13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(6):2634-2654. doi:10.7150/thno.53139 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Encapsulation of LXR ligand by D-Nap-GFFY hydrogel enhances anti-tumorigenic actions of LXR and removes LXR-induced lipogenesis
1. College of Life Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical Biology, Key Laboratory of Bioactive Materials of Ministry of Education, Nankai University, Tianjin, China.
2. First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Metabolism and Regulation for Major Diseases of Anhui Higher Education Institutes, College of Food and Biological Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China.
4. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Center of Functional Biomaterials, Key Laboratory of Polymeric Composite Materials and Functional Materials of Ministry of Education, GD Research Center for Functional Biomaterials Engineering and Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
* These authors made equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
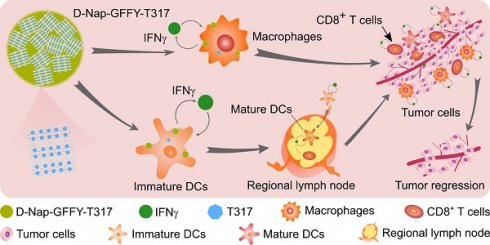
Background and purpose: Activation of liver X receptor (LXR) by its ligand T0901317 (T317) enhances interferon-γ (IFNγ) production to inhibit tumor growth. However, induction of severe hypertriglyceridemia and fatty liver by T317 limits its application. The naphthylacetic acid modified D-enantiomeric-glycine-phenylalanine-phenylalanine-tyrosine (D-Nap-GFFY) can form a nanofiber hydrogel which is selectively taken up by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). In this study, we determined if D-Nap-GFFY-encapsulated T317 (D-Nap-GFFY-T317) can potently inhibit tumor growth while having no adverse lipogenic effects on the liver.
Methods: We prepared D-Nap-GFFY-T317 nanofiber hydrogel and subcutaneously injected it into IFNγ deficient (IFNγ-/-) and wild-type (WT) mice with lung carcinoma, either inoculated LLC1 cells or urethane-induced carcinoma. Mice received oral T317 administration were used for comparison. Effects of treatment on tumor growth, lipogenesis and involved mechanisms were investigated.
Results: Compared with T317 oral administration, injection of D-Nap-GFFY-T317 more potently inhibited LLC1 tumor growth in mice. The inhibition was dependent on LXR-activated IFNγ expression in APCs. D-Nap-GFFY-T317 increased M1 while reducing M2 type macrophages in tumors. Associated with activation of IFNγ expression, D-Nap-GFFY-T317 enhanced dendritic cell maturation and infiltration into tumors, increased CD3+/CD8+ cells in tumors, and inhibited tumor angiogenesis. Similarly, D-Nap-GFFY-T317 more potently inhibited growth of urethane-induced lung carcinomas than T317 oral administration. In these two tumor models, T317 oral administration, but not D-Nap-GFFY-T317 injection, activated hepatic lipogenesis and induced fatty liver.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that D-Nap-GFFY-T317 inhibits lung tumor growth without adverse effects on the liver, indicating the hydrogel-encapsulated LXR ligand might be a novel therapy for tumor treatment.
Keywords: LXR, naphthylacetic acid modified D-enantiomeric-glycine-phenylalanine-phenylalanine-tyrosine (D-Nap-GFFY) hydrogel, urethane-induced pulmonary carcinomas, anti-tumor immune responses, IFNγ
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact