13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(10):4699-4709. doi:10.7150/thno.54546 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Peripheral eosinophil counts predict efficacy of anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy against B-lineage non-Hodgkin lymphoma
1. Department of Oncology, Xinqiao Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing 400037, China.
2. Chongqing Key Laboratory of Immunotherapy, Chongqing 400037, China.
3. Department of Thoracic Oncology, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University and Collaborative Innovation Center, Chengdu 610041, China.
4. Department of Immunology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, USA.
5. R&D Department, HRAIN Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China.
6. Department of Oncology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 401120, China.
7. Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education/Beijing), Department of Lymphoma, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China.
8. Department of Bio-therapeutic, The First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China.
9. Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA; Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Pharmacology, University of Southern California, 3710 McClintock Ave., RTH506, Los Angeles, CA 90089, USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
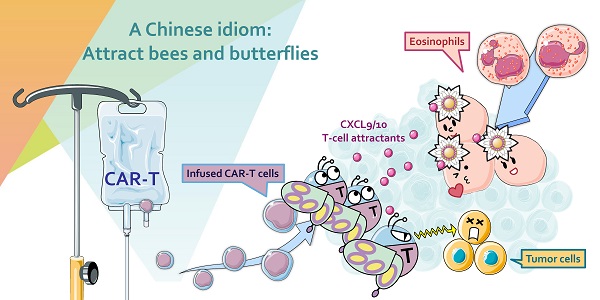
Rationale: The onset of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and in vivo persistence of anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells after infusion correlate with clinical responsiveness. However, there are no known baseline biomarkers that can predict the prognosis of patients with B-lineage non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL). The aim of this study was to identify blood cell populations associated with beneficial outcomes in B-NHL patients administered CAR-T cell immunotherapies.
Methods: We enumerated peripheral blood and CAR-T cells by retrospectively analyzing three CAR-T cell trials involving 65 B-NHL patients. We used a preclinical model to elucidate the eosinophil mechanism in CAR-T cell therapy.
Results: During an observation period up to 30 mo, B-NHL patients with higher baseline eosinophil counts had higher objective response rates than those with low eosinophil counts. Higher baseline eosinophil counts were also significantly associated with durable progression-free survival (PFS). The predictive significance of baseline eosinophil counts was validated in two independent cohorts. A preclinical model showed that eosinophil depletion impairs the intratumoral infiltration of transferred CAR-T cells and reduces CAR-T cell antitumor efficacy.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that peripheral eosinophils could serve as stratification biomarkers and a recruitment machinery to facilitate anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy in B-NHL patients.
Keywords: biomarker, B-NHL, CAR-T, eosinophil, infiltration
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact