13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(14):6167-6181. doi:10.7150/thno.46225 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The anti-microbial peptide LL-37/CRAMP levels are associated with acute heart failure and can attenuate cardiac dysfunction in multiple preclinical models of heart failure
1. Cardiac Regeneration and Ageing Lab, Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, School of Life Science, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
2. School of Medicine, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
3. School of Medicine, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China
4. Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China
5. NHC Key Laboratory of Assisted Circulation (Sun Yat-sen University), Guangzhou 510080, PR China.
6. Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
7. State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China
8. School of Food Science and Technology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China
9. Cardiovascular Division of the Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, USA
10. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Division of Clinical Microbiology, Karolinska University Hospital Huddinge, F68, Stockholm, Swede
11. Department of Cardiology, Laboratory of Experimental Cardiology, University Utrecht, University Medical Center Utrecht, 3584 CX Utrecht, The Netherlands
12. UMC Utrecht Regenerative Medicine Center, Circulatory Health Laboratory, University Medical Center Utrecht, 3508 GA Utrecht, The Netherlands
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
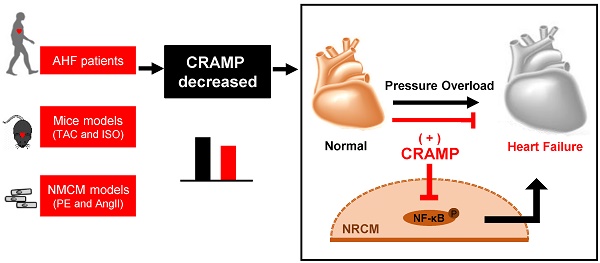
Rationale: Biomarkers for the diagnosis of heart failure (HF) are clinically essential. Circulating antimicrobial peptides LL-37 has emerged as a novel biomarker in cardiovascular disease, however, its relevance as a biomarker for acute HF are undetermined.
Methods: Acute HF patients were enrolled in this study and the serum levels of LL-37/CRAMP (cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide) were measured by ELISA. The receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curve was used to determine if serum LL-37 could be a biomarker for acute HF. Mouse CRAMP (mCRAMP, mouse homolog for human LL-37) was also determined in both heart and serum samples of, transverse aortic constriction (TAC)- and isoproterenol (ISO)-induced HF mice models, and phenylephrine (PE) and angiotensin II (AngII)-induced neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes (NMCMs) hypertrophic models, both intracellular and secreted, by ELISA. The protective effects of mCRAMP were determined in TAC, ISO, and AngII-induced HF in mice while whether HF was exacerbated in AngII-infused animals were checked in mCRAMP knockout mice. The underlying mechanism for protective effects of CARMP in pathological hypertrophy was determined by using a NF-κB agonist together with rCRAMP (rat homolog for human LL-37) in AngII or PE treated neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs).
Results: Serum levels of LL-37 were significantly decreased in acute HF patients (area under the curve (AUC) of 0.616), and negatively correlated with NT-proBNP. We further confirmed that mCRAMP was decreased in both heart and serum samples of TAC- and ISO-induced HF mice models. Moreover, in PE and AngII-induced NMCMs hypertrophic models, both intracellular and secreted mCRAMP levels were reduced. Functionally, mCRAMP could attenuate TAC, ISO, and AngII-induced HF in mice while CRAMP deficiency exacerbated HF. Mechanistically, the anti-hypertrophy effects of CRAMP were mediated by NF-κB signaling.
Conclusions: Collectively, serum LL-37 is associated with acute HF and increasing CRAMP is protective against deleterious NF-κB signaling in the rodent.
Keywords: Cathelicidin, CRAMP, LL-37, Heart Failure, Serum, Biomarker, NF-κB
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact