13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(22):9923-9936. doi:10.7150/thno.45988 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Lack of FGF21 promotes NASH-HCC transition via hepatocyte-TLR4-IL-17A signaling
1. Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY 40202, USA.
2. Department of Pathophysiology, Basic Medicine College, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, China.
3. Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China.
4. Department of Hematology, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China.
5. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, College of Life Science, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, China.
Abstract
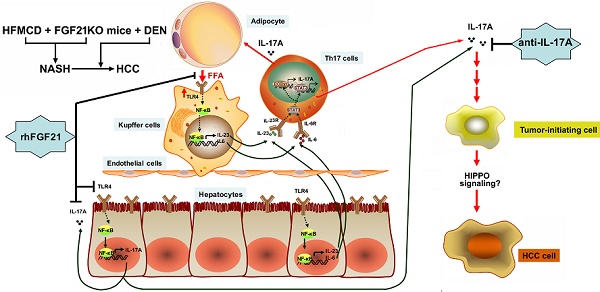
Rationale: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been increasingly recognized in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is reported to prevent NASH and delay HCC development. In this study, the effects of FGF21 on NASH progression and NASH-HCC transition and the potential mechanism(s) were investigated.
Methods: NASH models and NASH-HCC models were established in FGF21Knockout (KO) mice to evaluate NASH-HCC transition. IL-17A signaling was investigated in the isolated hepatic parenchymal cells, splenocytes, and hepatocyte and HCC cell lines.
Results: Lack of FGF21 caused significant up-regulation of the hepatocyte-derived IL-17A via Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and NF-κB signaling. Restoration of FGF21 alleviated the high NAFLD activity score (NAS) and attenuated the TLR4-triggered hepatocyte-IL-17A expression. The HCC nodule number and tumor size were significantly alleviated by treatments of anti-IL-17A antibody.
Conclusion: This study revealed a novel anti-inflammatory mechanism of FGF21 via inhibiting the hepatocyte-TLR4-IL-17A signaling in NASH-HCC models. The negative feedback loop on the hepatocyte-TLR4-IL-17A axis could be a potential anti-carcinogenetic mechanism for FGF21 to prevent NASH-HCC transition.
Keywords: Fibroblast growth factor 21, Nonalcoholic steatohepatities, Toll-like receptor 4, IL-17A, Hepatocellular carcinoma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact