13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(2):715-730. doi:10.7150/thno.51390 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor precursor in the immune system is a novel target for treating multiple sclerosis
1. Department of Anesthesiology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, 139 Ren-Min Central Road, Changsha City, Hunan 410011, China.
2. Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, School of Basic Medical Science, Central South University, Changsha City, Hunan 410011, China.
3. Department of Renal Medicine, Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide, SA 5000, Australia.
4. School of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences, Division of Health Sciences, University of South Australia, Adelaide, SA 5000, Australia.
5. Department of Medical Research Center and Clinical Laboratory, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
6. Department of Neurology, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
7. Department of Orthopedics, Tianjin General Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China.
8. Perinatology Research Branch, Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD, National Institutes of Health, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan 48201, USA.
* These authors contribute equally
# Senior authors contribute equally.
Abstract
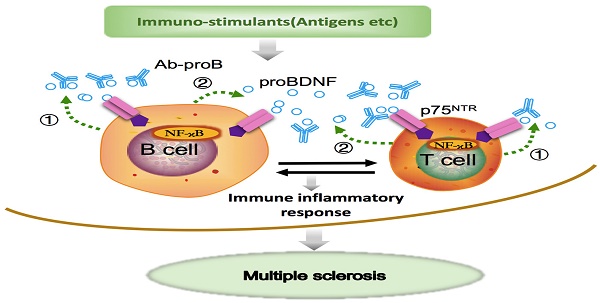
Rationale: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor precursor (proBDNF) is expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) and the immune system. However, the role of proBDNF in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS) is unknown.
Methods: Peripheral blood and post-mortem brain and spinal cord specimens were obtained from multiple sclerosis patients to analyze proBDNF expression in peripheral lymphocytes and infiltrating immune cells in the lesion site. The proBDNF expression profile was also examined in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model, and polyclonal and monoclonal anti-proBDNF antibodies were used to explore their therapeutic effect in EAE. Finally, the role of proBDNF in the inflammatory immune activity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) was verified in vitro experiments.
Results: High proBDNF expression was detected in the circulating lymphocytes and infiltrated inflammatory cells at the lesion sites of the brain and spinal cord in MS patients. In the EAE mouse model, proBDNF was upregulated in CNS and in circulating and splenic lymphocytes. Systemic but not intracranial administration of anti-proBDNF blocking antibodies attenuated clinical scores, limited demyelination, and inhibited proinflammatory cytokines in EAE mice. Immuno-stimulants treatment increased the proBDNF release and upregulated the expression of p75 neurotrophic receptors (p75NTR) in lymphocytes. The monoclonal antibody against proBDNF inhibited the inflammatory response of PBMCs upon stimulations.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that proBDNF from immune cells promotes the immunopathogenesis of MS. Monoclonal Ab-proB may be a promising therapeutic agent for treating MS.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosis, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, proBDNF, antibodies, immunotherapy, B cell, immune response
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact