13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(19):8558-8572. doi:10.7150/thno.44873 This issue Cite
Research Paper
E3 ligase ZFP91 inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metabolism Reprogramming by regulating PKM splicing
1. Biomedicine Research Center, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 510150, China.
2. Department of Surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 510260, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Protein Modification and Degradation, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 511436, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Rationale: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal cancers, and few molecularly targeted anticancer therapies have been developed to treat it. Thus, the identification of new therapeutic targets is urgent. Metabolic reprogramming is an important hallmark of cancer. However, how ubiquitin ligases are involved in the regulation of cancer metabolism remains poorly understood.
Methods: RT-PCR, western blot and IHC were used to determine ZFP91 expression. RNAi, cell proliferation, colony formation and transwell assays were used to determine the in vitro functions of ZFP91. Mouse xenograft models were used to study the in vivo effects of ZFP91. Co-IP together with mass spectrometry or western blot was utilized to investigate protein-protein interaction. Ubiquitination was analyzed using IP together with western blot. RNA splicing was assessed by using RT-PCR followed by restriction digestion. Lactate production and glucose uptake assays were used to analyze cancer metabolism.
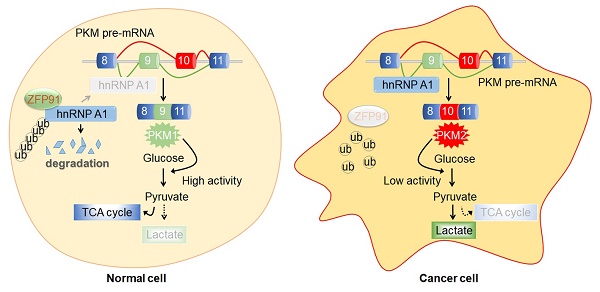
Results: We identified that an E3 ligase zinc finger protein 91 (ZFP91) suppressed HCC metabolic reprogramming, cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ZFP91 promoted the Lys48-linked ubiquitination of the oncoprotein hnRNP A1 at lysine 8 and proteasomal degradation, thereby inhibiting hnRNP A1-dependent PKM splicing, subsequently resulting in higher PKM1 isoform formation and lower PKM2 isoform formation and suppressing HCC glucose metabolism reprogramming, cell proliferation and metastasis. Moreover, HCC patients with lower levels of ZFP91 have poorer prognoses, and ZFP91 is an independent prognostic factor for patients with HCC.
Conclusions: Our study identifies ZFP91 as a tumor suppressor of hepatocarcinogenesis and HCC metabolism reprogramming and proposes it as a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target of HCC.
Keywords: E3 ligase, Ubiquitination, Metabolism reprogramming, Hepatocellular carcinoma, ZFP91
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact