13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(4):1732-1752. doi:10.7150/thno.45302 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Estrogen-induced circRNA, circPGR, functions as a ceRNA to promote estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell growth by regulating cell cycle-related genes
1. Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Innovative Drug Target Research, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiang'an South Road, Xiamen, Fujian 361102, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiang'an South Road, Xiamen, Fujian 361102, China.
3. Department of Orthopedics, The Fifth Hospital of Xiamen, Xiamen, Fujian 361101, China.
4. Department of Pathology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Shantou University Medical College, Dongxia North Road, Shantou, Guangdong 515041, China.
5. Computational Genomics Lab, Beijing Institutes of Life Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
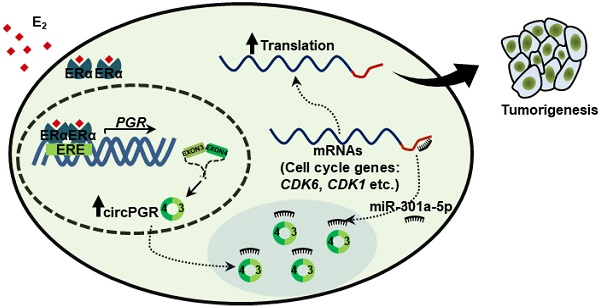
Estrogen and estrogen receptor (ER)-regulated gene transcriptional events have been well known to be involved in ER-positive breast carcinogenesis. Meanwhile, circular RNAs (circRNAs) are emerging as a new family of functional non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) with implications in a variety of pathological processes, such as cancer. However, the estrogen-regulated circRNA program and the function of such program remain uncharacterized.
Methods: CircRNA sequencing (circRNA-seq) was performed to identify circRNAs induced by estrogen, and cell proliferation, colony formation, wound healing, transwell and tumor xenograft experiments were applied to examine the function of estrogen-induced circRNA, circPGR. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and ceRNA network analysis wereperformed to identify circPGR's target genes and the microRNA (miRNA) bound to circPGR. Anti-sense oligonucleotide (ASO) was used to assess circPGR's effects on ER-positive breast cancer cell growth.
Results: Genome-wide circRNA profiling by circRNA sequencing (circRNA-seq) revealed that a large number of circRNAs were induced by estrogen, and further functional screening for the several circRNAs originated from PGR revealed that one of them, which we named as circPGR, was required for ER-positive breast cancer cell growth and tumorigenesis. CircPGR was found to be localized in the cytosol of cells and functioned as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to sponge miR-301a-5p to regulate the expression of multiple cell cycle genes. The clinical relevance of circPGR was underscored by its high and specific expression in ER-positive breast cancer cell lines and clinical breast cancer tissue samples. Accordingly, anti-sense oligonucleotide (ASO) targeting circPGR was proven to be effective in suppressing ER-positive breast cancer cell growth.
Conclusions: These findings reveled that, besides the well-known messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA (miRNA), long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and enhancer RNA (eRNA) programs, estrogen also induced a circRNA program, and exemplified by circPGR, these estrogen-induced circRNAs were required for ER-positive breast cancer cell growth, providing a new class of therapeutic targets for ER-positive breast cancer.
Keywords: estrogen and estrogen receptor, circRNA, miRNA, cell cycle, ER-positive breast cancer
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact