13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(6):2550-2563. doi:10.7150/thno.51232 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A bifunctional molecule-based strategy for the development of theranostic antibody-drug conjugate
National Engineering Research Center for the Emergency Drug, Beijing Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Beijing 100850, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
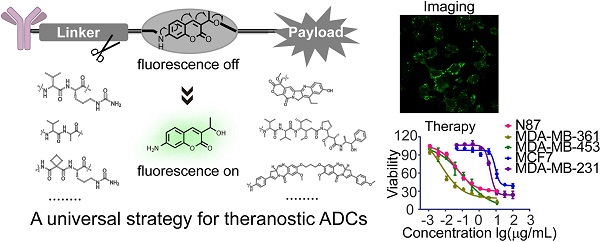
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are being developed worldwide with the potential to revolutionize current cancer treatment strategies. Developing novel theranostic ADCs with therapeutic utility and imaging capability is an attractive and challenging subject that promises advances in the field of personalized medicine. In this work, we propose a bifunctional molecule-based strategy for the development of theranostic ADCs.
Methods: We developed a theranostic ADC consisting of the anti-Her2 antibody Mil40, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) as the active payload, and a 7-amino-3-hydroxyethyl-coumarin (7-AHC)-based dipeptide linker, which functions as a novel bifunctional fluorescence probe that allows self-elimination cleavage in the presence of cathepsin B for payload release and fluorophore activation. The on-off fluorescence properties and the antitumor effect in vitro and in vivo were investigated.
Results: A 48-fold fluorescence enhancement was observed within 1 h when the 7-AHC-based linker was exposed to cathepsin B. Cleavage upon exposure to cathepsin B allows MMAE and fluorophore intracellular release and the monitoring of MMAE distribution using confocal microscopy. Additionally, the newly developed ADC retains the advantages of traditional p-aminobenzyloxycarbonyl-containing ADCs, such as good stability (t1/2 > 7 days) and high activity in vitro (IC50 = 0.09-3.74 nM). Importantly, the theranostic ADC exhibited the equivalent antitumor efficacy to the marketed ADC T-DM1 in the classic breast cancer model.
Conclusion: We suggest that the present strategy can be universally applied in all p-aminobenzyloxycarbonyl-containing ADCs. Overall, theranostic ADCs may play a role in developing new theranostic systems and promoting personalized medicine research.
Keywords: theranostic, 7-amino-3-hydroxyethyl-coumarin, antibody-drug conjugate, self-elimination, on-off fluorescence
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact