13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(3):1177-1191. doi:10.7150/thno.46992 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Apolipoprotein E, low-density lipoprotein receptor, and immune cells control blood-brain barrier penetration by AAV-PHP.eB in mice
1. Department of Neurological Surgery, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 160 Pujian Road, Shanghai 200127, P.R. China.
2. Department of Anesthesia, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 160 Pujian Road, Shanghai 200127, P.R. China.
3. Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 280 South Chongqing Road, Shanghai 200025, P.R. China.
4. Department of Neurological Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, 58 Zhongshan 2nd Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510080, P.R. China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
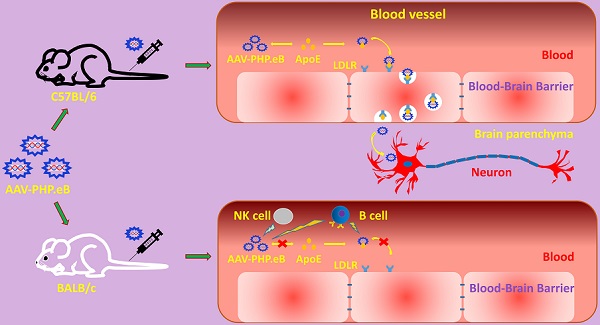
Rationale: The blood-brain barrier (BBB) prevents the effective delivery of therapeutic molecules to the central nervous system (CNS). A recently generated adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based vector, AAV-PHP.eB, has been found to penetrate the BBB more efficiently than other vectors including AAV-PHP.B. However, little is known about the mechanisms. In this study, we investigated how AAV-PHP.eB penetrates the BBB in mice.
Methods: We injected AAV-PHP.eB into the bloodstream of wild-type C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice as well as mouse strains carrying genetic mutation in apolipoprotein E gene (Apoe) or low-density lipoprotein receptor gene (Ldlr), or lacking various components of the immune system. Then, we evaluated AAV-PHP.eB transduction to the brain and spinal cord in these mice.
Results: We found that the transduction to the CNS of intravenous AAV-PHP.eB was more efficient in C57BL/6 than BALB/c mice, and significantly reduced in Apoe or Ldlr knockout C57BL/6 mice compared to wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Moreover, poor CNS transduction in BALB/c mice was dramatically increased by B-cell or natural killer-cell depletion.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that the ApoE-LDLR pathway underlies the CNS tropism of AAV-PHP.eB and that the immune system contributes to the strain specificity of AAV-PHP.eB.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier, AAV-PHP.eB, apolipoprotein E, low-density lipoprotein receptor, immune cells
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact