13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(3):1059-1078. doi:10.7150/thno.44364 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CXCL12-mediated monocyte transmigration into brain perivascular space leads to neuroinflammation and memory deficit in neuropathic pain
1. Department of Physiology and Pain Research Center, Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China.
2. Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Brain Function and Disease, Guangzhou 510080, China.
3. Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Clinic, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, China.
4. Division of Emergency Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, China.
5. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510080, China.
6. Department of Anesthesiology, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, Guangzhou, 510317, China.
7. Department of Critical Care & Respiratory Care Research (PMG), University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, USA.
8. Department of Neurology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
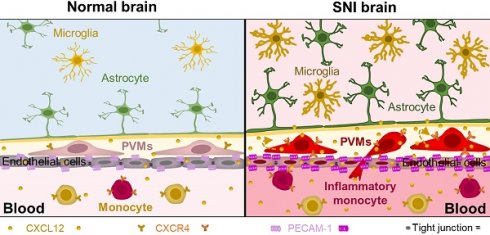
Emerging clinical and experimental evidence demonstrates that neuroinflammation plays an important role in cognitive impairment associated with neuropathic pain. However, how peripheral nerve challenge induces remote inflammation in the brain remains largely unknown.
Methods: The circulating leukocytes and plasma C-X-C motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12) and brain perivascular macrophages (PVMs) were analyzed by flow cytometry, Western blotting, ELISA, and immunostaining in spared nerve injury (SNI) mice. The memory function was evaluated with a novel object recognition test (NORT) in mice and with Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) in chronic pain patients.
Results: The classical monocytes and CXCL12 in the blood, PVMs in the perivascular space, and gliosis in the brain, particularly in the hippocampus, were persistently increased following SNI in mice. Using the transgenic CCR2RFP/+ and CX3CR1GFP/+ mice, we discovered that at least some of the PVMs were recruited from circulating monocytes. The SNI-induced increase in hippocampal PVMs, gliosis, and memory decline were substantially prevented by either depleting circulating monocytes via intravenous injection of clodronate liposomes or blockade of CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling. On the contrary, intravenous injection of CXCL12 at a pathological concentration in naïve mice mimicked SNI effects. Significantly, we found that circulating monocytes and plasma CXCL12 were elevated in chronic pain patients, and both of them were closely correlated with memory decline.
Conclusion: CXCL12-mediated monocyte recruitment into the perivascular space is critical for neuroinflammation and the resultant cognitive impairment in neuropathic pain.
Keywords: memory deficit, chronic pain, monocyte transmigration, hippocampus perivascular macrophage, neuroinflammation, CXCL12
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact