13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(4):1982-1990. doi:10.7150/thno.52508 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Fully end-to-end deep-learning-based diagnosis of pancreatic tumors
1. Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery of the First Affiliated Hospital, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310003, China.
2. College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China.
3. Research Units for Emotion and Emotion Disorders, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, MOE Frontier Science Center for Brain Research and Brain-Machine Integration, School of Brain Science and Brain Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China.
4. Department of Radiology of the Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China.
5. Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Pancreatic Disease, the First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China.
6. Zhejiang University Cancer Center, Hangzhou, China.
Abstract
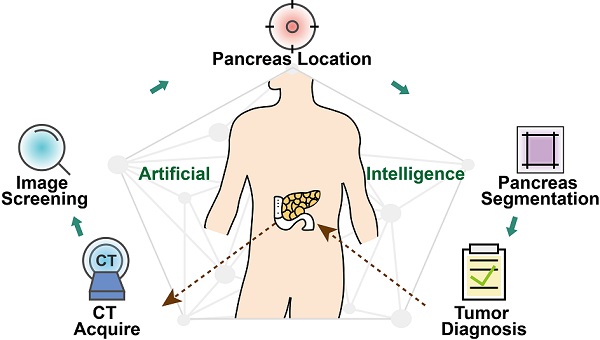
Artificial intelligence can facilitate clinical decision making by considering massive amounts of medical imaging data. Various algorithms have been implemented for different clinical applications. Accurate diagnosis and treatment require reliable and interpretable data. For pancreatic tumor diagnosis, only 58.5% of images from the First Affiliated Hospital and the Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine are used, increasing labor and time costs to manually filter out images not directly used by the diagnostic model.
Methods: This study used a training dataset of 143,945 dynamic contrast-enhanced CT images of the abdomen from 319 patients. The proposed model contained four stages: image screening, pancreas location, pancreas segmentation, and pancreatic tumor diagnosis.
Results: We established a fully end-to-end deep-learning model for diagnosing pancreatic tumors and proposing treatment. The model considers original abdominal CT images without any manual preprocessing. Our artificial-intelligence-based system achieved an area under the curve of 0.871 and a F1 score of 88.5% using an independent testing dataset containing 107,036 clinical CT images from 347 patients. The average accuracy for all tumor types was 82.7%, and the independent accuracies of identifying intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma were 100% and 87.6%, respectively. The average test time per patient was 18.6 s, compared with at least 8 min for manual reviewing. Furthermore, the model provided a transparent and interpretable diagnosis by producing saliency maps highlighting the regions relevant to its decision.
Conclusions: The proposed model can potentially deliver efficient and accurate preoperative diagnoses that could aid the surgical management of pancreatic tumor.
Keywords: artificial intelligence (AI), computed tomography (CT), deep learning, convolutional neural network (CNN), tumor
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact