13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(4):1609-1625. doi:10.7150/thno.48153 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Endothelial Klf2-Foxp1-TGFβ signal mediates the inhibitory effects of simvastatin on maladaptive cardiac remodeling
1. Key Laboratory of Arrhythmias of the Ministry of Education of China, Research Center for Translational Medicine, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
2. Department of Cardiology, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
3. Institute for Biomedical Engineering and Nano Science, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
4. Faculty of Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau SAR, China.
5. Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Wan Fang Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
6. Shenzhen Ruipuxun Academy for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Shenzhen, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
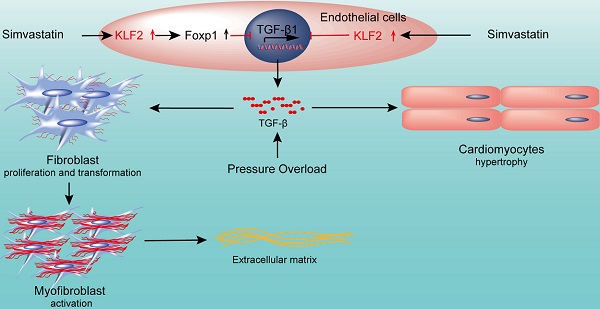
Aims: Pathological cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy are common features of left ventricular remodeling that often progress to heart failure (HF). Endothelial cells (ECs) are the most abundant non-myocyte cells in adult mouse heart. Simvastatin, a strong inducer of Krüppel-like Factor 2 (Klf2) in ECs, ameliorates pressure overload induced maladaptive cardiac remodeling and dysfunction. This study aims to explore the detailed molecular mechanisms of the anti-remodeling effects of simvastatin.
Methods and Results: RGD-magnetic-nanoparticles were used to endothelial specific delivery of siRNA and we found absence of simvastatin's protective effect on pressure overload induced maladaptive cardiac remodeling and dysfunction after in vivo inhibition of EC-Klf2. Mechanism studies showed that EC-Klf2 inhibition reversed the simvastatin-mediated reduction of fibroblast proliferation and myofibroblast formation, as well as cardiomyocyte size and cardiac hypertrophic genes, which suggested that EC-Klf2 might mediate the anti-fibrotic and anti-hypertrophy effects of simvastatin. Similar effects were observed after Klf2 inhibition in cultured ECs. Moreover, Klf2 regulated its direct target gene TGFβ1 in ECs and mediated the protective effects of simvastatin, and inhibition of EC-Klf2 increased the expression of EC-TGFβ1 leading to simvastatin losing its protective effects. Also, EC-Klf2 was found to regulate EC-Foxp1 and loss of EC-Foxp1 attenuated the protective effects of simvastatin similar to EC-Klf2 inhibition.
Conclusions: We conclude that cardiac microvasculature ECs are important in the modulation of pressure overload induced maladaptive cardiac remodeling and dysfunction, and the endothelial Klf2-TGFβ1 or Klf2-Foxp1-TGFβ1 pathway mediates the preventive effects of simvastatin. This study demonstrates a novel mechanism of the non-cholesterol lowering effects of simvastatin for HF prevention.
Keywords: Heart failure (HF), Maladaptive cardiac remodeling (cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy), HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, Simvastatin, Vascular endothelial cells (ECs), Krüppel-like Factor 2 (Klf2), Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGFβ1), Forkhead Box P1 (Foxp1)
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact