13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(13):5736-5748. doi:10.7150/thno.41714 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dendrimer-conjugated glutaminase inhibitor selectively targets microglial glutaminase in a mouse model of Rett syndrome
1. Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore MD, 21205
2. Center for Nanomedicine, Department of Ophthalmology, Wilmer Eye Institute Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore MD, 21231
3. Johns Hopkins Drug Discovery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore MD, 21205
4. Department of Neurology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore MD, 21205
5. Hugo W. Moser Research Institute at Kennedy Krieger Inc., Baltimore MD, 21205
6. Kennedy Krieger Institute - Johns Hopkins University for Cerebral Palsy Research Excellence, Baltimore, MD 21287
7. Departments of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore MD, 21218
Abstract
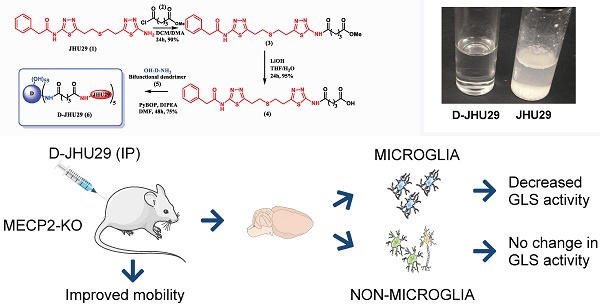
Background: Elevated glutamate production and release from glial cells is a common feature of many CNS disorders. Inhibitors of glutaminase (GLS), the enzyme responsible for converting glutamine to glutamate have been developed to target glutamate overproduction. However, many GLS inhibitors have poor aqueous solubility, are unable to cross the blood brain barrier, or demonstrate significant toxicity when given systemically, precluding translation. Enhanced aqueous solubility and systemic therapy targeted to activated glia may address this challenge. Here we examine the impact of microglial-targeted GLS inhibition in a mouse model of Rett syndrome (RTT), a developmental disorder with no viable therapies, manifesting profound central nervous system effects, in which elevated glutamatergic tone, upregulation of microglial GLS, oxidative stress and neuroimmune dysregulation are key features.
Methods: To enable this, we conjugated a potent glutaminase inhibitor, N-(5-{2-[2-(5-amino-[1,3,4]thiadiazol-2-yl)-ethylsulfanyl]-ethyl}-[1,3,4]thiadiazol-2-yl)-2-phenyl-acetamide (JHU29) to a generation 4 hydroxyl PAMAM dendrimer (D-JHU29). We then examined the effect of D-JHU29 in organotypic slice culture on glutamate release. We also examined GLS activity in microglial and non-microglial cells, and neurobehavioral phenotype after systemic administration of D-JHU29 in a mouse model of RTT.
Results: We report successful conjugation of JHU29 to dendrimer resulting in enhanced water solubility compared to free JHU29. D-JHU29 reduced the excessive glutamate release observed in tissue culture slices in a clinically relevant Mecp2-knockout (KO) RTT mouse. Microglia isolated from Mecp2-KO mice demonstrated upregulation of GLS activity that normalized to wild-type levels following systemic treatment with D-JHU29. Neurobehavioral assessments in D-JHU29 treated Mecp2-KO mice revealed selective improvements in mobility.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that glutaminase inhibitors conjugated to dendrimers are a viable mechanism to selectively inhibit microglial GLS to reduce glutamate production and improve mobility in a mouse model of RTT, with broader implications for selectively targeting this pathway in other neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: PAMAM dendrimer, microglia, glutaminase, Rett syndrome
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact