13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(18):8298-8314. doi:10.7150/thno.46934 This issue Cite
Research Paper
ATF6 aggravates acinar cell apoptosis and injury by regulating p53/AIFM2 transcription in Severe Acute Pancreatitis
1. Division of Hepatobiliopancreatic Surgery, Department of General Surgery, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
2. Department of the Electronic Microscope Room, Central Laboratory, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
3. School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
4. Department of Pathophysiology, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
5. Department of Occupational Health and Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Tropical Disease Research, School of Public Health, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
6. The First Clinical Medical College, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
7. Laboratory Animal Research Center of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
8. Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Center for Brain Science and Brain-Inspired Intelligence, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
9. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
10. Department of Respiratory and Crit Care Medicine, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
11. Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, National Clinical Research Center for Kidney Disease, State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, Guangdong Institute, Guangzhou, China.
12. Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
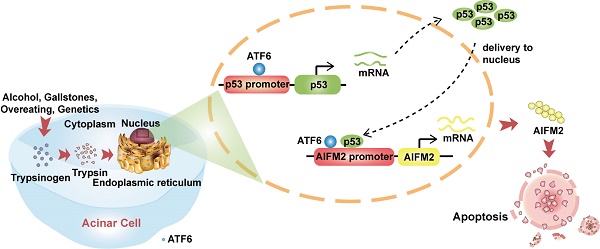
Background: There is no curative therapy for severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) due to poor understanding of its molecular mechanisms. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is involved in SAP and increased expression of ATF6 has been detected in SAP patients. Here, we aimed to investigate the role of ATF6 in a preclinical SAP mouse model and characterize its regulatory mechanism.
Methods: Pancreatic tissues of healthy and SAP patients were collected during surgery. Humanized PRSS1 transgenic mice were treated with caerulein to mimic the SAP development, which was crossed to an ATF6 knockout mouse line, and pancreatic tissues from the resulting pups were screened by proteomics. Adenovirus-mediated delivery to the pancreas of SAP mice was used for shRNA-based knockdown or overexpression. The potential functions and mechanisms of ATF6 were clarified by immunofluorescence, immunoelectron microscopy, Western blotting, qRT-PCR, ChIP-qPCR and luciferase reporter assay.
Results: Increased expression of ATF6 was associated with elevated apoptosis, ER and mitochondrial disorder in pancreatic tissues from SAP patients and PRSS1 mice. Knockout of ATF6 in SAP mice attenuated acinar injury, apoptosis and ER disorder. AIFM2, known as a p53 target gene, was identified as a downstream regulatory partner of ATF6, whose expression was increased in SAP. Functionally, AIFM2 could reestablish the pathological disorder in SAP tissues in the absence of ATF6. p53 expression was also increased in SAP mice, which was downregulated by ATF6 knockout. p53 knockout significantly suppressed acinar apoptosis and injury in SAP model. Mechanistically, ATF6 promoted AIFM2 transcription by binding to p53 and AIFM2 promoters.
Conclusion: These results reveal that ATF6/p53/AIFM2 pathway plays a critical role in acinar apoptosis during SAP progression, highlighting novel therapeutic target molecules for SAP.
Keywords: severe acute pancreatitis, ER stress, AIFM2, ATF6, p53, apoptosis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact