. Bangham AD, Standish MM, Watkins JC. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J Mol Biol. 1965;13:238-252
61. Lang JY, Zhao X, Wang XC, Zhao Y, Li YY, Zhao RF. et al. Targeted co-delivery of the iron Chelator deferoxamine and a HIF1 alpha inhibitor impairs pancreatic tumor growth. ACS Nano. 2020;14:1211-1211
62. Yang T, Li B, Qi S, Liu Y, Gai Y, Ye P. et al. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and Bmi1 siRNA by folate receptor targeted liposomes exhibits enhanced anti-tumor effects in vitro and in vivo. Theranostics. 2014;4:1096-1111
63. Zhang L, Su HT, Liu YJ, Pang N, Li J, Qi XR. Enhancing solid tumor therapy with sequential delivery of dexamethasone and docetaxel engineered in a single carrier to overcome stromal resistance to drug delivery. J Controlled Release. 2019;294:1-16
64. Zhang CM, Zhang SB, Zhi DF, Zhao YA, Cui SH, Cui JN. Co-delivery of paclitaxel and survivin siRNA with cationic liposome for lung cancer therapy. Colloids Surf A. 2020;585:124054
65. Xu ZG, Liu SY, Kang YJ, Wang MF. Glutathione- and pH-responsive nonporous silica prodrug nanoparticles for controlled release and cancer therapy. Nanoscale. 2015;7:5859-5868
66. Dutta B, Shetake NG, Barick BK, Barick KC, Pandey BN, Priyadarsini KI. et al. pH sensitive surfactant-stabilized Fe3O4 magnetic nanocarriers for dual drug delivery. Colloids Surf B. 2018;162:163-171
67. Chen SX, Ge LP, Mueller A, Carlson MA, Teusink MJ, Shuler FD. et al. Twisting electrospun nanofiber fine strips into functional sutures for sustained co-delivery of gentamicin and silver. Nanomed-Nanotechnol. 2017;13:1435-1445
68. Wang QS, Gao LN, Zhu XN, Zhang Y, Zhang CN, Xu D. et al. Co-delivery of glycyrrhizin and doxorubicin by alginate nanogel particles attenuates the activation of macrophage and enhances the therapeutic efficacy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics. 2019;9:6239-6255
69. Yang HW, Huang CY, Chih-Wen L, Liu HL, Huang CW, Liao SS. et al. Gadolinium-functionalized nanographene oxide for combined drug and microRNA delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials. 2014;35:6534-6542
70. Torchilin VP. Multifunctional, stimuli-sensitive nanoparticulate systems for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2014;13:813-827
71. Dai YL, Xu C, Sun XL, Chen XY. Nanoparticle design strategies for enhanced anticancer therapy by exploiting the tumour microenvironment. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46:3830-3852
72. Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:941-951
73. Guo X, Wei X, Chen Z, Zhang XB, Yang G, Zhou SB. Multifunctional nanoplatforms for subcellular delivery of drugs in cancer therapy. Prog Mater Sci. 2020;107:100599
74. Yang G, Wang J, Wang Y, Li L, Guo X, Zhou S. An implantable active-targeting micelle-in-nanofiber device for efficient and safe cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2015;9:1161-1174
75. Choi CH, Alabi CA, Webster P, Davis ME. Mechanism of active targeting in solid tumors with transferrin-containing gold nanoparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:1235-1240
76. Xiong XB, Lavasanifar A. Traceable multifunctional micellar nanocarriers for cancer-targeted co-delivery of MDR-1 siRNA and doxorubicin. ACS Nano. 2011;5:5202-5213
77. Qiu L, Qiao M, Chen Q, Tian C, Long M, Wang M. et al. Enhanced effect of pH-sensitive mixed copolymer micelles for overcoming multidrug resistance of doxorubicin. Biomaterials. 2014;35:9877-9887
78. Du JZ, Sun TM, Song WJ, Wu J, Wang J. A tumor-acidity-activated charge-conversional nanogel as an intelligent vehicle for promoted tumoral-cell uptake and drug delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:3621-3626
79. Wang X, Chen C, Huo D, Qian H, Ding Y, Hu Y. et al. Synthesis of beta-cyclodextrin modified chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) nanoparticles and use as drug carriers. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;90:361-369
80. Pecot CV, Calin GA, Coleman RL, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK. RNA interference in the clinic: challenges and future directions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:59-67
81. Duan XP, Xiao JS, Yin Q, Zhang ZW, Yu HJ, Mao SR. et al. Smart pH-sensitive and temporal-controlled polymeric micelles for effective combination therapy of doxorubicin and disulfiram. ACS Nano. 2013;7:5858-5869
82. Yu PC, Yu HJ, Guo CY, Cui ZR, Chen XZ, Yin Q. et al. Reversal of doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer by mitochondria-targeted pH-responsive micelles. Acta Biomater. 2015;14:115-124
83. She WC, Luo K, Zhang CY, Wang G, Geng YY, Li L. et al. The potential of self-assembled, pH-responsive nanoparticles of mPEGylated peptide dendron-doxorubicin conjugates for cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2013;34:1613-1623
84. Li YL, Zhu L, Liu ZZ, Cheng R, Meng FH, Cui JH. et al. Reversibly stabilized multifunctional dextran nanoparticles efficiently deliver doxorubicin into the nuclei of cancer cells. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:9914-9918
85. Meng FH, Hennink WE, Zhong Z. Reduction-sensitive polymers and bioconjugates for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2009;30:2180-2198
86. Van Laer K, Hamilton CJ, Messens J. Low-molecular-weight thiols in thiol-disulfide exchange. Antioxid Redox Signaling. 2013;18:1642-1653
87. Li S, Saw PE, Lin C, Nie Y, Tao W, Farokhzad OC. et al. Redox-responsive polyprodrug nanoparticles for targeted siRNA delivery and synergistic liver cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2020;234:119760
88. Yin Q, Shen JA, Chen LL, Zhang ZW, Gu WW, Li YP. Overcoming multidrug resistance by co-delivery of Mdr-1 and survivin-targeting RNA with reduction-responsible cationic poly(beta-amino esters). Biomaterials. 2012;33:6495-6506
89. Zhang XQ, Ren XM, Tang JY, Wang JT, Zhang X, He P. et al. Hyaluronic acid reduction-sensitive polymeric micelles achieving co-delivery of tumor-targeting paclitaxel/apatinib effectively reverse cancer multidrug resistance. Drug Delivery. 2020;27:825-835
90. Dong HN, Pang L, Cong HL, Shen YQ, Yu B. Application and design of esterase-responsive nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Drug Delivery. 2019;26:416-432
91. Bai Y, Liu CP, Chen D, Liu CF, Zhuo LH, Li H. et al. beta-Cyclodextrin-modified hyaluronic acid-based supramolecular self-assemblies for pH- and esterase-dual-responsive drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;246:116654
92. Salzano G, Costa DF, Sarisozen C, Luther E, Mattheolabakis G, Dhargalkar PP. et al. Mixed nanosized polymeric micelles as promoter of doxorubicin and miRNA-34a co-delivery triggered by dual stimuli in tumor tissue. Small. 2016;12:4837-4848
93. Qiu WX, Liu LH, Li SY, Lei Q, Luo GF, Zhang XZ. ACPI conjugated gold nanorods as nanoplatform for dual image guided activatable photodynamic and photothermal combined therapy in vivo. Small. 2017;13:1603956
94. Yu J, Ju Y, Zhao L, Chu X, Yang W, Tian Y. et al. Multistimuli-regulated photochemothermal cancer therapy remotely controlled via Fe5C2 nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2016;10:159-169
95. Lu F, Popa A, Zhou S, Zhu JJ, Samia AC. Iron oxide-loaded hollow mesoporous silica nanocapsules for controlled drug release and hyperthermia. Chem Commun. 2013;49:11436-11438
96. Shang MM, Sun X, Guo L, Shi DD, Liang P, Meng D. et al. pH- and ultrasound-responsive paclitaxel-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan nanodroplets for combined imaging and synergistic chemoradiotherapy. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:537-552
97. Yin T, Wang P, Li J, Wang Y, Zheng B, Zheng R. et al. Tumor-penetrating codelivery of siRNA and paclitaxel with ultrasound-responsive nanobubbles hetero-assembled from polymeric micelles and liposomes. Biomaterials. 2014;35:5932-5943
98. Baghbani F, Moztarzadeh F. Bypassing multidrug resistant ovarian cancer using ultrasound responsive doxorubicin/curcumin co-deliver alginate nanodroplets. Colloids Surf B. 2017;153:132-140
99. Shen J, Wang Q, Hu Q, Li Y, Tang G, Chu PK. Restoration of chemosensitivity by multifunctional micelles mediated by P-gp siRNA to reverse MDR. Biomaterials. 2014;35:8621-8634
100. Shapira A, Livney YD, Broxterman HJ, Assaraf YG. Nanomedicine for targeted cancer therapy: towards the overcoming of drug resistance. Drug Resist Updates. 2011;14:150-163
101. Pommier Y, Sordet O, Antony S, Hayward RL, Kohn KW. Apoptosis defects and chemotherapy resistance: molecular interaction maps and networks. Oncogene. 2004;23:2934-2949
102. Yuan H, Li X, Wu J, Li J, Qu X, Xu W. et al. Strategies to overcome or circumvent P-glycoprotein mediated multidrug resistance. Curr Med Chem. 2008;15:470-476
103. Wang H, Li F, Du C, Wang H, Mahato RI, Huang Y. Doxorubicin and lapatinib combination nanomedicine for treating resistant breast cancer. Mol Pharmcol. 2014;11:2600-2611
104. van Vlerken LE, Duan Z, Seiden MV, Amiji MM. Modulation of intracellular ceramide using polymeric nanoparticles to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4843-4850
105. Soma CE, Dubernet C, Bentolila D, Benita S, Couvreur P. Reversion of multidrug resistance by co-encapsulation of doxorubicin and cyclosporin A in polyalkylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2000;21:1-7
106. Li H, Sun Y, Liang J, Fan Y, Zhang X. pH-Sensitive pullulan-DOX conjugate nanoparticles for co-loading PDTC to suppress growth and chemoresistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3:8070-8078
107. Sun R, Liu XC, Li GZ, Wang H, Luo YX, Huang GX. et al. Photoactivated H-2 Nanogenerator for Enhanced Chemotherapy of Bladder Cancer. ACS Nano. 2020;14:8135-8148
108. Fan J, He QJ, Liu Y, Zhang FW, Yang XY, Wang Z. et al. Light-responsive biodegradable nanomedicine overcomes multidrug resistance via NO-enhanced chemosensitization. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:13804-13811
109. He C, Liu D, Lin W. Self-assembled nanoscale coordination polymers carrying siRNAs and cisplatin for effective treatment of resistant ovarian cancer. Biomaterials. 2015;36:124-133
110. Liu Y, Li LL, Qi GB, Chen XG, Wang H. Dynamic disordering of liposomal cocktails and the spatio-temporal favorable release of cargoes to circumvent drug resistance. Biomaterials. 2014;35:3406-3415
111. Chen Y, Zhang M, Jin H, Tang Y, Wu A, Xu Q. et al. Prodrug-like, PEGylated protein toxin trichosanthin for reversal of chemoresistance. Mol Pharmcol. 2017;14:1429-1438
112. Chen M, Song F, Liu Y, Tian J, Liu C, Li R. et al. A dual pH-sensitive liposomal system with charge-reversal and NO generation for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer. Nanoscale. 2019;11:3814-3826
113. He Q, Shi J. MSN anti-cancer nanomedicines: chemotherapy enhancement, overcoming of drug resistance, and metastasis inhibition. Adv Mater. 2014;26:391-411
114. Sun L, Wang D, Chen Y, Wang L, Huang P, Li Y. et al. Core-shell hierarchical mesostructured silica nanoparticles for gene/chemo-synergetic stepwise therapy of multidrug-resistant cancer. Biomaterials. 2017;133:219-228
115. Wang C, Guan W, Peng J, Chen Y, Xu G, Dou H. Gene/paclitaxel co-delivering nanocarriers prepared by framework-induced self-assembly for the inhibition of highly drug-resistant tumors. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:247-258
116. Szakacs G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA, Booth-Genthe C, Gottesman MM. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2006;5:219-234
117. Jensen PB, Holm B, Sorensen M, Christensen IJ, Sehested M. In vitro cross-resistance and collateral sensitivity in seven resistant small-cell lung cancer cell lines: preclinical identification of suitable drug partners to taxotere, taxol, topotecan and gemcitabin. Br J Cancer. 1997;75:869-877
118. Yu C, Zhou M, Zhang X, Wei W, Chen X, Zhang X. Smart doxorubicin nanoparticles with high drug payload for enhanced chemotherapy against drug resistance and cancer diagnosis. Nanoscale. 2015;7:5683-5690
119. Lee SM, O'Halloran TV, Nguyen ST. Polymer-caged nanobins for synergistic cisplatin-doxorubicin combination chemotherapy. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:17130-17138
120. McMeekin S, Dizon D, Barter J, Scambia G, Manzyuk L, Lisyanskaya A. et al. Phase III randomized trial of second-line ixabepilone versus paclitaxel or doxorubicin in women with advanced endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;138:18-23
121. Randall ME, Filiaci VL, Muss H, Spirtos NM, Mannel RS, Fowler J. et al. Randomized phase III trial of whole-abdominal irradiation versus doxorubicin and cisplatin chemotherapy in advanced endometrial carcinoma: a Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:36-44
122. Morton SW, Lee MJ, Deng ZJ, Dreaden EC, Siouve E, Shopsowitz KE. et al. A nanoparticle-based combination chemotherapy delivery system for enhanced tumor killing by dynamic rewiring of signaling pathways. Sci Signaling. 2014;7:ra44
123. He M, Wei MJ. Reversing multidrug resistance by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Chin J Cancer. 2012;31:126-133
124. Flemming A. Anticancer drugs: Finding the perfect combination. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2015;14:13-13
125. He Y, Li X, Ma J, Ni G, Yang G, Zhou S. Programmable codelivery of doxorubicin and apatinib using an implantable hierarchical-structured fiber device for overcoming cancer multidrug resistance. Small. 2019;15:e1804397
126. Rejman J, Oberle V, Zuhorn IS, Hoekstra D. Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J. 2004;377:159-169
127. Yu HJ, Cui ZR, Yu PC, Guo CY, Feng B, Jiang TY. et al. pH- and NIR light-responsive micelles with hyperthermia-triggered tumor penetration and cytoplasm drug release to reverse doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25:2489-2500
128. Creixell M, Peppas NA. Co-delivery of siRNA and therapeutic agents using nanocarriers to overcome cancer resistance. Nano Today. 2012;7:367-379
129. Hong W, Chen D, Zhang X, Zeng J, Hu H, Zhao X. et al. Reversing multidrug resistance by intracellular delivery of Pluronic(R) P85 unimers. Biomaterials. 2013;34:9602-9614
130. Zhang Z, Tan S, Feng SS. Vitamin E TPGS as a molecular biomaterial for drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2012;33:4889-4906
131. Yu P, Yu H, Guo C, Cui Z, Chen X, Yin Q. et al. Reversal of doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer by mitochondria-targeted pH-responsive micelles. Acta Biomater. 2015;14:115-124
132. Zhu H, Chen H, Zeng X, Wang Z, Zhang X, Wu Y. et al. Co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs with vitamin E TPGS by porous PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced chemotherapy against multi-drug resistance. Biomaterials. 2014;35:2391-2400
133. Assanhou AG, Li W, Zhang L, Xue L, Kong L, Sun H. et al. Reversal of multidrug resistance by co-delivery of paclitaxel and lonidamine using a TPGS and hyaluronic acid dual-functionalized liposome for cancer treatment. Biomaterials. 2015;73:284-295
134. He Q, Gao Y, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Gao F, Ji X. et al. A pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based multi-drug delivery system for overcoming multi-drug resistance. Biomaterials. 2011;32:7711-7720
135. de Fougerolles A, Vornlocher HP, Maraganore J, Lieberman J. Interfering with disease: a progress report on siRNA-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2007;6:443-453
136. Lammers T, Subr V, Ulbrich K, Peschke P, Huber PE, Hennink WE. et al. Simultaneous delivery of doxorubicin and gemcitabine to tumors in vivo using prototypic polymeric drug carriers. Biomaterials. 2009;30:3466-3475
137. Han M, Lv Q, Tang XJ, Hu YL, Xu DH, Li FZ. et al. Overcoming drug resistance of MCF-7/ADR cells by altering intracellular distribution of doxorubicin via MVP knockdown with a novel siRNA polyamidoamine-hyaluronic acid complex. J Controlled Release. 2012;163:136-144
138. Wu M, Meng Q, Chen Y, Zhang L, Li M, Cai X. et al. Large pore-sized hollow mesoporous organosilica for redox-responsive gene delivery and synergistic cancer chemotherapy. Adv Mater. 2016;28:1963-1969
139. Zhang J, Du Z, Pan S, Shi M, Li J, Yang C. et al. Overcoming multidrug resistance by codelivery of MDR1-targeting siRNA and doxorubicin using EphA10-mediated pH-sensitive lipoplexes: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:21590-21600
140. Wu M, Lin X, Tan X, Li J, Wei Z, Zhang D. et al. Photoresponsive nanovehicle for two independent wavelength light-triggered sequential release of P-gp shRNA and doxorubicin to optimize and enhance synergistic therapy of multidrug-resistant cancer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:19416-19427
141. Qin M, Lee YEK, Ray A, Kopelman R. Overcoming cancer multidrug resistance by codelivery of doxorubicin and verapamil with hydrogel nanoparticles. Macromol Biosci. 2014;14:1106-1115
142. Maiti C, Parida S, Kayal S, Maiti S, Mandal M, Dhara D. Redox-responsive core-cross-linked block copolymer micelles for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:5318-5330
143. Fathy Abd-Ellatef GE, Gazzano E, Chirio D, Hamed AR, Belisario DC, Zuddas C. et al. Curcumin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles bypass P-glycoprotein mediated doxorubicin resistance in triple negative breast cancer cells. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12:96
144. Lin S, Xie PL, Luo MM, Li Q, Li L, Zhang JZ. et al. Efficiency against multidrug resistance by co-delivery of doxorubicin and curcumin with a legumain-sensitive nanocarrier. Nano Res. 2018;11:3619-3635
145. Wang L, Guan H, Wang Z, Xing Y, Zhang J, Cai K. Hybrid mesoporous-microporous nanocarriers for overcoming multidrug resistance by sequential drug delivery. Mol Pharm. 2018;15:2503-2512
146. Guo RR, Tian Y, Wang YJ, Yang WL. Near-infrared laser-triggered nitric oxide nanogenerators for the reversal of multidrug resistance in cancer. Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27:1606398
147. Wan MM, Chen H, Da Wang Z, Liu ZY, Yu YQ, Li L. et al. Nitric oxide-driven nanomotor for deep tissue penetration and multidrug resistance reversal in cancer therapy. Adv Sci. 2021;8:2002525
148. Chu C, Lyu X, Wang Z, Jin H, Lu S, Xing D. et al. Cocktail polyprodrug nanoparticles concurrently release cisplatin and peroxynitrite-generating nitric oxide in cisplatin-resistant cancers. Chem Eng J. 2020;402:126125
149. Yao XX, Ma SP, Peng SJ, Zhou GX, Xie RH, Jiang Q. et al. Zwitterionic polymer coating of sulfur dioxide-releasing nanosystem augments tumor accumulation and treatment efficacy. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2020;9:1901582
150. van Vlerken LE, Duan ZF, Little SR, Seiden MV, Amiji MM. Augmentation of therapeutic efficacy in drug-resistant tumor models using ceramide coadministration in temporal-controlled polymer-blend nanoparticle delivery systems. AAPS J. 2010;12:171-180
151. Patel NM, Nozaki S, Shortle NH, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Newton TR, Rice S. et al. Paclitaxel sensitivity of breast cancer cells with constitutively active NF-kappaB is enhanced by IkappaBalpha super-repressor and parthenolide. Oncogene. 2000;19:4159-4169
152. Fan L, Li F, Zhang H, Wang Y, Cheng C, Li X. et al. Co-delivery of PDTC and doxorubicin by multifunctional micellar nanoparticles to achieve active targeted drug delivery and overcome multidrug resistance. Biomaterials. 2010;31:5634-5642
153. Cheng X, Li D, Sun M, He L, Zheng Y, Wang X. et al. Co-delivery of DOX and PDTC by pH-sensitive nanoparticles to overcome multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Colloids Surf B. 2019;181:185-197
154. Patel A, Patel M, Yang X, Mitra AK. Recent advances in protein and Peptide drug delivery: a special emphasis on polymeric nanoparticles. Protein Pept Lett. 2014;21:1102-1120
155. Wang H, Wang H, Liang J, Jiang Y, Guo Q, Peng H. et al. Cell-penetrating apoptotic peptide/p53 DNA nanocomplex as adjuvant therapy for drug-resistant breast cancer. Mol Pharmacol. 2014;11:3352-3360
156. Ezan E. Pharmacokinetic studies of protein drugs: past, present and future. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2013;65:1065-1073
Author contact
![]() Corresponding authors: School of Preclinical Medicine, Chengdu University, Chengdu 610106, P. R. China (X. Wei); College of Medicine, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, P. R. China (G. Yang); School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, P. R. China (Y. Wang). E-mail: weixiaoedu.cn (Xiao Wei); gyangedu.cn (Guang Yang); ywedu.cn (Yi Wang).
Corresponding authors: School of Preclinical Medicine, Chengdu University, Chengdu 610106, P. R. China (X. Wei); College of Medicine, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, P. R. China (G. Yang); School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, P. R. China (Y. Wang). E-mail: weixiaoedu.cn (Xiao Wei); gyangedu.cn (Guang Yang); ywedu.cn (Yi Wang).
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact