13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(9):3925-3938. doi:10.7150/thno.41378 This issue Cite
Research Paper
IL-23, but not IL-12, plays a critical role in inflammation-mediated bone disorders
1. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200092, China.
2. The Key Laboratory of Stem Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences (SIBS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS); University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China.
3. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Orthopaedic Implant, Department of Orthopaedics, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China.
Abstract
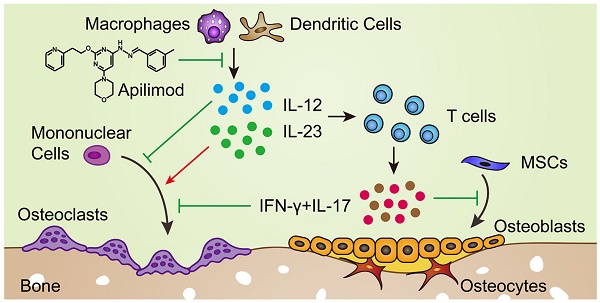
Interleukin-12 (IL-12) and IL-23 are thought to have central roles in inflammation and are critical to pathologies associated with inflammation-induced bone disorders. The deletion of IL-12p40 (a common subunit of IL-12 and IL-23) can improve bone regeneration. However, the relative roles of IL-12 and IL-23 in bone disorders are largely unknown.
Methods: Ectopic bone formation and skull defect models were established to evaluate the relative roles of IL-12 and IL-23 in inflammatory bone disorders. Differences in bone mass among WT, IL-12p35-/-, and IL-12p40-/- mice (young and elderly) were detected by micro-CT. Osteogenic and osteoclastic activities were explored using ELISA, qRT-PCR, and histological analysis. Moreover, the mechanisms by which IL-12 and IL-23 regulated the differentiation of BMMSCs and RAW264.7 cells were explored using Alizarin Red and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase staining in vitro. Apilimod was used to inhibit IL-12 and IL-23 production in vivo.
Results: Mice deficient in IL-12p40 promoted bone formation and protected against aging-related bone loss. By contrast, bone loss was aggravated in IL-12-/- mice, suggesting that IL-23 may play a dominant role in inflammation-related bone disorders. Mechanistically, IL-12 and IL-23 coupled osteogenesis and osteoclastic activities to regulate bone homeostasis and repair. IL-23 deficiency increased bone formation and inhibited bone resorption. Finally, apilimod treatment significantly improved bone regeneration and calvarial defect repair.
Conclusion: These data collectively uncover a previously unrecognized role of IL-23 in skeletal tissue engineering. Thus, IL-23 can act as a biomarker to predict diseases and treatment efficacy, and apilimod can be used as an effective therapeutic drug to combat inflammatory bone disorders
Keywords: IL-12, IL-23, BMMSCs, bone formation/resorption, bone regeneration
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact