13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(3):1310-1325. doi:10.7150/thno.50333 This issue Cite
Review
From biomarkers to therapeutic targets: the promise of PD-L1 in thyroid autoimmunity and cancer
1. ENT and Head and Neck surgery department, Institut Universitaire de la Face et du Cou, CHU de Nice, University Hospital, Côte d'Azur University, Nice, France.
2. Côte d'Azur University, CNRS, INSERM, Institute for Research on Cancer and Aging, FHU OncoAge, Nice, France.
3. Antoine Lacassagne Cancer Center, FHU OncoAge, Nice, France.
4. Laboratory of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, Côte d'Azur University and Biobank, Pasteur Hospital, University Côte d'Azur, FHU OncoAge, Nice, France.
*These authors contributed equally in this review.
Abstract
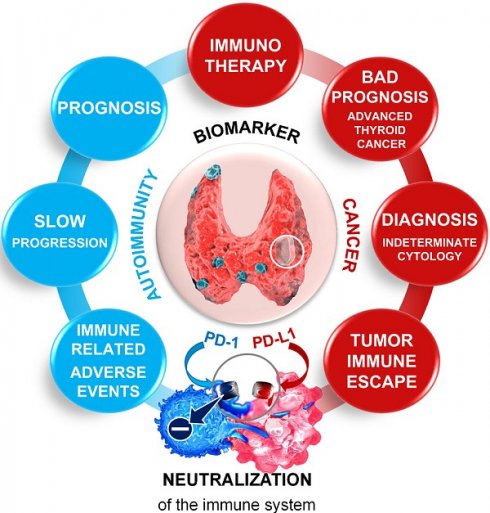
The programmed cell death-1/programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1) immune checkpoint proteins hold promise as diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic targets for precision oncology. By restoring antitumor T cell surveillance, the high degree of effectiveness of the immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has revolutionized cancer treatment. However, the majority of patients (65-80 %) treated with ICIs experience significant side effects, called immune-related adverse events (irAEs), resulting in autoimmune damage to various organs. Therefore, broadening the clinical applicability of these treatments to all cancer types requires an improved understanding of the mechanisms linking cancer immune evasion and autoimmunity. The thyroid is the endocrine gland the most frequently involved in autoimmunity and cancer, the growing incidence of which is raising serious public health issues worldwide. In addition, the risk of developing thyroid cancer is increased in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease and thyroid dysfunction is one of the most common irAEs, especially with PD‑1/PD-L1 blockade. Therefore, we chose the thyroid as a model for the study of the link between autoimmunity, irAEs, and cancer. We provide an update into the current knowledge of the PD‑1/PD-L1 axis and discuss the growing interest of this axis in the diagnosis, prognosis, and management of thyroid diseases within the context of autoimmunity and cancer, while embracing personalized medicine.
Keywords: Thyroid autoimmunity, thyroid cancer, PD-1/PD-L1, biomarker, immune checkpoint inhibitors
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact