13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(1):209-221. doi:10.7150/thno.49327 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hypoxia-induced myeloid derived growth factor promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through remodeling tumor microenvironment
1. State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211198, PR China.
2. Center for New Drug Safety Evaluation and Research, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211198, PR China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
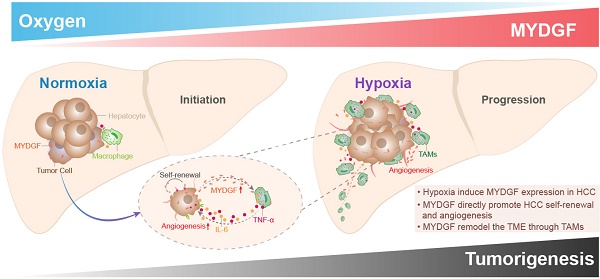
Purpose: Exploring and studying the novel target of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been extremely important for its treatment. The principal objective of this project is to investigate whether myeloid derived growth factor (MYDGF) could accelerate the progression of HCC, and how it works.
Methods: Cell proliferation, clonal formation, sphere formation and xenograft tumor experiments were used to prove the critical role of MYDGF in HCC progression. Tumor angiogenesis, immune cell infiltration, macrophage chemotaxis and inflammatory cytokines detection were utilized to clarify how MYDGF remodeled the tumor microenvironment (TME) to accelerate the progress of HCC.
Results: Here, we reported a secretory protein MYDGF, which could be induced by hypoxia, was significantly upregulated in HCC and associated with poor clinical outcomes. Using bioinformatics and experimental approaches, we found that MYDGF promotes cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo through a mechanism that might involve enhanced self-renewal of liver CSCs. Furthermore, MYDGF can also promote tumor angiogenesis, induce macrophages to chemotaxis into tumor tissue, and then release various inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6 and TNF-α, which ultimately aggravate inflammation of tumor microenvironment and accelerate HCC progression.
Conclusions: We provided evidence that MYDGF could directly affect the self-renewal of liver CSCs, and indirectly aggravate the inflammatory microenvironment to accelerate the progression of HCC.
Keywords: MYDGF, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Cancer stem cell, Tumor inflammatory microenvironment, Tumor-associated macrophages
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact