13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(9):4088-4100. doi:10.7150/thno.42416 This issue Cite
Research Paper
IL-37/ STAT3/ HIF-1α negative feedback signaling drives gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer
1. Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin's Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Department of Pancreatic Cancer, Tianjin, PR China.
2. Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA.
*The first three authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
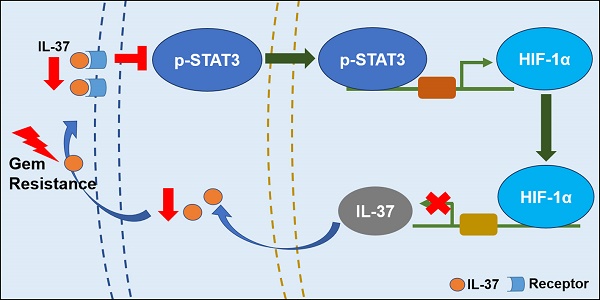
Human interleukin (IL)-37 is a member of the IL-1 family with potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. Previously, it has been reported that IL-37 suppresses tumor growth and progression. However, the roles of IL-37 in pancreatic cancer development and chemo-resistance remain unknown.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry was used to analyze the correlation between IL-37 expression and clinicopathological features of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Western-blot and RT-PCR was used to verify the correlation between IL-37 and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α. We performed chromatin immunoprecipitation and luciferase assays to validate HIF-1α suppression of IL-37 expression. Moreover, gain- and loss-of-function studies in vitro and in vivo were used to demonstrate the biological function of IL-37 on PDAC development and chemo-resistance.
Results: Our results showed that IL-37 expression was remarkably decreased in PDAC tissues when compared to adjacent normal pancreatic tissues. Reduced IL-37 expression in PDACs was associated with increased PDAC histological grade, tumor size, lymph node metastasis and vessel invasion. IL-37 low patients also have remarkably shorter relapse-free and overall survival. Importantly, IL-37 expression was positively correlated with Gemcitabine efficacy. Mechanistically, HIF-1α attenuated IL-37 transcription by binding to the hypoxia response elements (HREs) in IL-37 promoter. Conversely, IL-37 suppressed HIF-1α expression through STAT3 inhibition. Functionally, downregulation of IL-37 in PDAC cells promoted chemo-resistance, migration and progression in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusions: Collectively, our data uncovered IL-37/ STAT3/ HIF-1α negative feedback signaling drives Gemcitabine resistance in PDAC.
Keywords: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, IL-37, Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) -1α, Gemcitabine resistance
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact