13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(5):2318-2333. doi:10.7150/thno.48739 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hypermethylation of GNA14 and its tumor-suppressive role in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Division of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Department of Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine
2. NHC Key Laboratory of Combined Multi-organ Transplantation
3. Key Laboratory of the diagnosis and treatment of organ Transplantation, Research Unit of Collaborative Diagnosis and Treatment For Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Cancer, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (2019RU019)
4. Key Laboratory of Organ Transplantation, Research Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatobiliary Diseases, Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310003,China
*Equally contributed to this article.
Abstract
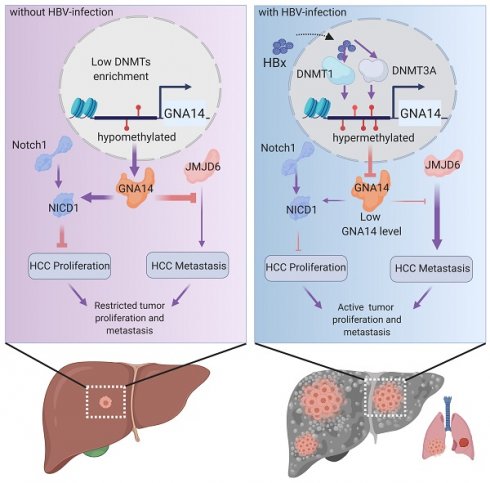
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal cancers worldwide, and its specific mechanism has not been fully elucidated. Inactivation of tumor suppressors may contribute to the occurrence, progression, and recurrence of HCC. DNA methylation is a crucial mechanism involved in regulating the occurrence of HCC. Herein, we aimed to identify the key methylation-related tumor suppressors as well as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in HCC.
Methods: Combined analysis of TCGA and GEO databases was performed to obtain potential methylation-related tumor suppressors in HCC. Methyl-target sequencing was performed to analyze the methylation level of the GNA14 promoter. The diagnostic value of GNA14 as a predictor of HCC was evaluated in HCC tumor samples and compared with normal tissues. The functional role of GNA14 and its upstream and downstream regulatory factors were investigated by gain-of-function and loss-of-function assays in vitro. Subcutaneous tumorigenesis, lung colonization, and orthotopic liver tumor model were performed to analyze the role of GNA14 in vivo.
Results: The expression of GNA14 was found to be downregulated in HCC and it was negatively correlated with hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, vascular invasion, and prognosis of HCC. DNA methylation was demonstrated to be responsible for the altered expression of GNA14 and was regulated by HBV-encoded X protein (HBx). GNA14 regulated the RB pathway by promoting Notch1 cleavage to inhibit tumor proliferation, and might inhibit tumor metastasis by inhibiting the expression of JMJD6.
Conclusion: GNA14 could be regulated by HBx by modulating the methylation status of its promoter. We identified GNA14 as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: HCC, DNA methylation, GNA14, HBV, HBx
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact