13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(16):7273-7286. doi:10.7150/thno.44668 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Complementary autophagy inhibition and glucose metabolism with rattle-structured polydopamine@mesoporous silica nanoparticles for augmented low-temperature photothermal therapy and in vivo photoacoustic imaging
1. CAS Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing 100190, P. R. China.
2. Department of General Surgery, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, P. R. China.
3. Beijing Key Laboratory of Organic Materials Testing Technology and Quality Evaluation, Beijing Center for Physical and Chemical Analysis, Beijing, 100089, China.
4. The Key Laboratory of Beijing City on Preparation and Processing of Novel Polymer Materials, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029, China.
5. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, P. R. China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
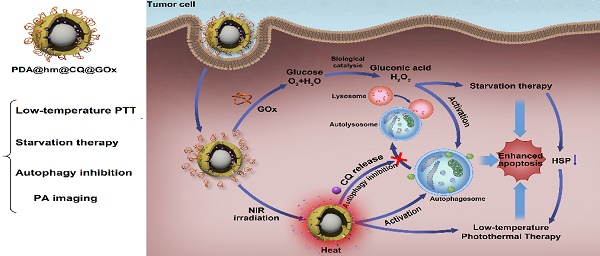
Rattle-structured nanoparticles with movable cores, porous shells and hollow interiors have shown great effectiveness in drug delivery and cancer theranostics. Targeting autophagy and glucose have provided alternative strategies for cancer intervention therapy. Herein, rattle-structured polydopamine@mesoporous silica nanoparticles were prepared for in vivo photoacoustic (PA) imaging and augmented low-temperature photothermal therapy (PTT) via complementary autophagy inhibition and glucose metabolism.
Methods: The multifunctional rattle-structured nanoparticles were designed with the nanocore of PDA and the nanoshell of hollow mesoporous silica (PDA@hm) via a four-step process. PDA@hm was then loaded with autophagy inhibitor chloroquine (CQ) and conjugated with glucose consumer glucose oxidase (GOx) (PDA@hm@CQ@GOx), forming a corona-like structure nanoparticle.
Results: The CQ and GOx were loaded into the cavity and decorated onto the surface of PDA@hm, respectively. The GOx-mediated tumor starvation strategy would directly suppress the expression of HSP70 and HSP90, resulting in an enhanced low-temperature PTT induced by PDA nanocore. In addition, autophagy inhibition by the released CQ made up for the loss of low-temperature PTT and starvation efficiencies by PTT- and starvation-activated autophagy, realizing augmented therapy efficacy. Furthermore, the PDA nanocore in the PDA@hm@CQ@GOx could be also used for PA imaging.
Conclusion: Such a “drugs” loaded rattle-structured nanoparticle could be used for augmented low-temperature PTT through complementarily regulating glucose metabolism and inhibiting autophagy and in vivo photoacoustic imaging.
Keywords: autophagy inhibition, rattle structure, polydopamine, glucose oxidase, low-temperature PTT
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact