13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(12):5242-5258. doi:10.7150/thno.43744 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Discrete functional and mechanistic roles of chromodomain Y-like 2 (CDYL2) transcript variants in breast cancer growth and metastasis
1. Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Medical Epigenetics, International Co-laboratory of Medical Epigenetics and Metabolism, Ministry of Science and Technology, Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
2. Cancer Institute, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
3. Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
4. Department of Breast Surgery, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
5. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Breast Cancer, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
# These authors contributed equally to the work.
Abstract
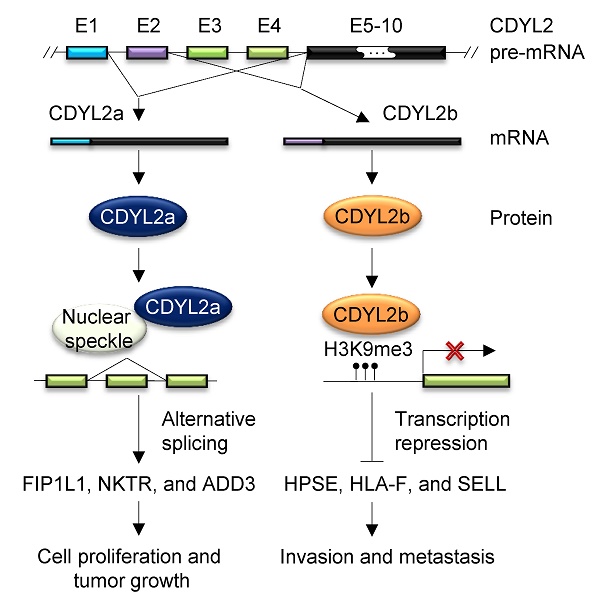
Rationale: Chromodomain Y-like 2 (CDYL2) is a member of the CDY gene family involved in spermatogenesis, but its role in human cancer has not been reported. Analyses of publicly available databases demonstrate that CDYL2 is abundantly expressed in breast tumors. However, whether CDYL2 is involved in breast cancer progression remains unknown.
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR and immunoblotting assays were used to determine the expression levels of CDYL2 transcript variants in breast cancer cell lines and primary breast tumors. The effect of CDYL2 transcript variants on the malignant phenotypes of breast cancer cells was examined through in vitro and in vivo assays. Immunofluorescent staining, RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, and ChIP-qPCR were used to investigate the underlying mechanisms behind the aforementioned observations.
Results: Here we show that CDYL2 generated four transcript variants, named CDYL2a-CDYL2d. CDYL2a and CDYL2b were the predominant variants expressed in breast cancer cell lines and breast tumors and exerted strikingly discrete functions in breast cancer growth and metastasis. CDYL2a was upregulated in the majority of the breast cancer cell lines and tumors, and promoted breast cancer cell proliferation, colony formation in vitro, and tumorigenesis in xenografts. In contrast, CDYL2b was mainly expressed in luminal- and HER2-positive types of breast cancer cell lines and tumors, and suppressed the migratory, invasive, and metastatic potential of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, CDYL2a partially localized to SC35-positive nuclear speckles and promoted alternative splicing of a subset of target genes, including FIP1L1, NKTR, and ADD3 by exon skipping. Elimination of full-length FIP1L1, NKTR, and ADD3 rescued the impaired cell proliferation through CDYL2a depletion. In contrast, CDYL2b localized to heterochromatin and transcriptionally repressed several metastasis-promoting genes, including HPSE, HLA-F, and SELL. Restoration of HPSE, HLA-F, or SELL expression in CDYL2b-overexpressing cells attenuated the ability of CDYL2b to suppress breast cancer cell migration and invasion.
Conclusions: Collectively, these findings establish an isoform-specific function of CDYL2 in breast cancer development and progression and highlight that pharmacological inhibition of the CDYL2a, but not the CDYL2b, isoform may be an effective strategy for breast cancer therapy.
Keywords: Breast cancer, CDYL2, transcript variants, alternative splicing, transcriptional repression
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact