13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(4):1641-1654. doi:10.7150/thno.46119 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Immunomodulation by systemic administration of human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of cell-based therapy for treatment of myocardial infarction
1. Cardiology Division, Department of Medicine, Queen Mary Hospital, the University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China.
2. Shenzhen Institutes of Research and Innovation, the University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China.
3. Hong Kong-Guangdong Joint Laboratory on Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, the University of Hong Kong and Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, China.
4. Department of Medicine, Shenzhen Hong Kong University Hospital, Shenzhen, China.
*These authors contributed equally to the supervision of this work and are co-corresponding authors.
Abstract
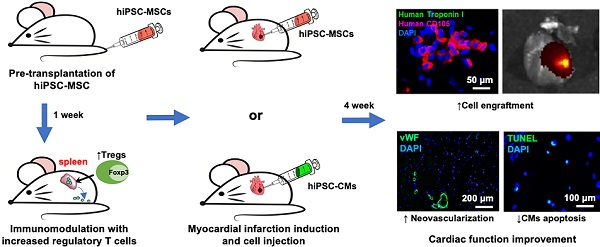
Rationale: Poor survival and engraftment are major hurdles of stem cell therapy in the treatment of myocardial infarction (MI). We sought to determine whether pre-transplantation systemic intravenous administration of human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (hiPSC-MSCs) could improve the survival of hiPSC-MSCs or hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) following direct intramyocardial transplantation in a mouse model of MI.
Methods: Mice were randomized to undergo intravenous administration of saline or 5×105 hiPSC-MSCs one week prior to MI, induced by ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Mice were further assigned to undergo direct intramyocardial transplantation of hiPSC-MSCs (1×106) or hiPSC-CMs (1×106) 10 minutes following MI. Echocardiographic and invasive hemodynamic assessment were performed to determine cardiac function. In-vivo fluorescent imaging analysis, immunofluorescence staining and polymerase chain reaction were performed to detect cell engraftment. Flow cytometry of splenic regulatory T cells (Tregs) and natural killer (NK) cells was performed to assess the immunomodulatory effects.
Results: Pre-transplantation systemic administration of hiPSC-MSCs increased systemic Tregs activation, decreased the number of splenic NK cells and inflammation, and enhanced survival of transplanted hiPSC-MSCs and hiPSC-CMs. These improvements were associated with increased neovascularization and decreased myocardial inflammation and apoptosis at the peri-infract zone with consequent improved left ventricular function four weeks later. Co-culture of splenic CD4 cells with hiPSC-MSCs also modulated their cytokine expression profile with a decreased level of interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interleukin (IL)-17A, but not IL-2, IL-6 and IL-10.
Conclusion: Pre-transplantation systemic intravenous administration of hiPSC-MSCs induced immunomodulation and facilitated the survival of intramyocardially transplanted cells to improve cardiac function in MI.
Keywords: human induced pluripotent stem cell, immunomodulation, mesenchymal stromal cell, cardiomyocyte, myocardial infarction
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact