13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(3):1345-1363. doi:10.7150/thno.51383 This issue Cite
Review
Targeting transforming growth factor-β signaling for enhanced cancer chemotherapy
1. National Engineering Research Center for Nanomedicine, College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, China.
2. Hepatic Surgery Center, and Hubei Key Laboratory of Hepatic-Biliary-Pancreatic Diseases, National Medical Center for Major Public Health Events, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics of Ministry of Education, College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, China.
4. Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry and Materia Medical, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074, China.
5. GBA Research Innovation Institute for Nanotechnology, Guangdong, 510530, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
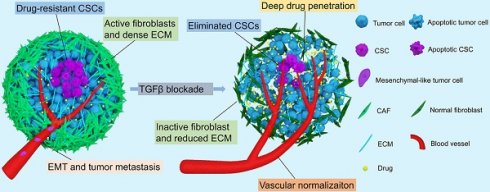
During the past decades, drugs targeting transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) signaling have received tremendous attention for late-stage cancer treatment since TGFβ signaling has been recognized as a prime driver for tumor progression and metastasis. Nonetheless, in healthy and pre-malignant tissues, TGFβ functions as a potent tumor suppressor. Furthermore, TGFβ signaling plays a key role in normal development and homeostasis by regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, apoptosis, and immune evasion, and by suppressing tumor-associated inflammation. Therefore, targeting TGFβ signaling for cancer therapy is challenging. Recently, we and others showed that blocking TGFβ signaling increased chemotherapy efficacy, particularly for nanomedicines. In this review, we briefly introduce the TGFβ signaling pathway, and the multifaceted functions of TGFβ signaling in cancer, including regulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) and the behavior of cancer cells. We also summarize TGFβ targeting agents. Then, we highlight TGFβ inhibition strategies to restore the extracellular matrix (ECM), regulate the tumor vasculature, reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and impair the stemness of cancer stem-like cells (CSCs) to enhance cancer chemotherapy efficacy. Finally, the current challenges and future opportunities in targeting TGFβ signaling for cancer therapy are discussed.
Keywords: transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ), extracellular matrix (ECM), tumor vasculature, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cancer stem-like cells (CSCs), cancer chemotherapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact