13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(7):3151-3163. doi:10.7150/thno.41362 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PI3K/AKT inhibition reverses R-CHOP resistance by destabilizing SOX2 in diffuse large B cell lymphoma
1. Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center and Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
2. Department of Pathology, Zhongshan Hospital, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
3. Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
4. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology, Institute of Biomedical Sciences and School of Life Sciences, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China.
Abstract
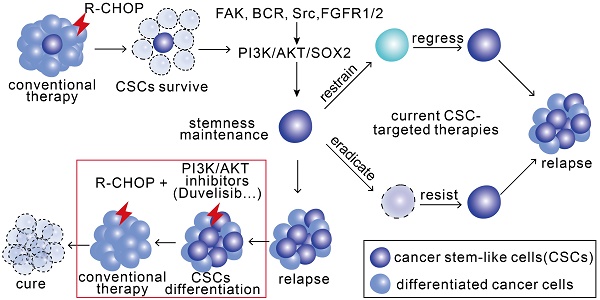
Up to one-third of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients eventually develop resistance to R-CHOP regimen, while the remaining therapeutic options are limited. Thus, understanding the underlying mechanisms and developing therapeutic approaches are urgently needed.
Methods: We generated two germinal center B cell-like (GCB) and activated B cell-like (ABC) subtype R-CHO resistant DLBCL cell lines, of which the tumor-initiating capacity was evaluated by serial-transplantation and stemness-associated features including CD34 and CD133 expression, side population and ALDH1 activity were detected by flow cytometry or immunoblotting. Expression profiles of these resistant cells were characterized by RNA sequencing. The susceptibility of resistant cells to different treatments was evaluated by in vitro CytoTox-glo assay and in tumor-bearing mice. The expression levels of SOX2, phos-AKT, CDK6 and FGFR1/2 were detected in 12 R-CHOP-resistant DLBCL clinical specimens by IHC.
Results: The stem-like CSC proportion significantly increased in both resistant DLBCL subtypes. SOX2 expression level remarkably elevated in both resistant cell lines due to its phosphorylation by activated PI3K/AKT signaling, thus preventing ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Further, multiple factors, including BCR, integrins, chemokines and FGFR1/2 signaling, regulated PI3K/AKT activation. CDK6 in GCB subtype and FGFR1/2 in ABC subtype were SOX2 targets, whose inhibition potently re-sensitized resistant cells to R-CHOP treatment. More importantly, addition of PI3K inhibitor to R-CHOP completely suppressed the tumor growth of R-CHO-resistant DLBCL cells, most likely by converting CSCs to chemo-sensitive differentiated cells.
Conclusions: The PI3K/AKT/SOX2 axis plays a critical role in R-CHOP resistance development and the pro-differentiation therapy against CSCs proposed in this study warrants further study in clinical trials for the treatment of resistant DLBCL.
Keywords: DLBCL, drug resistance, PI3K/AKT, SOX2, cancer stem-like cells
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact