13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(16):7287-7318. doi:10.7150/thno.46288 This issue Cite
Review
Versatile Nanoplatforms with enhanced Photodynamic Therapy: Designs and Applications
1. College of Bioresources Chemical and Materials Engineering, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi'an 710021, China.
2. School of Science, Xi'an Key Laboratory of Sustainable Energy Material Chemistry, MOE Key Laboratory for Nonequilibrium Synthesis and Modulation of Condensed Materials, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, P. R. China.
3. Key Laboratory of Testing Technology for Manufacturing Process of Ministry of Education, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, P. R. China.
4. Institute of Textiles & Clothing, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
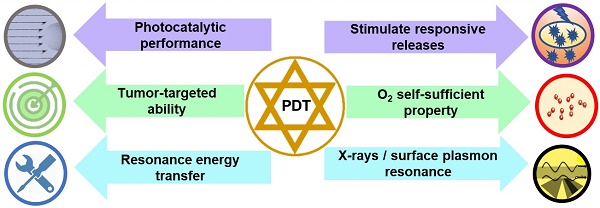
As an emerging antitumor strategy, photodynamic therapy (PDT) has attracted intensive attention for the treatment of various malignant tumors owing to its noninvasive nature and high spatial selectivity in recent years. However, the therapeutic effect is unsatisfactory on some occasions due to the presence of some unfavorable factors including nonspecific accumulation of PS towards malignant tissues, the lack of endogenous oxygen in tumors, as well as the limited light penetration depth, further hampering practical application. To circumvent these limitations and improve real utilization efficiency, various enhanced strategies have been developed and explored during the past years. In this review, we give an overview of the state-of-the-art advances progress on versatile nanoplatforms for enhanced PDT considering the enhancement from targeting or responsive, chemical and physical effect. Specifically, these effects mainly include organelle-targeting function, tumor microenvironment responsive release photosensitizers (PS), self-sufficient O2 (affinity oxygen and generating oxygen), photocatalytic water splitting, X-rays light stimulate, surface plasmon resonance enhancement, and the improvement by resonance energy transfer. When utilizing these strategies to improve the therapeutic effect, the advantages and limitations are addressed. Finally, the challenges and prospective will be discussed and demonstrated for the future development of advanced PDT with enhanced efficacy.
Keywords: photodynamic therapy, malignant tumor, versatile nanoplatforms, microenvironment
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact