13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(13):5979-5997. doi:10.7150/thno.40122 This issue Cite
Review
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in tissue repair: challenges and opportunities
1. Center for Molecular Medicine, University Medical Center Utrecht, Universiteitsweg 100, 3584 CG, Utrecht, The Netherlands
2. Regenerative Medicine Center, Uppsalalaan 8, 3584 CT, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Abstract
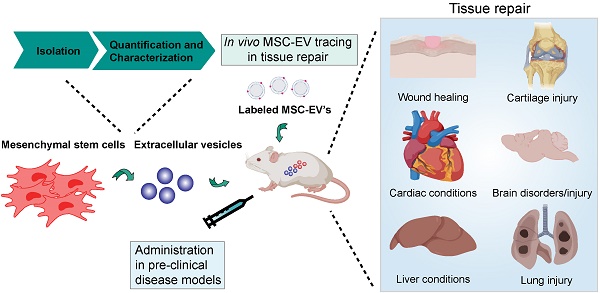
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) are important players in tissue homeostasis and regeneration owing to their immunomodulatory potential and release of trophic factors that promote healing. They have been increasingly used in clinical trials to treat multiple conditions associated with inflammation and tissue damage such as graft versus host disease, orthopedic injuries and cardiac and liver diseases. Recent evidence demonstrates that their beneficial effects are derived, at least in part, from their secretome. In particular, data from animal models and first-in-man studies indicate that MSC-derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) can exert similar therapeutic potential as their cells of origin. MSC-EVs are membranous structures loaded with proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids, which play an important role in cell-cell communication and may represent an attractive alternative for cell-based therapy. In this article we summarize recent advances in the use of MSC-EVs for tissue repair. We highlight several isolation and characterization approaches used to enrich MSC-derived EVs. We discuss our current understanding of the relative contribution of the MSC-EVs to the immunomodulatory and regenerative effects mediated by MSCs and MSC secretome. Finally we highlight the challenges and opportunities, which come with the potential use of MSC-EVs as cell free therapy for conditions that require tissue repair.
Keywords: mesenchymal stromal/stem cells, extracellular vesicles, isolation, in vivo, tissue repair
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact